
Concept explainers
In a classic study, Loftus and Palmer (1974) investigated the relationship between memory for eyewitnesses and the questions they are asked. In the study, participants watched a film of an automobile accident and then were questioned about the accident. One group was asked how fast the cars were going when they "smashed into" each other. A second group was asked about the speed when the ears "hit" each other and a third group was not asked any question about the speed of the ears. A week later, the participants returned to answer additional questions about the accident, including whether they recalled seeing any broken glass. Although there was no broken glass in the film, several students claimed to remember seeing it. The following table shows the Frequency distribution of responses for each group.
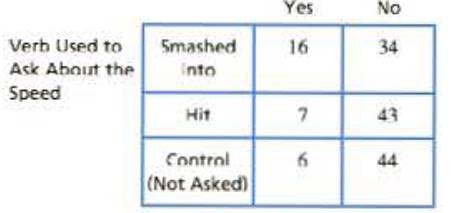
- a. Does the proportion of participants who claim to remember broken glass differ significantly from group to group? Test with or α = .05
- b. Compute Cramér's V to measure the size of the treatment effect.
- c. Describe how the phrasing of the question influenced the participants' memories.
- d. Write a sentence demonstrating how the outcome of the hypothesis lest and the measure of effect size would be reported in a journal article
a.
To check: Whether the proportions of participants who claim to remember broken glass differ significantly from group to group for the given question.
Answer to Problem 13P
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
A sample of 150 students were involved in a study based on “the response they gave regarding the broken glass or verb used for speed”. The distribution is given in the question. Use
Calculations:
Step 1: Null Hypothesis and Alternate Hypothesis are:
Step 2: For the given sample, degrees of freedom equals:
With
Step 3:
The formula to calculate expected frequency is:
Substitute
For the category “smashed into”, the expected frequencies are:
For the category “Hit”, the expected frequencies are:
Similarly, for the category “control”, the expected frequencies are:
The observed and expected frequency is given below:
| Yes | No | Total | |
| Smashed into | 16 (9.66) | 34 (40.33) | 50 |
| Hit | 7 (9.66) | 43 (40.33) | 50 |
| Control (not asked) | 6 (9.66) | 44 (40.33) | 50 |
| Total | 29 | 121 | 150 |
Here the values within the braces are the expected frequencies.
Finally substitute the values in the
Step 4: Rejection rule:
Reject
Since
Step 5: Conclusion
Reject the null hypothesis and conclude that proportion of participants who claim to remember broken glass differ significantly from group to group.
b.
To find: The value of Cramer’s V to measure the size of the treatment effect.
Answer to Problem 13P
Explanation of Solution
Calculations:
The formula for Cramer’s V is:
Here,
Substitute 7.77 for
Hence, value of Cramer’s V is 0.227
c.
To describe: How does the phrasing of the question influence the participant’s memories.
Answer to Problem 13P
Explanation of Solution
Cramer’s V is used as post-test to determine strengths of association once the chi-square has determined significance. A value of 0.227 indicates a small effect. That is, a little association between the groups.
d.
Answer to Problem 13P
Explanation of Solution
The result showed that the proportion of participants who claim to remember broken glass differ significantly from group to group.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Essentials of Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap Course List)
 Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill


