
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The electron-pair geometry for the molecules,
Concept introduction:
The electron pairs in Lewis diagrams repel each other in real molecule and therefore, they distribute themselves in positions around the central atoms that are as far away from one another. This arrangement of electron pairs is known as electron-pair geometry. The electron pairs may be shared in covalent bond, or they may be lone pairs.
Answer to Problem 19E
The Lewis diagrams for
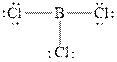

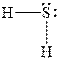
The wedge-and-dash diagrams for

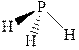
![]()
The electron pair geometry for
Explanation of Solution
To write the Lewis diagram for a compound first the number of valence electrons is to be calculated. In the molecule,
Similarly, in the molecule,
In the molecule,
The atom which is least electronegative is the central atom. In
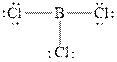
Figure 1
In

Figure 2
In
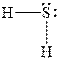
Figure 3
The electron-pair geometry depends on the number of electron pairs around the central atoms. In the molecule
In the molecule
In the molecule
The wedge-and-dash diagram for the molecule

Figure 4
The wedge-and-dash diagram for the molecules
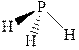
Figure 5
The wedge-and-dash diagram for the molecules
![]()
Figure 6
The Lewis and wedge-and-dash diagrams for
(b)
Interpretation:
The molecular geometry predicted by the valence shell electron-pair repulsion theory for the molecules
Concept introduction:
Molecular geometry is the precise term that is used to describe the shape of molecules and arrangement of atoms around the central atom. The molecular geometry of a molecule is predicted by valence shell electron-pair repulsion theory or in short VSEPR theory. VSEPR theory applies to substances in which a second period element is bonded to two, three, four, or other atoms.
Answer to Problem 19E
The Lewis diagrams for
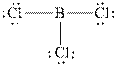

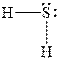
The wedge-and-dash diagrams for

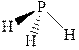
![]()
The molecular geometry for
Explanation of Solution
To write the Lewis diagram for a compound first the number of valence electrons is to be calculated. In the molecule,
Similarly, in the molecule,
In the molecule,
The atom which is least electronegative is the central atom. In

Figure 1
In

Figure 2
In
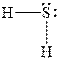
Figure 3
The molecular geometry depends on the number of electron pairs as well as number of unpaired electron on the central atoms. In the molecule
In the molecule
In the molecule
The wedge-and-dash diagram for the molecule

Figure 4
The wedge-and-dash diagram for the molecule
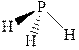
Figure 5
The wedge-and-dash diagram for the molecule
![]()
Figure 6
The Lewis and wedge-and-dash diagrams for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach
- Write answers to the following questions for these compounds: SO2 (sulfur in the middle with the two oxygens attached to it) C2H2 (carbons attached to each other with one hydrogen attached to each carbon CO2 (carbon in the middle with two oxygens attached to it). 1. determine the number of valence electrons for each compound 2. draw a Lewis structure and include non-bonding electrons if necessary 3. write the electron group geometry and molecular geometry terms 4. determine whether or not the compound is polar or non-polararrow_forwardStep 1 – Write the Lewis structure from the molecular formula.Step 2 – Assign an electron-group arrangement by counting all electron groups (bonding plus nonbonding) around the central atom (or around each centralatom, if more than one central atom in structure).Step 3 – Predict the ideal bond angle from the electron-group arrangement and the effect of any deviation caused by lone pairs or double bonds.Step 4 – Name the molecular shape by counting bonding groups and nonbonding groups separately.Step 5 – Predict whether the molecule is polar or nonpolarStep 6 – Describe the hybridization around the central atom and identify the total number of σ and π bonds in the structurearrow_forwardNH3 vs BH3 NH3 BH3 polar nonpolar polar nonpolar Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry Question 1b: How does the molecular geometry (trigonal pyramidal vs trigonal planar) affect the polarity?arrow_forward
- Use the Molecule Shape simulator (http://openstaxcollege.org/l/16MolecShape) to build amolecule. Starting with the central atom, click on the double bond to add one double bond. Then add one single bond and one lone pair. Rotate the molecule to observe the complete geometry. Name the electron group geometry and molecular structure and predict the bond angle. Then click the check boxes at the bottom and right of the simulator to check your answers.arrow_forwardFor the polyatomic ion NO3-, answer the following: (a) total number of valence electrons in the ion (enter a number only) (b) identity of the central atom (element symbol) Now draw the Lewis Structure and answer the following questions: (c) number of electron groups on the central atom (enter a number only) (d) number of bonding groups on the central atom (enter a number only) (e) number of double bonds in the ion (enter a number only) (f) number of single bonds in the ionarrow_forwardDraw the shapes of the following molecules and ions in 3-dimension. Show clearly any lone pairs of electrons on the central atom, state the number of bond pairs and lone pairs of electrons on the central atom and name the shape of the molecule or ion. (a) AIH4-, aluminium hydride ion (b) CH3-, methyl carbanion (c) POCl3, phosphorus oxychloride Provide everything stated in the instructions for each compound.arrow_forward
- For each of the following ions/molecules, state the number of bond pairs state the number of lone pairs state the bond angle(s) state, or draw, the shapearrow_forwardFind the total number of valence electrons, lewis structure, name of electron and molecular geometry, and 3D diagram for SEI2 and SbBr3.arrow_forwarddiagram of a molecule that shows atoms based on their a periodic table symbols. These symbols are surrounded by pairs of dots to show valence electrons that could be lone pairs or bonding pairs?arrow_forward
- Polar and nonpolar molecules contain polar bonds. True or false?arrow_forward'Geometry and Polarity of Molecules'arrow_forwardDraw the Lewis structure for SeCI2 (selenium dichloride), then answer all of the following questions. For those questions in which a numerical response is required, express your answer with an integer (0, 1, 2, 3 etc.). a) Provide the symbol for the central element. This answer is case-sensitive. b) How many lone pair of electrons are surrounding the central element? c) How many lone pair of electrons in total are present in this molecule? d) How many non-bonding electrons are there in total in this molecule? e) How many electrons are being shared in total? f) How many single bonds are present in this molecule? g) How many double bonds are present in this molecule? h) How many triple bonds are present in this molecule?arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning



