
Concept explainers
An advanced spatial disorientation trainer allows the cab to rotate around multiple axes, as well as to extend inward and outward. It can be used to simulate driving, fixed-wing aircraft flying, and helicopter maneuvering. In one training scenario, the trainer rotates and translates in the horizontal plane, where the location of the pilot is defined by the relationships
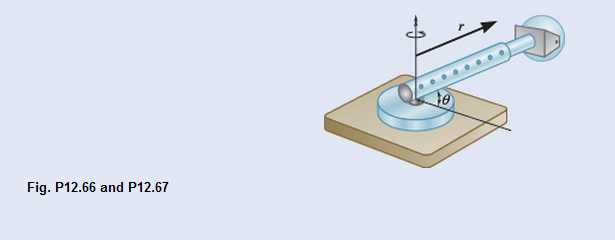
(a)
The magnitude of the resulting force on pilot.
Answer to Problem 12.66P
We got force
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Time
Concept used:
Calculation:
Derivatives,
Force components,
Resultant force,
Conclusion:
We got force
(b)
Plot the radial and transverse components of force.
Answer to Problem 12.66P
Plot is in explanation part.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Time
Concept used:
Calculation:
Derivatives,
Force components,
Table of
| t (sec) | 0.0 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 3.5 | 4.0 | 4.5 | 5.0 | 5.5 |
| Fr (lb) | -12.6 | -11.0 | -11.3 | -13.6 | -18.0 | -26.1 | -40.7 | -65.6 | -104.1 | -157.1 | -221.8 | -291.5 |
| t (sec) | 6.0 | 6.5 | 7.0 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 8.5 | 9.0 | 9.5 | 10.0 |
| Fr (lb) | -356.9 | -408.8 | -441.7 | -457.0 | -464.0 | -478.9 | -520.7 | -604.9 | -738.2 |
Plot,
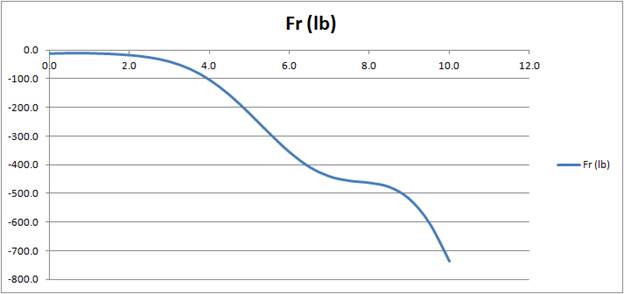
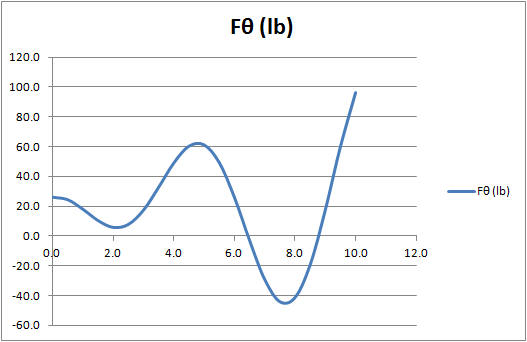
Table of
| t (sec) | 0.0 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 3.5 | 4.0 | 4.5 | 5.0 | 5.5 |
| F? (lb) | 26.1 | 24.4 | 18.0 | 10.4 | 5.8 | 7.7 | 17.4 | 32.8 | 49.2 | 60.4 | 61.4 | 49.4 |
| t (sec) | 6.0 | 6.5 | 7.0 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 8.5 | 9.0 | 9.5 | 10.0 |
| F? (lb) | 26.0 | -3.0 | -29.4 | -44.3 | -41.5 | -19.5 | 17.5 | 60.2 | 96.5 |
Plot,
Conclusion:
Plots are mentioned the explanation part.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
- A satellite is in circular orbit around Earth at an altitude of three Earth radii above the surface. If the satellite uses onboard retro rockets to cut its speed to one half, at what distance from Earth can it establish a new stable circular orbit? Hint: vorbit =arrow_forwardQuestion 1:A cyclist is riding a bicycle at a constant speed of 20 km/h to the east. Simultaneously, a strong wind is blowing from the north at a speed of 10 km/h. Determine the cyclist's resultant velocity with respect to the ground.arrow_forwardThe airplane above now moves due east while the alien pilot points the plane somewhat south of east, toward a steady wind that blows to the northeast. The plane Phas velocity ⃗vP W relative to the wind W , with an airspeed (speed relative to the wind) of 215 km/h, directed at angle θ south of east. The wind has velocity ⃗vWG relative to the ground G with speed 65.0 km/h, directed 20.0◦ east of north. What is the magnitude of the velocity ⃗vP G of the plane relative to the ground, and what is θ?arrow_forward
- For a perfectly elastic collision, u1+v1=u2+v2, or alternatively, u2−u1=v1−v2. If object 2 is initially at rest, then u2=0. Then v1−v2=−u1. However, for a partially elastic collision the relative velocity after the collision will have a smaller magnitude than the relative velocity before the collision. We can express this mathematically as v1−v2=−ru1, where r (a number less than one) is called the coefficient of restitution. For some kinds of bodies, the coefficient r is a constant, independent of v1 and v2. Show that in this case the final kinetic energy of the motion relative to the center of mass is less than the initial kinetic energy of this motion by a factor of r2. Furthermore, derive expressions for v1 and v2 in terms of u1 and r.arrow_forwardQ1: Explain the following cases that have been occurring while curve ranging. (CLO1; C2; PLO1) 1) When the whole curve cannot be set out from the Tangent point, Vision being obstructeda) When P.C is inaccessibleb) When P.T is inaccessiblec) When both P.T and P.C is inaccessibled) When both P.T and P.I is inaccessiblee) When both P.C and P.I is inaccessible1) When the obstacle to chaining occurs.arrow_forwardTwo smooth discs A and B have a mass of 0.5 kg. Both discs are moving with velocities shown when they collide. The coeff. of restitution, e=0.5. Suppose that (vA)1=8m/s and (vB)1=3m/s. Find: a) Final velocity of A b) Angle of A measure counterclockwise from the positive x axis c) The final velocity of B d) The angle of B measured clockwise from the negative x axisarrow_forward
- The region of flow trailing the body where the effects of the body are felt is called (a) Wake (b) Separated region (c) Stall (d ) Vortice (e) Irrotationalarrow_forwardThe 2kg particle A has a speed of 10m/s. moment about 0 its momentum angular momentum about 0arrow_forwardA 12-lb weight stretches a spring 2 ft. The weight is released from a point that is 1 ft below the equilibrium position with an upward velocity of 4 ft s-1.arrow_forward
- Particles C and D are moving in the positive x-direction, with A behind B initially. Particle A has speed 20 m/S and mass 1 g whilst B has speed 12 m/s and mass 3 g. At some time later the particles coalesce. If momentum is conserved, what is the loss in KE? (A) There is a gain in KE of 24 ] (B) 24] (C) 01 since energy is conserved (D) 0.024]arrow_forwardAn airplane is flying with an airspeed of 310 knots on a heading of 50°. If a 78-knot wind is blowing from a heading of 125°, determine the speed and direction of the plane relative to the ground.arrow_forwardA 100 kg vehicle initially travels clockwise in a circular path with a radius of 10 m at a speed of 5 m/s. If a counterclockwise couple moment of 100 Nm is applied for 10 s, and the vehicle continues to travel on a circular path at 5 m/s, then the circular path radius must drop to from 10 m to 8 m. True Falsearrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





