
(a)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
Dienes are the compounds that contain carbon-carbon double bonds. The term conjugated dienes is used when the double bonds are present alternatively in a hydrocarbon chain. The mathematical function that describes the wave like behavior of the electron in a molecule is expressed by molecular orbital. The physical and chemical properties are found with the help of molecular orbital.
Answer to Problem 15.1P
The bonding molecular orbitals are
The anti-bonding molecular orbitals are
The molecular orbitals of conjugated
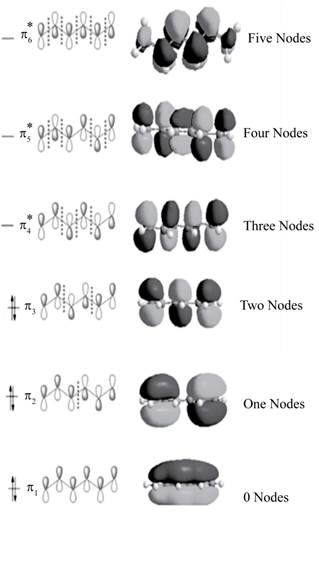
Explanation of Solution
In
The three bonding molecular orbitals are
The three anti bonding molecular orbitals are
The sketch showing the molecular orbital of conjugated
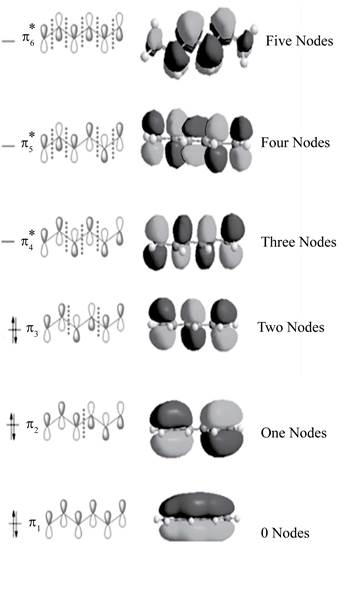
Figure 1
The three bonding molecular orbitals are
The three anti bonding molecular orbitals are
The sketch showing the molecular orbital of conjugated
(b)
Interpretation:
The total number of nodes in the
Concept introduction:
The term conjugated dienes is used when the double bonds are present alternatively in a hydrocarbon chain. The mathematical function that describes the wave like behavior of an electron in a molecule is expressed by molecular orbital. The molecular orbital contains nodes and lobes. Nodes are the regions in the molecular orbital of conjugated system in which the adjoining orbital lobes undergoes a phase change.
Answer to Problem 15.1P
The total number of nodes that the molecular orbital (MOs) of conjugated
Explanation of Solution
There is no change of phase occurs in lobes in the
There is one change of phase occurs in lobes in the
There is two change of phase occurs in lobes in the
There are four change of phase occurs in lobes in the
There are five change of phase occurs in lobes in the
There are six change of phase occurs in lobes in the
The number of nodes that molecular orbital (MOs) of conjugated
| Molecular Orbital | Number of Nodes |
| Zero | |
| One | |
| Two | |
| Three | |
| Four | |
| Five |
The number of nodes that molecular orbital (MOs) of conjugated
(c)
Interpretation:
The position of the nodes in
Concept introduction:
The term conjugated dienes is used when the double bonds are present alternatively in a hydrocarbon chain. The mathematical function that describes the wave like behavior of the electron in a molecule is expressed by molecular orbital. The molecular orbital contains nodes and lobes. Nodes are the regions in the molecular orbital of conjugated system in which the adjoining orbital lobes undergoes a phase change.
Answer to Problem 15.1P
The position of the nodes in
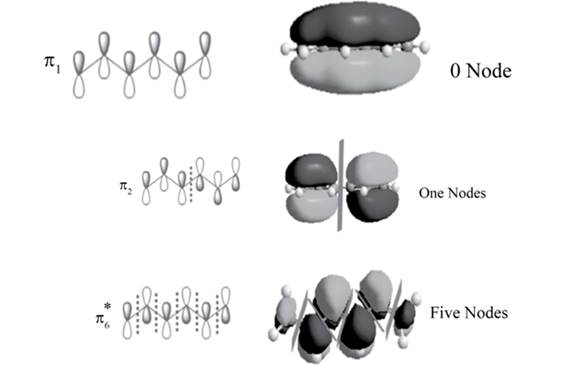
Explanation of Solution
There is no change of phase occurs in lobes in the
.
The sketch of
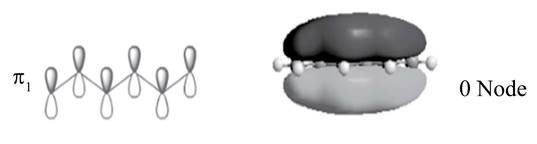
Figure 2
There is one change of phase occurs in lobes in the
The sketch of

Figure 3
There are 6 change of phase occurs in lobes in the
The
The sketch of

Figure 4
The position of the nodes in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- .For anion NO2-, (a) predict the stereochemistry. Justify your prediction with VSEPR theory and by formal charge; (b) indicate the hybridization appropriate to the stereochemistry; (c) describe the bond character of N-O for the resonance structure.arrow_forwardWhich of the structures below is not expected to contribute to the CO2 resonance hybrid?arrow_forwardConstruct the molecular-orbital energy level diagramsof (a) ethene and (b) ethyne on the basis that the moleculesare formed from the appropriately hybridized CH2 or CH fragmentsarrow_forward
- the following figure shows the bond distances for the homonuclear diatomics of the 2 nd period p-block elements, as well as those for some of the ions derived from these species. i) Note that N 2 + has a longer bond distance than N 2, but O 2 + has a shorter bond distance than O 2. Explain this difference. ii) Estimate the bond distance of N 2 - and justify your answer.arrow_forwardUse molecular orbital theory to account for the trend in the λmax values observed in the UV absorption spectra of polyenes 5-7.arrow_forwardProvide an overall assessment of the ability of the MMFF94 force field for representation of a water trimer structure. Would you suggest the use of this force field to study larger molecules?arrow_forward
- The dipole moment of bromobenzene is 5.17 × 10−30 C m and its polarizability volume is approximately 1.5 × 10−29 m3. Estimate its relative permittivity at 25 °C, when its mass density is 1491 kg m−3.arrow_forwardUsing the molecular orbital method and its qualitative explanations, justify that the bond formation energy in the B2 molecule is equal to -297 kJ mol-1, while in the ionized N2+ molecule it is equal to -842 kJ mol-1. Explain whether these molecules are diamagnetic or paramagnetic.arrow_forward1. How many molecular orbitals describe 2,4,6-Octatriene ?arrow_forward
- The kinetic energy of an electron ejected from the σ*2s molecular orbital of N2 using58.4 nm radiation is 4.23 x 10-19 J. What is the ionization energy, in both kJ/mol and eV,of an electron from this orbital?arrow_forwardIdentify the bond order and magnetic effect for N2+1.arrow_forwardWhy is the bond order and magnetic of C2?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

