
a)
To find:
Individual’s full income, number of working hours if 75% income is devoted to leisure.
a)
Explanation of Solution
Total number of working hours = 8000
Wage per hour = $5
Total income annually :
Amount sacrificed for leisure = $5
Amount to be spent on leisure :
Number of hours for leisure:
Number of working hours= Total hours − Leisure Time
Total working hours is 2000.
Introduction: Envelop theorem states that changes in exogeneous variables must be considered for profit maximizing equations, ignoring the change in endogeneous variable.
b)
To know:
Number of working hours if 75% income is devoted to leisure when rich uncle dies
b)
Explanation of Solution
An annual income, which is left by a rich uncle = $4000
Labor income:
Total number of working hours = 8000
Wage per hour = $5
Labor income annually :
Total income :
Amount spent on leisure:
Therefore, number of leisure hours :
So, Work = Total time − Leisure time
Introduction: Envelop theorem states that changes in exogeneous variables must be considered for profit maximizing equations, ignoring the change in endogeneous variable.
c)
To ascertain:
Number of working hours if 75% income is devoted to leisure when hourly wage is $10.
c)
Explanation of Solution
New wage rate = $10
Non labor income = $4000
Total annual earned income:
Total income:
Amount spent on leisure:
Therefore, time spent on leisure:
So, work = Total time − Leisure time
Introduction: Envelop theorem states that changes in exogeneous variables must be considered for profit maximizing equations, ignoring the change in endogeneous variable.
d)
To Plot:
Graphical representation of supply labor curve..
d)
Explanation of Solution
The supply curve is shown below in the graph:
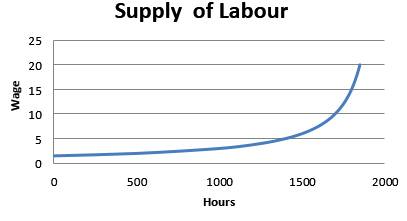
When the wage rate is $5 per hour, number of working hours is S1500
When the wage rate is $10 per hour, number of working hours is 1650.
Introduction: Envelop theorem states that changes in exogeneous variables must be considered for profit maximizing equations, ignoring the change in endogeneous variable.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- The utility of Amanda for leisure (L) and income (Y) is U = LY. The price of income is 1. If Amanda uses her spare L hours a day, (24 - L) hours will be labored. Since wages are w, the daily income is (24 - L). If the wages are positive, show that the optimal number of leisure hours that Amanda will use will always be the same. How much leisure time does Amanda demand and how much work time do she want to provide?arrow_forwardWhat is the budget line for consumption (C) and leisure (L) if a person faces a constant wage of $12 per hour, there are 110 hours in the week to work, and she receives nonlabor income of $300 per week?arrow_forwardConsider a worker who earns $20/hour in the labor market and receives $50 per week in non-labor income. Assume the total number of hours available for work (h) and leisure (L) is 168 hours per week (i.e., ? = 168 = ℎ + ?). What is the maximum value of consumption that this individual could achieve in a week? [i need this answer 4 upvotes]arrow_forward
- Suppose a worker is offered a wage of $5 per hour, plus a fixed payment of $40. What is the equation for the worker’s opportunity set in a given 24-hour day? What are the maximum total earnings the worker can earn in a day? The minimum? What is the price to the worker of consuming an additional hour of leisure?arrow_forwardSuppose you currently earn $30,000 a year. You are considering a job that will increase your lifetime earnings by $300,000 but that requires an MBA. The job will mean also attending business school for two years at an annual cost of $25,000. You already have a bachelor’s degree, for which you spent $80,000 in tuition and books. Which of the above information is relevant to your decision on whether to take the job?arrow_forwardSuppose the wage you are being paid per hour doubles form $15 to $30. Would you decide to work more hours or fewer hours ? Is there an income and substitution effect involved in your decision about how many hours you choose to work? If so, what is being substituted for what?arrow_forward
- Consider a couple (a husband and a wife) that jointly represents their collective preferences between combinations of household production time (X) and purchased goods and services (Y) according to the formula W = X2Y, where W represents the level of welfare. Suppose the maximum time available in a day is 16 hours and currently the wife devotes 6 hours to market work (H) at a wage of $16 per hour. a. What is the level of welfare associated with the wife’s current situation? b. How much additional purchasing power would the wife contribute if her market work hours increased to 8? c. How much of an increase in purchased goods and services would be necessary to compensate for the additional 2 hours of lost household production? d. Should this couple choose to have the wife increase her market work by 2 hours? e. If this couple is raising a child, suppose that combinations of household production and purchased goods are now ranked according to the formula U = X3Y. Would the additional 2…arrow_forwardSuppose your only source of income is work and that you are paid $20 per hour. This determines a budget constraint. You can buy free time at the expense of your income by working less. Likewise, you can get more income at the expense of your free time by working more. Suppose that you can choose how many hours you work. 2. Calculate your weekly income if you work 40 hours per week. Now suppose that your hourly rate drops to $15 because of an economic downturn and you decide to work 43 hours a week. How much is your weekly income going to be? (Show your calculations)arrow_forwardAssume you can work as many hours you wish at £12 per hour (net of tax). If you do not work, you have no income. You have no ability to borrow or lend, so your consumption, c, is simply equal to your income. b) Assume that your optimal choice of consumption and leisure is to work 8 hours per day. Illustrate this choice diagrammatically using the feasible set and indifference curves.arrow_forward
- Anne has a job that requires her to travel three out of every four weeks. She has an annual travel budget and can travel either by train or by plane. The airline on which she typically flies das a frequent-travel program that reduces the cose of her tickets according to the number of miles she has flown in a given year. When she reaches 25,000 miles, the airline will reduce the price of her tickects by 25 percent for the remainder of the year. when she reaches 50,000 miles, the airline will reduce the price by 50 percent for the remainder of ther year. Graph Anne's budget line with train miles on the vertical axis and plan miles on the horizontal axis Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forwardSusan obtains utility by consuming carrots C and enjoying leisure L. Suppose that she has a daily non-wage income Y of £100 and is paid a fixed hourly wage rate of £10 for every hour she works in a local coffee shop. Assume that Susan is a utility maximiser and is free to choose x hours of work per day where 0 ≤ x ≤ 10. Assume also that the unit price of C is £1. a) Suppose that L is measured on the horizontal axis and C on the vertical axis. Use these axes to draw the set of all C and L combinations that Susan can choose from. Write down Susan’s budget equation. b) Suppose that Susan’s preferences over carrots and leisure are expressed by the following utility function: U(C,L) = min{C, 10L}. Calculate Susan’s optimal consumption bundle, both algebraically and graphically. Calculate the value of MRS at the optimal choice. c) Suppose instead that Susan’s preferences are such that indifference curves in the L-C space are strictly convex to the origin, and that she chooses to work 5…arrow_forwardSuppose that there are, at most, 112 hour of leisure each week. In a fully labeled diagram in leisure-income space, depict graphically the following situation:a) if the wage rate is $10/hour, the optimal work-week would be 40 hours;b) if the wage rate is $15/hour, the optimal work-week would be 80 hours; c) if the wage rate is $20/hour, the optimal work-week would be 60 hours.d) from the above information, does it appear that the worker has a target income? Explain what the term “target income” means and indicate what does it appears to be in this example.arrow_forward
 Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning


