
Concept explainers
The solid-state structure of silicon is shown below.
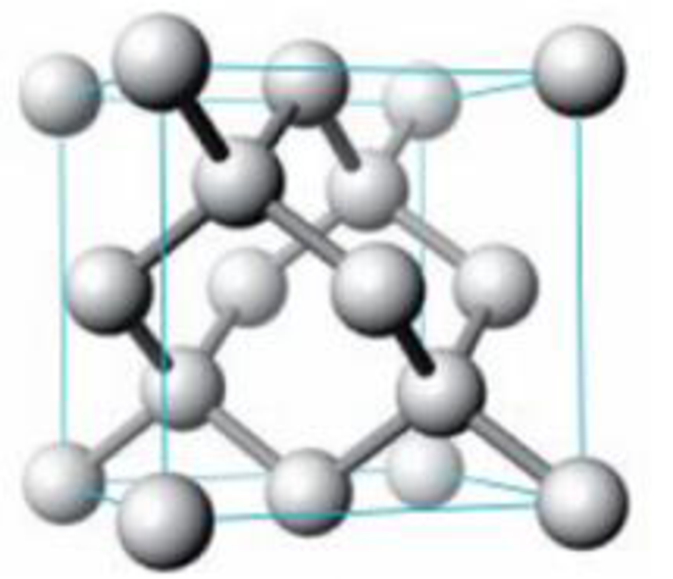
Unit cell for silicon
- (a) Describe this crystal as pc, bcc, or fcc.
- (b) What type of holes are occupied in the lattice?
- (c) How many Si atoms are there per unit cell?
- (d) Calculate the density of silicon in g/cm3 (given that the cube edge has a length of 543.1 pm).
- (e) Estimate the radius of the silicon atom. (Note: The Si atoms on the edges do not touch one another.)
(a)
Interpretation:
Given silicon crystal has to be described for PC, BCC or FCC.
Concept introduction:
- An ionic radii are the radius of an atom's ion in ionic crystals structure.
- An ionic solid is made up cations and anions held together by electrostatic forces in a rigid array or lattice.
- Positive charge ions are cations and negative charge ions are anions.
- Lattice Energy is mainly depends on the charge on the ion and radius or size of the ion.
- Ionic radius increases from top to bottom on the periodic table.
Ionic radius decreases from left to right the periodic table.
- The density of the unit cell:
- The face-centered cubic system:
It has lattice points on the faces of the cube, that each gives exactly one half contributions, in addition to the corner lattice points, giving a total of 4 lattice points per unit cell
Answer to Problem 51GQ
The types of the lattice is face center cubic crystal
Explanation of Solution
The types of the lattice is face center cubic crystal, because It has lattice points on the faces of the cube, that each gives exactly one half contribution, in addition to the corner lattice points, giving a total of 4 lattice points per unit cell
(b)
Interpretation:
The types of holes that are occupied in the lattice has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
- An ionic radii are the radius of an atom's ion in ionic crystals structure.
- An ionic solid is made up cations and anions held together by electrostatic forces in a rigid array or lattice.
- Positive charge ions are cations and negative charge ions are anions.
- Lattice Energy is mainly depends on the charge on the ion and radius or size of the ion.
- Ionic radius increases from top to bottom on the periodic table.
Ionic radius decreases from left to right the periodic table.
- The density of the unit cell:
- The face-centered cubic system:
It has lattice points on the faces of the cube, that each gives exactly one half contribution, in addition to the corner lattice points, giving a total of 4 lattice points per unit cell
Answer to Problem 51GQ
Silicon atoms are located in one half of the tetrahedral holes
Explanation of Solution
Silicon atoms are located in one half of the tetrahedral holes.
(c)
Interpretation:
Number of silicon atoms per unit cell has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
- An ionic radii are the radius of an atom's ion in ionic crystals structure.
- An ionic solid is made up cations and anions held together by electrostatic forces in a rigid array or lattice.
- Positive charge ions are cations and negative charge ions are anions.
- Lattice Energy is mainly depends on the charge on the ion and radius or size of the ion.
- Ionic radius increases from top to bottom on the periodic table.
Ionic radius decreases from left to right the periodic table.
- The density of the unit cell:
- The face-centered cubic system:
It has lattice points on the faces of the cube, that each gives exactly one half contribution, in addition to the corner lattice points, giving a total of 4 lattice points per unit cell
Answer to Problem 51GQ
Totally eight atoms in the unit cell
Explanation of Solution
Silicon atoms are located in one half of the tetrahedral holes.
(d)
Interpretation:
The density of the silicon atom has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
- An ionic radii are the radius of an atom's ion in ionic crystals structure.
- An ionic solid is made up cations and anions held together by electrostatic forces in a rigid array or lattice.
- Positive charge ions are cations and negative charge ions are anions.
- Lattice Energy is mainly depends on the charge on the ion and radius or size of the ion.
- Ionic radius increases from top to bottom on the periodic table.
Ionic radius decreases from left to right the periodic table.
- The density of the unit cell:
- The face-centered cubic system:
It has lattice points on the faces of the cube, that each gives exactly one half contribution, in addition to the corner lattice points, giving a total of 4 lattice points per unit cell
Answer to Problem 51GQ
Density is
Explanation of Solution
The density of the silicon atom is given below,
(e)
Interpretation:
The radius of the silicon atom has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
- An ionic radii are the radius of an atom's ion in ionic crystals structure.
- An ionic solid is made up cations and anions held together by electrostatic forces in a rigid array or lattice.
- Positive charge ions are cations and negative charge ions are anions.
- Lattice Energy is mainly depends on the charge on the ion and radius or size of the ion.
- Ionic radius increases from top to bottom on the periodic table.
Ionic radius decreases from left to right the periodic table.
- The density of the unit cell:
- The face-centered cubic system:
It has lattice points on the faces of the cube, that each gives exactly one half contribution, in addition to the corner lattice points, giving a total of 4 lattice points per unit cell
Answer to Problem 51GQ
Radius is
Explanation of Solution
The radius of silicon atom can be calculated as,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
General Chemistry: Atoms First
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Chemistry
Chemistry: Structure and Properties
- The unit cell of silicon carbide, SiC, is illustrated below. (a) In what type of unit cell are the (dark gray) C atoms arranged? (b) If one edge of the silicon carbide unit cell is 436.0 pm, what is the calculated density of this compound? A portion of the solid-state structure of silicon carbide.arrow_forwardLithium hydride (LiH) has the sodium chloride structure, and the length of the edge of the unit cell is 4.086 108 cm. Calculate the density of this solid.arrow_forwardRutile, TiO2, crystallizes in a structure characteristic of many other ionic compounds How many formula units of TiO2 are in the unit cell illustrated here? (The oxide ions marked by an x are wholly within the cell; the others are in the cell faces.) Unit cell for rufflearrow_forward
- Outline a two-dimensional unit cell for the pattern shown here. If the black squares are labeled A and the white squares are B, what is the simplest formula for a compound based on this pattern?arrow_forwardSilicon carbide, SiC, is a very hard, high-melting solid. What kind of crystal forces account for these properties?arrow_forwardIf an ionic solid has an fcc lattice of anions (X) and all of the tetrahedral holes are occupied by metal cations (M), is the formula of the compound MX, MX2, or M2X?arrow_forward
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





