
Concept explainers
Complete the following summary of Morgan’s crosses involving the mutant white-eyed fly by filling in the Punnett square and indicating the genotypes and
Genotypes
_____ _____ _____ _____
Phenotypes
_____ _____ _____ _____
To complete: The summary of Morgan’s cross that involves the mutant white-eyed fly by filling in the Punnett square and by indicating the genotypes and phenotypes of the F2 generation.
Introduction: Sex chromosomes are those chromosomes that play a crucial role in determination of sex of the individual. They have important function in the development of sexual characteristics in the organisms.
Answer to Problem 1IQ
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 represents the summary of Morgan’s cross that involves the mutant white-eyed fly by filling in the Punnett square and by indicating the genotypes and phenotypes of the F2 generation.
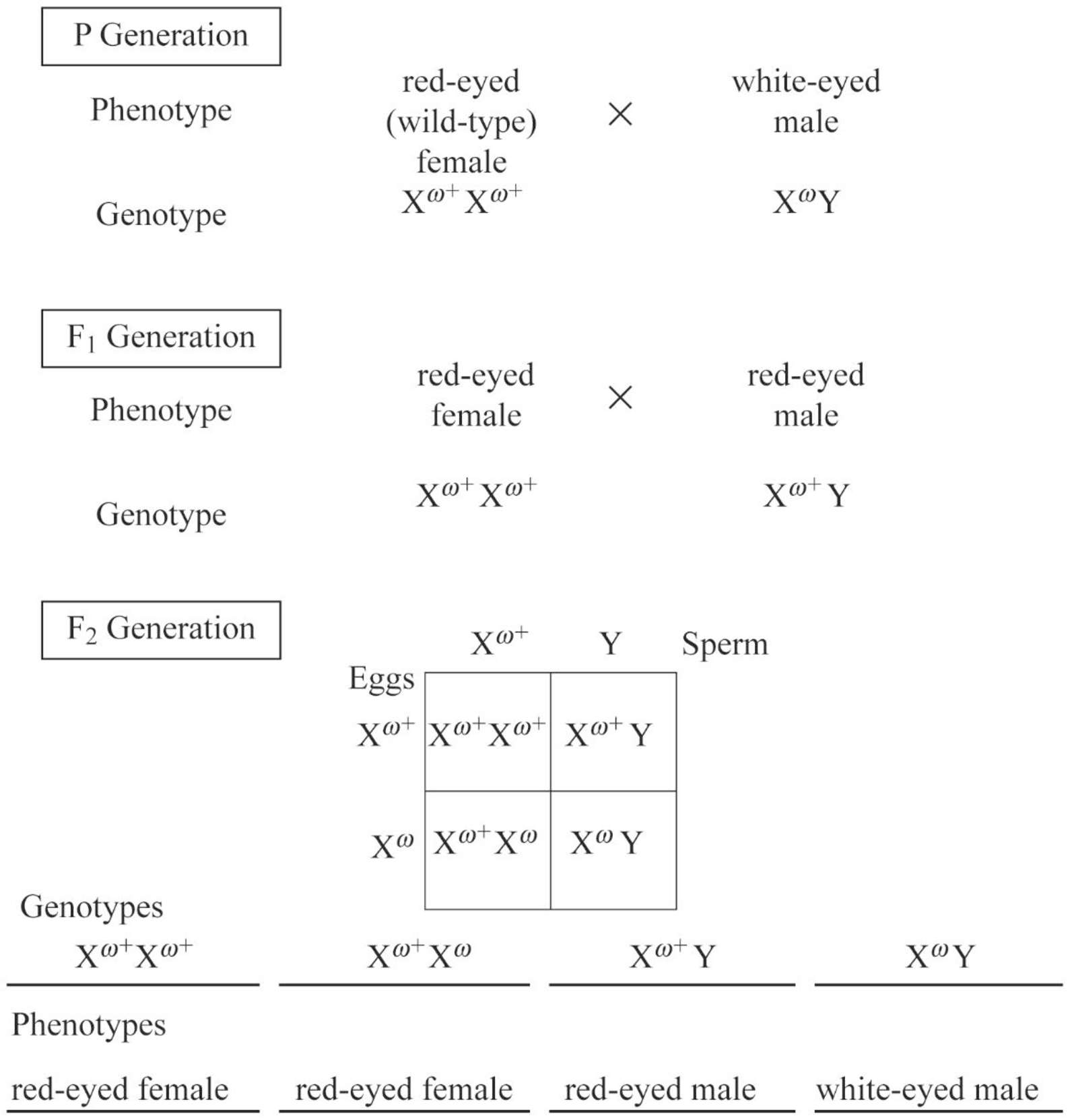
Fig.1: Morgan’s cross of mutant white-eyed fly with the genotypes and phenotypes of the F2 generation
Explanation of Solution
The X and Y chromosomes act as sex chromosomes in most of the organisms. The genes that are present on the sex chromosome are called sex-linked genes. There are approximately 1,100 X-linked genes. On the other hand, Y chromosome contains relatively very few genes.
The sex-linked genes display a unique pattern of inheritance. The expression of recessive X-linked trait requires two copies of alleles in females (homozygous) and only one copy of the allele in males (hemizygous). The probability of a male to receive a single mutated X-linked gene from their mother is high as compared to a female receiving both the X-linked mutated genes from the mother (carrier) and father (carrier).
When Morgan crossed red-eyed female (wild-type) with white-eyed male (mutant), all the offspring were red-eyed in the first generation (F1). Then, he again crossed the F1red-eyed female to the red-eyed male of F1. The typical ratio of 3:1 (red-eyed flies: white eyed flies) was observed in the F2 generation, but all white-eyed flies were males.
Morgan concluded that this could be due to hemizygous condition (presence of single X-chromosome “XW+Y”) of the males. Females required both the mutated alleles to express the phenotype (white eye color), while males needed only one mutated allele to show the phenotype. The probability to inherit both mutated copies is less.
Hence, four genotypes of F2 generation are as follows:
- XW+XW+
- XW+XW
- XW+Y
- XWY
The four phenotypes of F2 generation are as follows:
- Red-eyed female
- Red-eyed female
- Red-eyed male
- White-eyed male.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Study Guide for Campbell Biology
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction (13th Edition)
Concepts of Genetics (11th Edition)
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
- DIHYBRID CROSS Heterozygous Yellow and heterozygous round seed crossed with homozygous yellow and heterozygous round seed. Find the following: 1. Alleles of both parents (given problems) 2. Genotype 3. Phenotype ratio 4. Write the punnet square -Please answer this on the paper and explain the answer step by step. Thank you asaparrow_forwardIf the proband (III-2) marries a carrier woman, what is the probability that they will have an affected son? affected daughter? (Please show complete solution. Thanks.)arrow_forwardIn a well-publicized paternity case, the following facts were determined: the mother, a beautiful, twice-convicted axe murderer, is blood type A. Her child, Lizzie, is type O and the alleged father, a mild-mannered felon convicted of check fraud, is type B. On the last day of the trial, another father – a missionary worker with blood type O is identified. Which of the two could be Lizzie’s father? Use the space below to support your conclusion. I am really confused with the queshtion and need help finding the answer and how to prove can somone explain the answer and show it in a punnet sqaure pleasearrow_forward
- Pedro and Karli have a baby girl Ella by in vitro fertilization. Ella does not resemble either one of her parents, so they suspect that the clinic made a mistake during the procedure and implanted the wrong embryo. At Ella’s first well-baby checkup they insist that she get her blood typed. Baby Ella is type A-positive. Pedro is A-negative and Karli is O-positive. Given this information answer the following questions. (a) What are Ella’s possible genotypes? (b) What are Pedro’s possible genotypes? (c) What are Karli’s possible genotypes? (d) Is it possible that Ella is Pedro and Karli’s daughter? (e) Explain your answer in (d). (f) If baby Ella needed a blood transfusion, could either of his parents serve as a blood donor? ______ If so, which one? ______________________________ (g) Explain your answer in (f). ________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Kara is B-positive and her father has A-negative blood. Kara marries Ryan,…arrow_forwardwhat is the probability that if the couple has three children, none of them will be affected by the syndrome. refer to the attached picture and show solution. is it 107/144? can you verify my answer. please refer to the picture below.arrow_forwardAlbinism is a recessive disorder where there is a lack of melanin. Andrea and her husband Claude both have normal skin pigmentation. Andrea’s mother has the albino phenotype, but her father and her brother do not (normal pigmentation). Claude’s parents are both normal, but he has a sister who has the condition (is albino). Answer the following questions Determine the genotypes for Claude, Claude’s parents, and sister. NOTE: Draw a punnet square or show your work.arrow_forward
- Hemophilia is an X-linked disorder that affects the body’s ability to create blood clots. The allele for normal blood clotting, XH, is dominant over the allele for hemophilia, Xh. An unaffected female that is not a carrier mated with an affected male. Which of the following rows identifies the possible genotypes of the offspring? Select one: a. Female Male XHXH and XHXh XHY and XhY b. Female Male XHXh XHY c. Female Male XHXh XHY and XhY d. Female Male XHXH and XHXh XHYarrow_forwardA woman homozygous for normal height, with freckles, almond-shaped eyes, small nose, and Type A blood, has a Type O mother with no freckles and a type AB father with round eyes. She is engaged to a man with achondroplasia, round eyes and medium sized nose. Unlike his father, hismother is of normal height. Both his parents have Type O blood but nobody from both sides of his family has or had freckles. a. Write the COMPLETE genotypes of the man and the woman. Clearly indicate which genotype belongs to whom. b. Based on their genotypes, what is the probability that they will have: b.1 a child with Achondroplasia? b.2 a child of normal height? b.3 a child with type AB blood? b.4 a daughter with round eyes, freckles, and medium sized nose? b.5 a son with almond eyes, no freckles, and small nose?b.6 a daughter with same genotype as the woman? b.7 a son with same genotype as the man?arrow_forwardGiven the karyotype shown at right, is this a male or a female? Normal or abnormal? What would the phenotype of this individual be?arrow_forward
- Identify the sex and any genetic conditions by analyzing the karyotype of this individual. 1.a) male b) female 2. a) normal b) triploid c) patau d) edwards syndrome e) down syndrome f) triplo-X g) turners syndrome h) klinefelter syndromearrow_forwardWhat is the probability of producing a child that will phenotypically resemble either one (one OR the other) of the two parents in the following crosses? a) Aa bb cc dd X AA BB CC DD b) Aa Bb Cc Dd X Aa Bb Cc Dd c) Aa bb cc dd X aa bb cc dd Make sure to show your work in details.arrow_forwardWhat is the karyotype for women who have an extra X-chromosome? Discuss all the ways you can test for this abnormality.arrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
