
Concept explainers
What masses of sodium chloride, magnesium chloride, sodium sulfate, calcium chloride, potassium chloride, and sodium bicarbonate are needed to produce 1 L of artificial seawater for an aquarium? The required ionic concentrations are (Na+) = 2.56 M, (K+] = 0.0090 M, [Mg2+] = 0.054 M, [Ca2+] = 0.010 M, [HCO3−] = 0.0020 M, [Cl−] = 2.60 M, [SO42-] = 0.051 M.
Interpretation:
Masses of Sodium chloride, Potassium chloride, Sodium sulphate, Calcium chloride, Magnesium chloride and Sodium bicarbonate are required to produce 1L of artificial sea water has to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
Mass is the determination of the quantity of the matter in an object. Unit of mass is gram (g) or kilogram (kg). Mass is calculated by multiplying the volume of the compound into its density.
Answer to Problem 13.106QP
Amount of given salts to produce artificial sea water are,
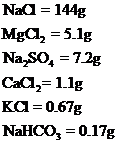
Explanation of Solution
Given data
Required ionic concentrations are,
To calculate the calculation of all ions
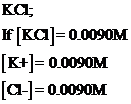
To calculate subtotal of sodium and chloride ion
- The subtotal of chloride ion
Since the required concentration of chloride ion is 2.60M, so the difference is,
- The subtotal of Sodium ion
Since the required concentration of Sodium ion is 2.56M, so the difference is,
By adding the sodium and chloride ions concentration, the subtotal respective ions have calculated.
To calculate mass of the compounds required
By plugging in the value of mass of the given compounds and number of moles of the compound, the mass required to produce 1L of artificial sea water has calculated.
Masses of Sodium chloride, Potassium chloride, Sodium sulphate, Calcium chloride, Magnesium chloride and Sodium bicarbonate are required to produce 1L of artificial sea water has been calculated.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Chemistry: Atoms First
- For each of the following pairs of solutions, select the solution for which solute solubility is greatest. a. Oxygen gas in water with P = 1 atm and T = 10C Oxygen gas in water with P = 1 atm and T = 20C b. Nitrogen gas in water with P = 2 atm and T = 50C Nitrogen gas in water with P = 1 atm and T = 70C c. Table salt in water with P = 1 atm and T = 40C Table salt in water with P = 1 atm and T = 70C d. Table sugar in water with P = 3 atm and T = 30C Table sugar in water with P = 1 atm and T = 80Carrow_forwardThe dispersed phase of a certain colloidal dispersion consists of spheres of diameter 1.0 102 nm. (a) What are the volume (V=43r2) and surface area (A = r2) of each sphere? (b) How many spheres are required to give a total volume of 1.0 cm3? What is the total surface area of these spheres in square meters?arrow_forwardSpecifications for lactated Ringers solution, which is used for intravenous (IV) injections, are as follows to reach 100. mL of solution: 285315 mg Na+ 14.117.3 mg K+ 4.9Q.O mg Ca2+ 368408 mg Cl 231261 mg lactate, C3H5O3 a. Specify the amount of NaCl, KCl, CaCl2 2H2O, and NaC3H5O3 needed to prepare 100. mL lactated Ringers solution. b. What is the range of the osmotic pressure of the solution at 37C, given the preceding specifications?arrow_forward
- Match each of the following statements about the dissolving of the ionic solid NaCl in water with the term hydrated ion, hydrogen atom, or oxygen atom. a. A Na+ ion surrounded with water molecules b. A Cl ion surrounded with water molecules c. The portion of a water molecule that is attracted to a Na+ ion d. The portion of a water molecule that is attracted to a Cl ionarrow_forwardIn the 1986 Lake Nyos disaster (see the chapter introduction), an estimated 90 billion kilograms of CO2 was dissolved in the lake at the time. (a) What volume of gas is this at standard temperature and pressure? (b) Assuming that this dissolved gas was in equilibrium with the normal partial pressure of CO2 in the atmosphere (0.038%, or 0.29 torr), use the Henrys law constant for CO2 in water to estimate the volume of Lake Nyos.arrow_forwardWill red blood cells swell, remain the same size, or shrink when placed in each of the solutions in Problem 8-101? Classify each of the following solutions as hypotonic, isotonic, or hypertonic relative to red blood cells? a. 0.92%(m/v) glucose solution b. 0.92%(m/v) NaCl solution c. 2.3%(m/v) glucose solution d. 5.0%(m/v) NaCl solutionarrow_forward
- Predict the relative solubility of each compound in the two solvents, on the basis of intermolecular attractions. (a) Is Br2 more soluble in water or in carbon tetrachloride? (b) Is CaCl2 more soluble in water or in benzene (C6H6)? (c) Is chloroform (CHCl3) more soluble in water or in diethyl ether [(C2H5)2O]? (d) Is ethylene glycol (HOCH2CH2OH) more soluble in water or in benzene (C6H6)?arrow_forwardInstead of using NaCl to melt the ice on your sidewalk you decide to use CaCl2. If you add 35.0 g of CaCl2 to 150. g of water, what is the freezing point of the solution? (Assume i = 2.7 for CaCl2.)arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





