
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bromination:

2-methyl propane undergoes radical bromination which yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane.because bromination will occur where the tertiary radical is present.(Bromination reactions are more selective reaction).
The mechanism of monobromination of ethane (as an example) includes three steps,
- (i) Initiation
- (ii) Propagation
- (iii) Termination
Thus the mechanism of monobromination of ethane is shown below,
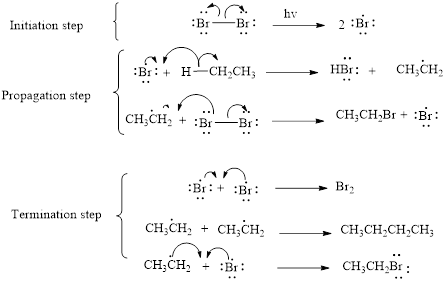
In a halogenation reaction, one or more halogen atoms are introduced into an organic compound. Generally, these reactions are initiated in the presence of light or heat.
Bromination will occur on tertiary radical than the secondary than primary radical, tertiary radical is more stable radical than the other radicals.
(a)
Answer to Problem 12P
3-methyl hexane undergoes radical bromination and yields the 3-bromo-3-methylhexane which is shown below
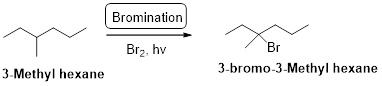
Explanation of Solution
3-methyl hexane undergoes radical bromination and yields the 3-bromo-3-methylhexane according to the above mentioned mechanism steps. The reaction is shown below,
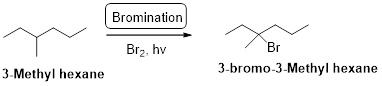
(b)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Chlorination:
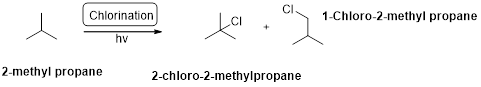
2-methyl propane undergoes radical chlorination and yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane and 1-bromo-2-methyl propane.
The mechanism of monochlorination of ethane includes three steps,
- (i) Initiation
- (ii) Propagation
- (iii) Termination
The mechanism of monochlorination of ethane is shown below,
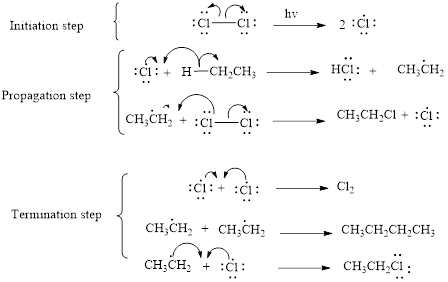
In a halogenation reaction, one or more halogen atoms are introduced into an organic compound. Generally, these reactions are initiated in the presence of light or heat.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
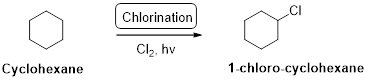
Cyclohexane undergoes radical chlorination; all the carbons in cyclohexane are secondary. Therefore, it yields the 1-chloro cyclohexane according to the above mentioned mechanism steps. And the reaction is shown above.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Chlorination:
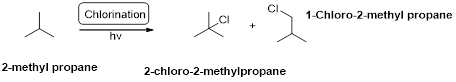
2-methyl propane undergoes radical chlorination and yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane and 1-bromo-2-methyl propane.
The mechanism of monochlorination of ethane includes three steps,
- (i) Initiation
- (ii) Propagation
- (iii) Termination
The mechanism of monochlorination of ethane is shown below,

In a halogenation reaction, one or more halogen atoms are introduced into an organic compound. Generally, these reactions are initiated in the presence of light or heat.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
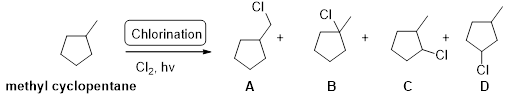
Methyl cyclopentane undergoes radical chlorination; the carbons in cyclopentane are secondary and primary. Therefore, it yields the four types of chlorocyclopentane according to the above mentioned mechanism steps. And the reaction is shown below
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry (3rd Edition)
- (a) Identify the major product of the following reaction. (b) Explain why the other product is not the major product.arrow_forwardDraw the products formed in each Wittig reaction. Draw the major stereoisomer when applicable.arrow_forwardDraw the major product (with stereochemistry) of the following reaction. Draw only one enantiomer for a racemic mixture.arrow_forward
- Draw the substitution product formed (including stereochemistry) when (R)-hexan-2-ol is treated with each series of reagents: (a) NaH, followed by CH3I; (b) TsCl and pyridine, followed by NaOCH3; (c) PBr3, followed by NaOCH3. Which two routes produce identical products?arrow_forwardDraw the major product for the following substitution reaction and include stereochemistry when appropriatearrow_forwardDehydration of 1,2,2-trimethylcyclohexanol with H2SO4 affords 1-tert-butylcyclopentene as a minor product. (a) Draw a stepwise mechanism that shows how this alkene is formed. (b) Draw other alkenes formed in this dehydration. At least one must contain a ve-membered ring.arrow_forward
- Show a stepwise mechanism by pushing arrows and drawing all intermediates. Draw a detailed mechanism for the addition of H2O to 2-methyl-2-pentene in the presence of H2SO4.arrow_forwardWhich substituent is the strongest deactivator to EAS reactions? -NO2 -Cl -CH3 -OHarrow_forwardDehydration of 1,2,2-trimethylcyclohexanol with H2SO4 affords 1-tertbutylcyclopentene as a minor product. (a) Draw a stepwise mechanism that shows how this alkene is formed. (b) Draw other alkenes formed in this dehydration. At least one must contain a five-membered ring.arrow_forward
