
Concept explainers
a) Interpretation:
The total estimated mass Zr and Te disposed as nuclear waste by the nuclear technician
Concept Introduction:
(uranium) undergoes a fission reaction which is neutron induced. On doing so, it will split into two smaller nuclei
(zirconium) and (tellurium). In the process, neutrons and gamma rays are released. The
Answer to Problem 14.59PAE
Solution:
3.231 metric ton
Explanation of Solution
The total amount of electrical energy generated by all the nuclear reactors is
From the problem 14.55, we know the amount of energy released during the fission of 1 kg of is
Hence,
Total mass of used =
For every fission of 236.133 grams of , 233.83627 grams of nuclear waste is generated.
Hence, the total estimated mass of Zr and Te (which are the products of fission of ) disposed as nuclear waste is
(b) Interpretation:
Whether any of the products Zr and Te obtained from the fission of
are available in measurable quantities in the nuclear waste
Concept Introduction: (uranium) undergoes a fission reaction which is neutron induced. On doing so, it will split into two smaller nuclei (zirconium) and (tellurium). In the process, neutrons and gamma rays are released. The nuclear equation for this reaction is as follows:
Answer to Problem 14.59PAE
Solution:
Only a measurable quantity of Zr will be left in the waste
Explanation of Solution
The half life of is 16.749 hours. The half life of is 2.49 seconds. As would undergo Beta-minus decay, it would get degraded within 2.49 seconds whereas Zr having larger half life will be present in measurable quantities.
(c) Interpretation:
Decay series of each isotope and
Concept Introduction: (uranium) undergoes a fission reaction which is neutron induced. On doing so, it will split into two smaller nuclei (zirconium) and (tellurium). In the process, neutrons and gamma rays are released. The nuclear equation for this reaction is as follows:
Answer to Problem 14.59PAE
Solution:
The decay series for Te
Explanation of Solution
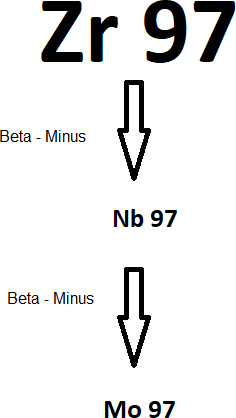
The decay series of is
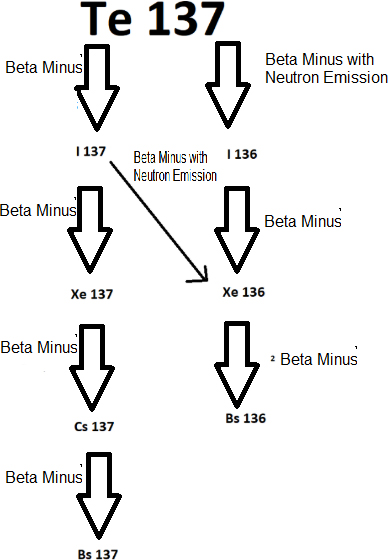
The decay series of is
The decay series of has Cs 137 which will remain in waste for many years.
(d) Interpretation:
The difference between the total mass of the waste using the stable isotope products and the technician’s estimated total mass.
Concept Introduction: (uranium) undergoes a fission reaction which is neutron induced. On doing so, it will split into two smaller nuclei (zirconium) and (tellurium). In the process, neutrons and gamma rays are released. The nuclear equation for this reaction is as follows:
Answer to Problem 14.59PAE
Solution:
The technician’s estimates of total waste were off by 0.079751 kg.
Explanation of Solution
Mass of the stable isotope products =
Mass of the waste so obtained = kg or 3.2309273 metric ton
The difference between the technician’s estimated mass and the above calculated mass is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Chemistry for Engineering Students
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning





