
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To indicate whether B vitamin thiamin is involved in (1) glycolysis, (2) gluconeogenesis, (3) lactate fermentation, or (4) glycogenolysis as a cofactor.
Concept introduction: Vitamins are defined as the micronutrients that are needed in a small amount for the proper functioning of the metabolic activities in the organisms.
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. Cofactors cannot perform on their own alone.
In the glycolysis metabolic pathway, a glucose molecule breaks down into two pyruvate molecules. In gluconeogenesis process, glucose is produced from non-carbohydrate substances. Glycogenolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glycogen to
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase enzymes in the human body. In this reaction, NADH is oxidized to
Niacin
(a)
Answer to Problem 13.117EP
None of the given processes includes B vitamin thiamin as a cofactor. B vitamin thiamin is needed as a cofactor in the conversion of pyruvate to
Explanation of Solution
B vitamin thiamin is encountered in the form of thiamin pyrophosphate (TPP) in the carbohydrate metabolism. TPP in not involved in glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, lactate fermentation, and glycogenolysis. Hence, none of the given processes includes vitamin thiamin as a cofactor.
Pyruvate is converted to
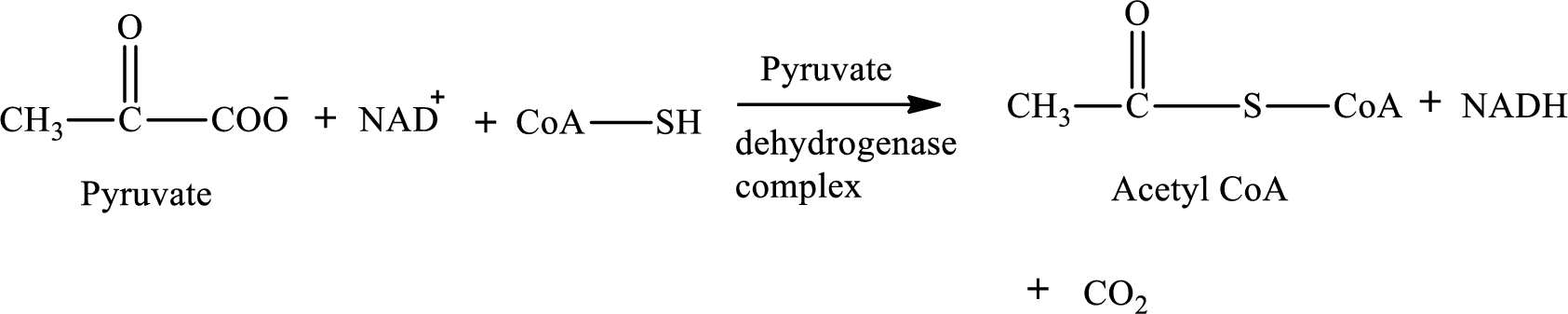
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex contains three different enzymes. Each enzyme contains numerous subunits. The overall reaction requires FAD,
(b)
Interpretation: To indicate B vitamin riboflavin is involved in (1) glycolysis, (2) gluconeogenesis, (3) lactate fermentation, or (4) glycogenolysis as a cofactor.
Concept introduction: Vitamins are defined as the micronutrients that are needed in a small amount for the proper functioning of the metabolic activities in the organisms.
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. Cofactors cannot perform on their own alone.
In the glycolysis metabolic pathway, a glucose molecule breaks down into two pyruvate molecules. In gluconeogenesis process, glucose is produced from non-carbohydrate substances. Glycogenolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glycogen to
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase enzymes in the human body. In this reaction, NADH is oxidized to
Niacin
(b)
Answer to Problem 13.117EP
None of the given processes includes vitamin riboflavin as a cofactor. B vitamin riboflavin is needed as a cofactor in the citric acid cycle.
Explanation of Solution
B vitamin riboflavin is encountered in the form of FAD(Flavin adenine dinucleotide) in the carbohydrate metabolism. FAD in not involved in glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, lactate fermentation, and glycogenolysis. Hence, none of the given processes includes B vitamin riboflavin as a cofactor.
The citric acid cycle is the third stage of the biochemical energy production process. The cycle includes the reactions in which the acetyl part of acetyl CoA is oxidized and leads to the formation of carbon dioxide and
(c)
Interpretation: To indicate whether B vitamin pantothenic acid is involved in (1) glycolysis, (2) gluconeogenesis, (3) lactate fermentation, or (4) glycogenolysis as a cofactor.
Concept introduction: Vitamins are defined as the micronutrients that are needed in a small amount for the proper functioning of the metabolic activities in the organisms.
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. Cofactors cannot perform on their own alone.
In the glycolysis metabolic pathway, a glucose molecule breaks down into two pyruvate molecules. In gluconeogenesis process, glucose is produced from non-carbohydrate substances. Glycogenolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glycogen to
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase enzymes in the human body. In this reaction, NADH is oxidized to
Niacin
(c)
Answer to Problem 13.117EP
None of the given processes includes B vitamin pantothenic acid as a cofactor. B vitamin pantothenic acid is needed as a cofactor in the conversion of pyruvate to
Explanation of Solution
B vitamin pantothenic acid is encountered in the form of
Pyruvate is converted to
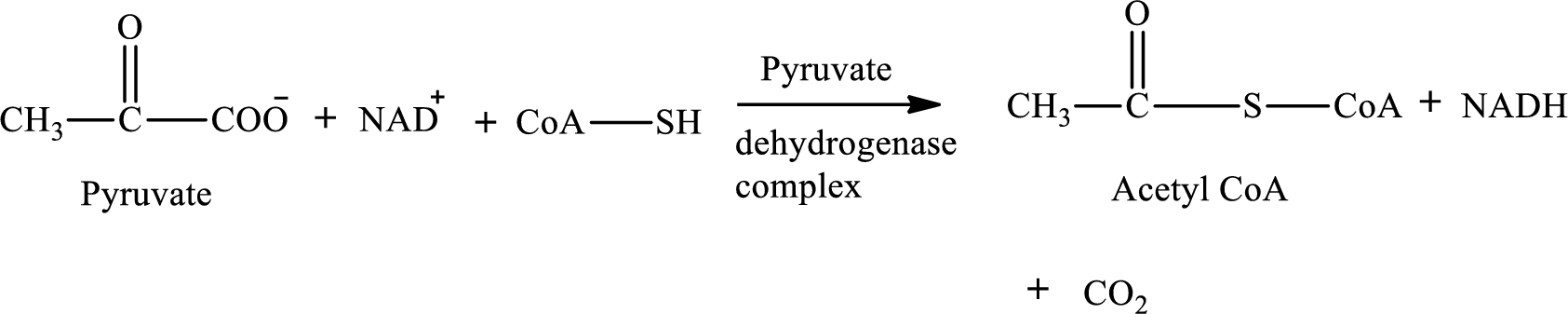
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex contains three different enzymes. Each enzyme contains numerous subunits. The overall reaction requires FAD,
(d)
Interpretation: To indicate
Concept introduction: Vitamins are defined as the micronutrients that are needed in a small amount for the proper functioning of the metabolic activities in the organisms.
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. Cofactors cannot perform on their own alone.
In the glycolysis metabolic pathway, a glucose molecule breaks down into two pyruvate molecules. In gluconeogenesis process, glucose is produced from non-carbohydrate substances. Glycogenolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glycogen to
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase enzymes in the human body. In this reaction, NADH is oxidized to
Niacin
Answer to Problem 13.117EP
Explanation of Solution
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- Explain why monitoring blood lactate levels might be a useful technique to gauge the amount of conditioning in an Olympic runner.arrow_forwardClassify anabolism and catabolism as synthetic or degradative processes.arrow_forwardWhich nutrient provides energy in its most concentrated form?arrow_forward
- Glucose-6-phosphate detours to the hexose monophosphate shunt pathway in erythrocytes because: Question 73 options: A) They lack mitochondria making them incapable of the TCA cycle B) They lack endoplasmic reticulum making them incapable of the TCA cycle C) Erythrocytes have no energy needs D) Erythrocytes utilize glucose directly for energyarrow_forwardWhat is produced by the reduction of pyruvate in the body under anaerobic conditions? a) acetate b) acetyl CoA c) lactate d) pyruvatearrow_forwardWhat are the hormones formed from the precursor cholesterol? Give at least five.arrow_forward
- Consider the docosanoic acid, C21H43CO2H Label the alpha and beta Carbons. Draw each acyl CoA derived from this fatty acid. How many acetyl Co A molecules are formed by complete beta-oxidation? How many cycles of beta-oxidation are needed for complete oxidation? How many molecules of ATP are formed from the complete catabolism of this fatty acid? Show the complete computation. How many moles of ATP per gram of fatty acid is formed from the complete catabolism of the given fatty acid? What is the molar mass of the given fatty acid?arrow_forwardName two fat soluble vitamins, their sources and the diseases caused due to their deficiency in diet.arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning




