
Cardiopulmonary Anatomy & Physiology
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781337794909
Author: Des Jardins, Terry.
Publisher: Cengage Learning,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 14, Problem 10RQ
Summary Introduction
To review:
The given blank space in the statement using the following ECG graph.
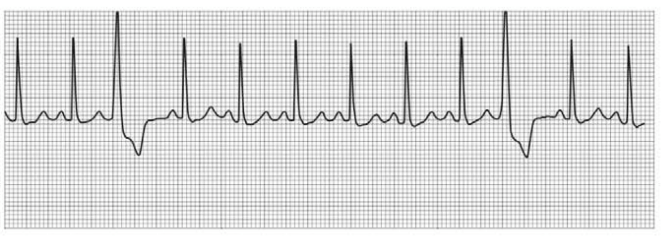
QR QRS duration: __________ QT duration: ____________
Ventricular rate and rhythm: _____________
Atrial rate rhythm: _____________________
PR interval: __________________________
Interpretation: ________________________
Introduction:
Electrocardiogram (ECG) is used to monitor the heart rate of the patients as it is a diagnostic machine. The heartbeat is recorded in the form of wave components, such as P, Q, R, S, T, and U. Doctors interpret the ECG through a systemic approach.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
One of the following is a life-threatening arrhythmia and an absolute emergency that should immediately be notified by the MA to the physician in the event it appears in the EKG strips.
One of the following is a life-threatening arrhythmia and an absolute emergency that should immediately be notified by the MA to the physician in the event it appears in the EKG strips.
Sinus rhythm
Sinus tachycardia
Sinus bradycardia
Ventricular fibrillation
In electrocardiography (=EKG, =ECG), what causes a P wave?______
A.
atrial repolarization
B.
ventricular repolarization
C.
atrial depolarization
D.
ventricular depolarization
The standard EKG consists of 10 sensors that record 12 leads of the heart’s electrical activity from different angles, allowing for a thorough three-dimensional interpretation of its activity. This is transmitted by the electrodes to the equipment to be interpreted and is used to diagnose cardiac medical conditions. In case of an abnormal EKG, the second step would be to use a Holter monitor.
How would you explain to your classmates how to perform an EKG (steps)?
Where will you place the electrodes when performing and EKG? Why?
What are the different lead types, connections, and placements?
When you conclude an EKG, what are the different components that you need to observe and confirm before you disconnect the patient? Can you explain the difference between normal, abnormal, and artifacts?
What is a Holter monitor? Under what circumstances would one be ordered for a patient?
How do you use a Holter monitor?
Educate a patient: What you will do before, during, and after an…
Chapter 14 Solutions
Cardiopulmonary Anatomy & Physiology
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The standard EKG consists of 10 sensors that record 12 leads of the heart’s electrical activity from different angles, allowing for a thorough three-dimensional interpretation of its activity. This is transmitted by the electrodes to the equipment to be interpreted and is used to diagnose cardiac medical conditions. In case of an abnormal EKG, the second step would be to use a Holter monitor. How would you explain how to perform an EKG (steps)? Where will you place the electrodes when performing and EKG? Why? What are the different lead types, connections, and placements? When you conclude an EKG, what are the different components that you need to observe and confirm before you disconnect the patient? Can you explain the difference between normal, abnormal, and artifacts? What is a Holter monitor? Under what circumstances would one be ordered for a patient? How do you use a Holter monitor? Educate a patient: What you will do before, during, and after an electrocardiogram or…arrow_forwardIf pulse pressure is calculated to equal 40 mm Hg and diastolic pressure is 70 mm Hg, then systolic pressure must have been __________. 30 mm Hg 90 mm Hg 110 mm Hg 140 mm Hg none of the abovearrow_forwardAn U.S. unit is being used to measure the patient’s heartbeat using a 10 MHz signal – if theDoppler signal is 700 Hz (as a result of the motion of the RBCs) and we assume scanning in softtissue and at a 60 degree angle, what is the velocity of the RBC’s at the Aorta?arrow_forward
- Interpret the following ECG rhythm stripsarrow_forwardWhy is percussion omitted in heart assessment?arrow_forwardMark the following coordinates on the image about: 1. repolarization of the ventricles 2. conduction through the atrioventricular node, 3. depolarization of the ventricles and repolarization of the atria. 4. First deflection corresponding to the movement of current when the atria depolarizearrow_forward
- During which phase of the cardiac cycle is the ST segment present on an EKG? Group of answer choices Atrial systole Isovolumetric ventricular contraction Rapid ventricular ejection Isovolumetric ventricular relaxation Rapid ventricular fillingarrow_forwardA person’s blood pressure is measured at 118/78 and the person’s peripheral pulse is 72. Which of the following statements is correct? Group of answer choices The person’s pulse pressure is 40 mm Hg The person’s MAP is 98 mm Hg The person’s MAP is 66 mm Hg The person’s pulse was measured at the heartarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Cardiopulmonary Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781337794909Author:Des Jardins, Terry.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Basic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...NursingISBN:9781285244662Author:WhitePublisher:Cengage
Cardiopulmonary Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781337794909Author:Des Jardins, Terry.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Basic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...NursingISBN:9781285244662Author:WhitePublisher:Cengage- Understanding Health Insurance: A Guide to Billin...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337679480Author:GREENPublisher:Cengage
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning

Cardiopulmonary Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781337794909
Author:Des Jardins, Terry.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,


Basic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...
Nursing
ISBN:9781285244662
Author:White
Publisher:Cengage

Understanding Health Insurance: A Guide to Billin...
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:9781337679480
Author:GREEN
Publisher:Cengage

Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:9781337711067
Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna Balac
Publisher:Cengage Learning
