
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The molecular formula for the given compound has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Organic compounds are the important basis of life. They include gasoline, coal, dyes, and clothing fibers etc. The compounds that are obtained from living organisms are termed as organic compounds and those obtained from the earth are known as inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are found in earth also apart from living organisms. All the organic compounds contain the element carbon. Urea was synthesized in the laboratory which is an organic compound.
Hydrocarbons are the organic compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbon derivatives are the one in which the compounds contain hydrogen and carbon atoms along with one or more additional elements. The additional elements that can be present in hydrocarbon derivatives are oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, bromine etc.
Hydrocarbons are further classified into two categories. They are saturated hydrocarbons and
(a)
Answer to Problem 13.33EP
Molecular formula of the compound is
Explanation of Solution
Given structure is,
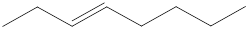
Carbon atoms are present at the intersection and at the end points. The above structure has six intersections and two end points. Therefore, there is a total of eight carbon atoms. The given compound is found to have one double bond in it. The molecular formula for the given compound can be found by substituting in the general molecular formula of alkene that contain a single double bond as shown below,
The molecular formula of the given compound is identified as
The molecular formula for the given structure is identified.
(b)
Interpretation:
The molecular formula for the given compound has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Organic compounds are the important basis of life. They include gasoline, coal, dyes, and clothing fibers etc. The compounds that are obtained from living organisms are termed as organic compounds and those obtained from the earth are known as inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are found in earth also apart from living organisms. All the organic compounds contain the element carbon. Urea was synthesized in the laboratory which is an organic compound.
Hydrocarbons are the organic compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbon derivatives are the one in which the compounds contain hydrogen and carbon atoms along with one or more additional elements. The additional elements that can be present in hydrocarbon derivatives are oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, bromine etc.
Hydrocarbons are further classified into two categories. They are saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. The hydrocarbons that contain single bonds between carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as saturated hydrocarbon. The hydrocarbons that contain atleast one double or triple bond between two carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Alkanes are a class of saturated hydrocarbons that do not contain a ring of carbon atoms but a chain of carbon atoms with carbon‑carbon single bonds. The general molecular formula for alkanes is
Alkenes and cycloalkenes are a class of unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain at least one double bond in its structure. The general molecular formula for alkene with one double bond is
(b)
Answer to Problem 13.33EP
Molecular formula of the compound is
Explanation of Solution
Given structure is,
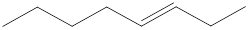
Carbon atoms are present at the intersection and at the end points. The above structure has six intersections and two end points. Therefore, there is a total of eight carbon atoms. The given compound is found to have one double bond in it. The molecular formula for the given compound can be found by substituting in the general molecular formula of alkene that contain a single double bond as shown below,
The molecular formula of the given compound is identified as
The molecular formula for the given structure is identified.
(c)
Interpretation:
The molecular formula for the given compound has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Organic compounds are the important basis of life. They include gasoline, coal, dyes, and clothing fibers etc. The compounds that are obtained from living organisms are termed as organic compounds and those obtained from the earth are known as inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are found in earth also apart from living organisms. All the organic compounds contain the element carbon. Urea was synthesized in the laboratory which is an organic compound.
Hydrocarbons are the organic compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbon derivatives are the one in which the compounds contain hydrogen and carbon atoms along with one or more additional elements. The additional elements that can be present in hydrocarbon derivatives are oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, bromine etc.
Hydrocarbons are further classified into two categories. They are saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. The hydrocarbons that contain single bonds between carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as saturated hydrocarbon. The hydrocarbons that contain atleast one double or triple bond between two carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Alkanes are a class of saturated hydrocarbons that do not contain a ring of carbon atoms but a chain of carbon atoms with carbon‑carbon single bonds. The general molecular formula for alkanes is
Alkenes and cycloalkenes are a class of unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain at least one double bond in its structure. The general molecular formula for alkene with one double bond is
(c)
Answer to Problem 13.33EP
Molecular formula of the compound is
Explanation of Solution
Given structure is,
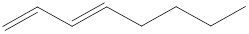
Carbon atoms are present at the intersection and at the end points. The above structure has six intersections and two end points. Therefore, there is a total of eight carbon atoms. The given compound is found to have two double bonds in it. The molecular formula for the given compound can be found by substituting in the general molecular formula of alkene that contain two double bonds as shown below,
The molecular formula of the given compound is identified as
The molecular formula for the given structure is identified.
(d)
Interpretation:
The molecular formula for the given compound has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Organic compounds are the important basis of life. They include gasoline, coal, dyes, and clothing fibers etc. The compounds that are obtained from living organisms are termed as organic compounds and those obtained from the earth are known as inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are found in earth also apart from living organisms. All the organic compounds contain the element carbon. Urea was synthesized in the laboratory which is an organic compound.
Hydrocarbons are the organic compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbon derivatives are the one in which the compounds contain hydrogen and carbon atoms along with one or more additional elements. The additional elements that can be present in hydrocarbon derivatives are oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, bromine etc.
Hydrocarbons are further classified into two categories. They are saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. The hydrocarbons that contain single bonds between carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as saturated hydrocarbon. The hydrocarbons that contain atleast one double or triple bond between two carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Alkanes are a class of saturated hydrocarbons that do not contain a ring of carbon atoms but a chain of carbon atoms with carbon‑carbon single bonds. The general molecular formula for alkanes is
Alkenes and cycloalkenes are a class of unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain at least one double bond in its structure. The general molecular formula for alkene with one double bond is
(d)
Answer to Problem 13.33EP
Molecular formula of the compound is
Explanation of Solution
Given structure is,
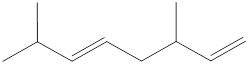
Carbon atoms are present at the intersection and at the end points. The above structure has six intersections and four end points. Therefore, there is a total of ten carbon atoms. The given compound is found to have two double bonds in it. The molecular formula for the given compound can be found by substituting in the general molecular formula of alkene that contain two double bonds as shown below,
The molecular formula of the given compound is identified as
The molecular formula for the given structure is identified.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
- How many secondary carbon atoms are present in each of the structures in Problem 12-96? a. b. c. d.arrow_forwardHow many hydrogen atoms are present in a molecule of each of the compounds in Problem 13-26? a. 2-methylcyclopentene b. 1,3-cyclopentadiene c. 2,3-dimethylpentane d. 1-ethyl-2-methylcyclohexenearrow_forward11-48 How are the boiling points of hydrocarbons during petroleum refining related to their molecular weight?arrow_forward
- Answer true or false. Combustion of alkanes is an endothermic reaction. The products of complete combustion of an alkane are carbon dioxide and water. Halogenation of an alkane converts it to a haloalkane.arrow_forwardAssign each of the compounds in Problem 13-108 an IUPAC name in which the substituents on the benzene ring are located using the ortho-, meta-, para-prefix system.arrow_forward12-25 Write the IUPAC name for each unsaturated hydrocarbon. (d)c=ch2 ch3ch,ch2arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning



