
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the alcohol has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain single hydroxyl group:
- • Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains hydroxyl group also. The chain name is obtained by replacing the letter “-e” in
alkane with “-ol”. If the compound contains a unsaturated bond, then the respective name has to be changed with regard to alkane. - • The numbering has to be given so that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering.
- • Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- • If in a ring the hydroxyl group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
- • Hydroxyl group as a substituent in a molecule is named as hydroxy group rather than hydroxyl group.
- • If the compound contains bulky groups on same side of the double bond, then it is a cis isomer and if the bulkyl groups are present on opposite side of the double bond, then it is a trans isomer.
- • In case of cycloalkane compounds, if the substitutions are present on same side of the ring of carbon atoms, it is a cis isomer. If the substitutions are present above and below the ring, then it is a trans isomer.
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain more than one hydroxyl group:
- • The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of hydroxyl groups that is present.
(a)
Answer to Problem 14.27EP
The IUPAC name of the given alcohol is trans-2-buten-1-ol.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of alcohol is,
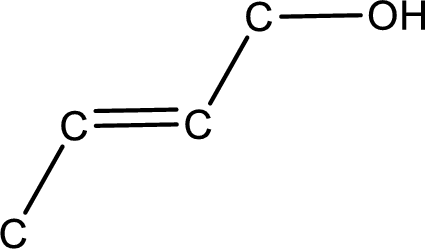
The longest carbon chain in the above structure with the hydroxyl group is found to be a four carbon chain. Hence, the parent alkane is butane. As there is a double bond present in the carbon chain, the name is converted as butene. The hydroxyl group is found to be present on first carbon atom. Therefore, the name of the given alcohol can be given as 2-buten-1-ol.
Looking for the stereochemistry, the given structure has bulky group on opposite side of the double bond and hence this is a trans isomer. This has to be included in the IUPAC name. Therefore, IUPAC name of the given compound is trans-2-buten-1-ol.
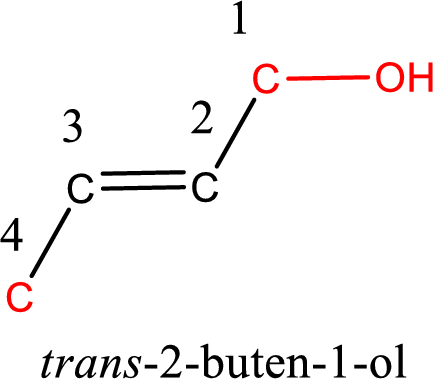
IUPAC name for the given alcohol is trans-2-buten-1-ol.
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the alcohol has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain single hydroxyl group:
- • Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains hydroxyl group also. The chain name is obtained by replacing the letter “-e” in alkane with “-ol”. If the compound contains a unsaturated bond, then the respective name has to be changed with regard to alkane.
- • The numbering has to be given so that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering.
- • Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- • If in a ring the hydroxyl group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
- • Hydroxyl group as a substituent in a molecule is named as hydroxy group rather than hydroxyl group.
- • If the compound contains bulky groups on same side of the double bond, then it is a cis isomer and if the bulkyl groups are present on opposite side of the double bond, then it is a trans isomer.
- • In case of cycloalkane compounds, if the substitutions are present on same side of the ring of carbon atoms, it is a cis isomer. If the substitutions are present above and below the ring, then it is a trans isomer.
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain more than one hydroxyl group:
- • The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of hydroxyl groups that is present.
(b)
Answer to Problem 14.27EP
The IUPAC name of the given alcohol is cis-3-penten-1-ol.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of alcohol is,
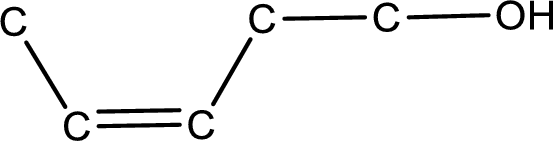
The longest carbon chain in the above structure with the hydroxyl group is found to be a five carbon chain. Hence, the parent alkane is pentane. As there is a double bond present in the carbon chain, the name is converted as pentene. The hydroxyl group is found to be present on first carbon atom and the double bond between third and fourth carbon atom. Therefore, the name of the given alcohol can be given as 3-penten-1-ol.
Looking for the stereochemistry, the given structure has bulky group on same side of the double bond and hence this is a cis isomer. This has to be included in the IUPAC name. Therefore, IUPAC name of the given compound is cis-3-penten-1-ol.
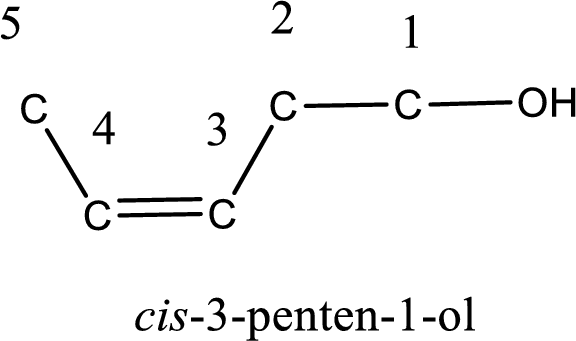
IUPAC name for the given alcohol is cis-3-penten-1-ol.
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the alcohol has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain single hydroxyl group:
- • Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains hydroxyl group also. The chain name is obtained by replacing the letter “-e” in alkane with “-ol”. If the compound contains a unsaturated bond, then the respective name has to be changed with regard to alkane.
- • The numbering has to be given so that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering.
- • Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- • If in a ring the hydroxyl group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
- • Hydroxyl group as a substituent in a molecule is named as hydroxy group rather than hydroxyl group.
- • If the compound contains bulky groups on same side of the double bond, then it is a cis isomer and if the bulkyl groups are present on opposite side of the double bond, then it is a trans isomer.
- • In case of cycloalkane compounds, if the substitutions are present on same side of the ring of carbon atoms, it is a cis isomer. If the substitutions are present above and below the ring, then it is a trans isomer.
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain more than one hydroxyl group:
- • The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of hydroxyl groups that is present.
(c)
Answer to Problem 14.27EP
The IUPAC name of the given alcohol is cis-2-methylcyclohexanol.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of alcohol is,
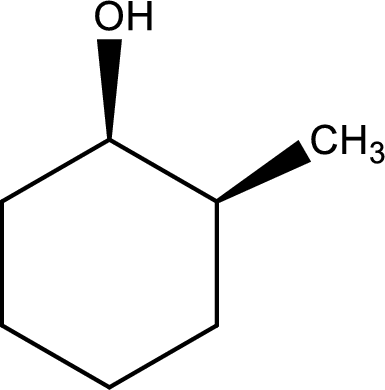
The longest carbon chain in the above structure with the hydroxyl group is found to be a six carbon cyclic chain. Hence, the parent cycloalkane is cyclohexane. As a hydroxyl group is present in the ring, the name can be given as cyclohexanol. Looking for the substituents present in the ring, it is found that a methyl group is present in the second position. Therefore, the name of the given alcohol can be given as 2-methylcyclohexanol.
Looking for the stereochemistry, the given structure has substituents on same side of the ring of carbon atoms and hence this is a cis isomer. This has to be included in the IUPAC name. Therefore, IUPAC name of the given compound is cis-2-methylcyclohexanol.
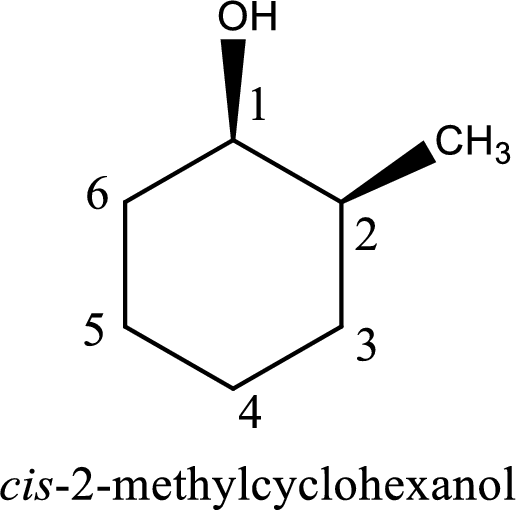
IUPAC name for the given alcohol is cis-2-methylcyclohexanol.
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the alcohol has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain single hydroxyl group:
- • Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains hydroxyl group also. The chain name is obtained by replacing the letter “-e” in alkane with “-ol”. If the compound contains a unsaturated bond, then the respective name has to be changed with regard to alkane.
- • The numbering has to be given so that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering.
- • Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- • If in a ring the hydroxyl group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
- • Hydroxyl group as a substituent in a molecule is named as hydroxy group rather than hydroxyl group.
- • If the compound contains bulky groups on same side of the double bond, then it is a cis isomer and if the bulkyl groups are present on opposite side of the double bond, then it is a trans isomer.
- • In case of cycloalkane compounds, if the substitutions are present on same side of the ring of carbon atoms, it is a cis isomer. If the substitutions are present above and below the ring, then it is a trans isomer.
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain more than one hydroxyl group:
- • The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of hydroxyl groups that is present.
(d)
Answer to Problem 14.27EP
The IUPAC name of the given alcohol is trans-3-chlorocyclohexanol.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of alcohol is,
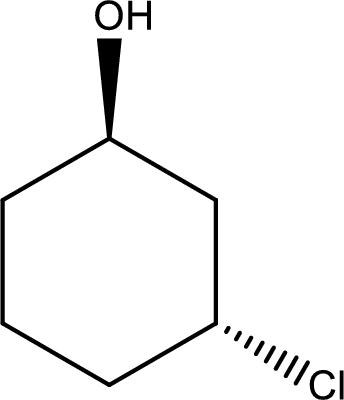
The longest carbon chain in the above structure with the hydroxyl group is found to be a six carbon cyclic chain. Hence, the parent cycloalkane is cyclohexane. As a hydroxyl group is present in the ring, the name can be given as cyclohexanol. Looking for the substituents present in the ring, it is found that a chloro is present in the third position. Therefore, the name of the given alcohol can be given as 3-chlorocyclohexanol.
Looking for the stereochemistry, the given structure has substituents above and below the ring of carbon atoms and hence this is a trans isomer. This has to be included in the IUPAC name. Therefore, IUPAC name of the given compound is trans-3-chlorocyclohexanol.
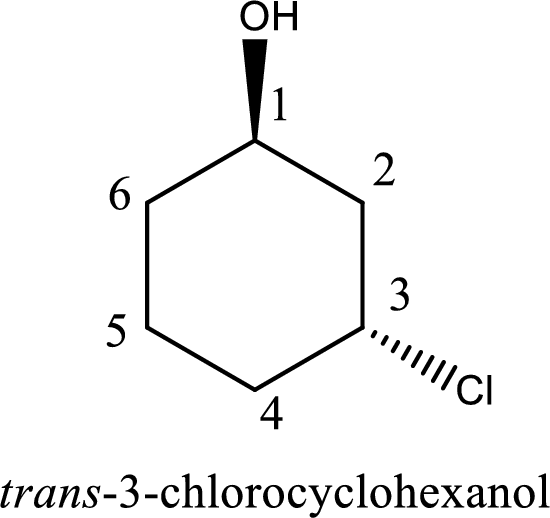
IUPAC name for the given alcohol is trans-3-chlorocyclohexanol.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
- Classify each of the following alcohols as a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol. a. 1-pentanol b. 2-pentanol c. 2-methyl-1-pentanol d. 2-methyl-2-pentanolarrow_forwardAssign an IUPAC name to each of the following compounds. a. CH3(CH2)4SH b. CH3(CH2)4OHarrow_forwardAssign an IUPAC name to each of the compounds in Problem 12-63. a. b. c. d.arrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning


