
Concept explainers
What
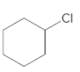
a.
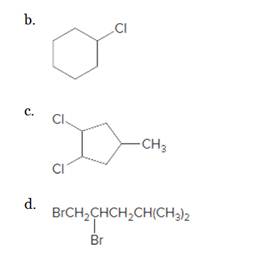
(a)
Interpretation:
The starting material and the reagents needed to prepare following alkyl halide should be determined:
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Answer to Problem 59P
Starting alkene-
Reagent -
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated alkene molecules react with
Refer to the below reaction:
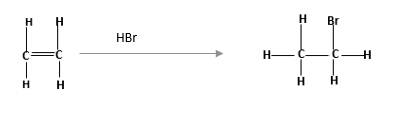
(b)
Interpretation:
The starting material and the reagents needed to prepare following alkyl halide should be determined:
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Answer to Problem 59P
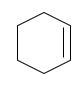
Starting alkene −
Reagent -
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated alkene molecules react with
Refer to the below reaction;
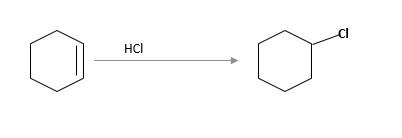
(c)
Interpretation:
The starting material and the reagents needed to prepare following alkyl halide should be determined:
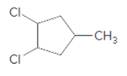
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Answer to Problem 59P
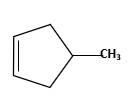 Starting alkene −
Starting alkene −
Reagent -
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated alkene molecules react with
Refer to the below reaction;
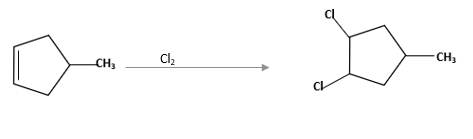
(d)
Interpretation:
The starting material and the reagents needed to prepare following alkyl halide should be determined:

Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Answer to Problem 59P
Starting alkene −
Reagent -
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated alkene molecules react with
Refer to the below reaction:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Basic Chemistry (5th Edition)
Inorganic Chemistry
The Organic Chem Lab Survival Manual: A Student's Guide to Techniques
Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (3rd Edition)
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
- Isooctane is the common name of the isomer of C8H18 used as the standard of 100 for the gasoline octane rating: (a) What is the IUPAC name for the compound? (b) Name the other isomers that contain a five-carbon chain with three methyl substituents.arrow_forwardName each alkyne: a.CH3CHCHCH2CH2CH3arrow_forwardName and draw a structural formula for the product of each alkene addition reaction. (a) (b)arrow_forward
- . How is a monosubstituted benzene named? Give the structures and names of two examples. Also give two examples of monosubstituted benzenes that have special names.arrow_forwardExplain why unbranched alkenes can form geometric isomers while unbranched alkanes cannot. Does this explanation involve the macroscopic domain or the microscopic domain?arrow_forwardWhat functional group distinguishes each of the following hydrocarbon derivatives? a. halohydrocarbons b. alcohols c. ethers d. aldehydes e. ketones f. carboxylic acids g. esters h. amines Give examples of each functional group. What prefix or suffix is used to name each functional group? What are the bond angles in each? Describe the bonding in each functional group. What is the difference between a primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohol? For the functional groups in ah, when is a number required to indicate the position of the functional group? Carboxylic acids are often written as RCOOH. What does COOH indicate and what does R indicate? Aldehydes are sometimes written as RCHO. What does CHO indicate?arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning  Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





