
Principles of Economics 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781947172364
Author: Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 15, Problem 7SCQ
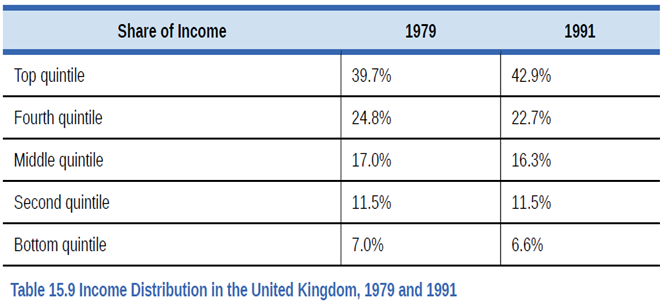
Table 15.9 shows the share of income going to each quintile of the income distribution for the United Kingdom in 1979 and 1991. Use this data to calculate what the points on a Lorenz curve would be, and sketch the Lorenz curve. How did inequality in the United Kingdom shift over this time period? How can you see the patterns in the quintiles in the Lorenz curves?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
Principles of Economics 2e
Ch. 15 - Describe how each of these changes is likely to...Ch. 15 - Jonathan is a single father with one child. He can...Ch. 15 - Imagine that the government reworks the welfare...Ch. 15 - We have discovered that the welfare system...Ch. 15 - How does the TANF attempt to loosen the poverty...Ch. 15 - A group 0f 10 people have the following annual...Ch. 15 - Table 15.9 shows the share of income going to each...Ch. 15 - Using two demand and supply diagrams, one for the...Ch. 15 - Using two demand and supply diagrams, one for the...Ch. 15 - Here is one hypothesis: A well-funded social...
Ch. 15 - Here is a second hypothesis: A well-funded social...Ch. 15 - Which set of policies is more likely to cause a...Ch. 15 - Why is there reluctance on the part of some in the...Ch. 15 - How is the poverty rate calculated?Ch. 15 - What is the poverty line?Ch. 15 - What is the difference between poverty and income...Ch. 15 - How does the poverty trap discourage people from...Ch. 15 - How can the effect of the poverty trap be reduced?Ch. 15 - Who are the near-poor?Ch. 15 - What is the safety net?Ch. 15 - Briefly explain the differences between TANF, the...Ch. 15 - Who is included in the top income quintile?Ch. 15 - What is measured on the two axes of a Lorenz...Ch. 15 - If a country had perfect income equality what...Ch. 15 - How has the inequality of income changed in the...Ch. 15 - What are some reasons why a certain degree of...Ch. 15 - What are the main reasons economists give for the...Ch. 15 - Identify some public policies that can reduce the...Ch. 15 - Describe how a push for economic equality might...Ch. 15 - What goods and services would you include in an...Ch. 15 - If a family of three earned 20,000, would they be...Ch. 15 - Exercise 15.2 and Exercise 15.3 asked you to...Ch. 15 - Explain how you would create a government program...Ch. 15 - Many critics of government programs to help...Ch. 15 - Think about the business cycle: during a...Ch. 15 - Explain how a country may experience greater...Ch. 15 - The demand for skilled workers in the United...Ch. 15 - Explain a situation using the supply and demand...Ch. 15 - What do you think is more important to focus on...Ch. 15 - To reduce income inequality, should the marginal...Ch. 15 - Redistribution of income occurs through the...Ch. 15 - How does a society or a country make the decision...Ch. 15 - Explain what the long- and short-term consequences...Ch. 15 - In country A, the population is 300 million and 50...Ch. 15 - In country B, the population is 900 million and...Ch. 15 - Susan is a single mother with three children. She...Ch. 15 - A group of 10 people have the following annual...
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
E5-20 Journalizing purchase transactions
Learning Objective 2 July 24 Kerch. Inv. $64 CR
(
Howie Jewelers had ...
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
E2-13 Identifying increases and decreases in accounts and normal balances
Learning Objective 2
Insert the mis...
Horngren's Accounting (11th Edition)
Why are the social security and Medicare taxes paid by the employee not included in labor burden?
Construction Accounting And Financial Management (4th Edition)
What is the relationship between management by exception and variance analysis?
Cost Accounting (15th Edition)
Define cost object and give three examples.
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Discussion Questions 1. What characteristics of the product or manufacturing process would lead a company to us...
Managerial Accounting (5th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc


 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:OpenStax

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:9781544336329
Author:Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:SAGE Publications, Inc




Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337617383
Author:Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:Cengage Learning