
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305389892
Author: Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13, Problem 3TYK
Individuals affected by a condition known as polydactyly have extra fingers or toes. The following pedigree shows the pattern of inheritance of this trait in one family:
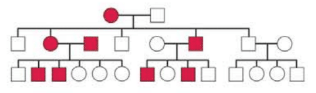
From the pedigree, can you tell if polydactyly comes from a dominant or recessive allele? Is the trait sex-linked? As far as you can determine, what is the genotype of each person in the pedigree with respect to the trait?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
The following pedigree shows the inheritance of Huntington’s disease, a fatal genetic disorder that causes neurodegeneration. Since signs and symptoms usually do not appear until adulthood, many who are carriers may not realize their risk of passing on the disease-causing allele. The following pedigree represents a family in which some people are affected by Huntington’s disease.
Using just the information on this pedigree, is Huntington’s disease caused by a dominant allele or recessive alleles?
What are the genotypes of the grandparents (I-1 and I-2)?
What are the genotypes of the parents (II-6 and II-7)?
If the parents above have another child, what is the chance that they will be affected by the Hungtington’s disease allele?
What are the genotypes of the unaffected children (III-8, 9, 10)?
What is the chance that the unaffected children above will pass on a Huntington’s disease allele to their children?
What is the genotype of the affected child (III-11)?
What is the chance…
For a recessive condition, two normal heterozygous individuals have children.
What is the likelihood of their children being affected by this condition?
What is the likelihood of their children being carriers without the condition?
What is the likelihood of their asymptomatic children being carriers?
Suppose that an individual with the condition has children with a heterozygous individual, what is the likelihood of their children being carriers?
Using the pedigree chart attached:
Above is a pedigree for colorblindness. Based on the pedigree, is the disease dominant or recessive and is it sex-linked or autosomal? Why? Furthermore, what is the probability that 18 on this chart is affected but the condition, and what is the probability that 18 is a carrier? Why? Are the probability of being a carrier and an affected individual different? Why?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 13.1 - You want to determine whether genes a and b are...Ch. 13.2 - You have a true-breeding strain of...Ch. 13.3 - What mechanisms are responsible for: (a)...Ch. 13.4 - A man has Simpson syndrome, an addiction to a...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 2SBCh. 13.5 - Prob. 1SBCh. 13 - In humans, redgreen color blindness is an X-linked...Ch. 13 - The following pedigree shows the pattern of...Ch. 13 - Individuals affected by a condition known as...Ch. 13 - A number of genes carried on the same chromosome...
Ch. 13 - Prob. 5TYKCh. 13 - Discuss Concepts Can a linkage map be made for a...Ch. 13 - In Drosophila, two genes, one for body color and...Ch. 13 - Another gene in Drosophila determines wing length....Ch. 13 - Prob. 9TYKCh. 13 - You conduct a cross in Drosophila that produces...Ch. 13 - Discuss Concepts Crossing-over does not occur...Ch. 13 - Prob. 12TYKCh. 13 - Prob. 13TYKCh. 13 - Prob. 14TYKCh. 13 - Prob. 1ITDCh. 13 - Prob. 2ITDCh. 13 - Prob. 3ITDCh. 13 - Prob. 4ITD
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Read the following family history and draw a pedigree to determine the inheritance pattern for achondroplasia. Once the pedigree is assembled , label the genotypes of each individual using a capital "A to represent the dominant allele and a lower case "a " to represent the recessive allele and create a key to identify which version is the achondroplasia allele. If you are unsure of the genotype , label the individual with a "" in place of the unknown allele. Family History : Jada and Noel , both of short stature, have been married for twenty years. They have three children : an eighteen - year-old boy named Shawn , of short stature ; a fifteen- year- old boy named John , of short stature ; and a twelve -year -old girl named Ann , of average height Noel and Jada also had a male child bom with severe achondroplasia who died six months after birth from respiratory failure . Noel's father was of short stature , while his mother was average height . Noel has a brother and a…arrow_forwardIn pedigrees, individuals are usually specified by using a Roman numeral for their generation in the chart and an Arabic number for their position (reading left to right) within that generation. If we use the letter c for the allele that causes cystic fibrosis, what are the genotypes of individuals III-3 and III-4 (the third and fourth individuals shown in generation III) in the pedigree that shows this disease?arrow_forwardThe following pedigree illustrates the inheritance of ringed hair, a condition in which each hair is differentiated into light and dark zones. What mode or modes of inheritance are possible for the ringed-hair trait in this family?arrow_forward
- How does a positive ASO test for sickle-cell anemia determine that an individual is homozygous recessive for the mutation that causes sickle-cell anemia?arrow_forwardGiven the pedigree below: Is the trait dominant or recessive? What are the most likely genotypes of individuals I-1 and I-2? What is the probability that individual II-2 is a carrier?arrow_forwardIn humans, the genetic disease cystic fibrosis is caused by a recessive allele (a). The normal (healthy) allele is dominant (A). What is the genotype of someone who has cystic fibrosis? What are the two different genotypes that a healthy person could have? If two people were both heterozygous for the cystic fibrosis gene, what fraction of their children would be likely to have this disease? Hint: Draw a Punnett square to figure it out.arrow_forward
- Tay-Sachs disease is a recessive genetic disease. Two individuals, both of whom are heterozygous for a recessive allele that causes the disease have one child who does not have the disease. What is the probability that this child has the potential to pass the disease-causing allele on to the next generation? Tay-Sachs disease is a recessive genetic disease. Two individuals, both of whom are heterozygous for a recessive allele that causes the disease have one child who does not have the disease. What is the probability that this child has the potential to pass the disease-causing allele on to the next generation? 1/4 1/2 3/4 2/3arrow_forwardAlbinism is a recessive disorder where there is a lack of melanin. Andrea and her husband Claude both have normal skin pigmentation. Andrea’s mother has the albino phenotype, but her father and her brother do not (normal pigmentation). Claude’s parents are both normal, but he has a sister who has the condition (is albino). Answer the following questions If Andrea and Claude are carriers for the albino allele, what is the probability that they have an albino child? If Andrea and Claude have a second child, what is the probability this child be normal (non-albino)? NOTE: Draw a punnet square or show your work.arrow_forwardWhich mode of inheritance is suggested by the following pedigree? Based on this hypothesis, and assuming that the trait is rare and has complete penetrance, what are the possible genotypes of all individuals in this pedigree?arrow_forward
- What are the genotypes of the mother and father in the pedigree below? The pedigree shows albinism (an autosomal recessive trait). The shaded shapes represent albino individuals. a. mother - homozygous dominant; father - homozygous dominant b. mother - heterozygous; father - homozygous recessive c. mother - homozygous recessive; father - heterozygous d. mother - heterozygous; father - heterozygous e. mother - homozygous dominant; father - homozygous recessivearrow_forwardThe pedigree shown below shows the inheritance of cystic fibrosis, a disorder that causes severe damage to the lungs and digestive system. Individual 5 shows no family history of cystic fibrosis and is considered to be homozygous for the normal allele. What is the probability that individual 10 is a carrier for the allele leading to cystic fibrosis?arrow_forwardThe pedigree below shows a family affected by a disease. Assume that the individuals marked with an asterisk (*) do not carry any allele associated with the affected phenotype, no other mutation spontaneously occurred, and complete penetrance. Answer the following questions below. Use the notation XR for the allele associated with the dominant phenotype and Xr for the allele associated with the recessive phenotype. Q1) Give the genotypes for as many individuals in the pedigree as possible.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
How to solve genetics probability problems; Author: Shomu's Biology;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R0yjfb1ooUs;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Beyond Mendelian Genetics: Complex Patterns of Inheritance; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-EmvmBuK-B8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY