
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
To check whether the statement, “Aqueous solutions of
Concept Introduction:
Lewis acids are the ones which can accept a pair of electrons. Lewis bases are the ones which donate a pair of electrons. So, a substance which can donate a pair of electrons can be termed as a base.
Explanation of Solution
The general formula of amines is
Let us consider its reaction with water.

From the reaction, it is clear that the nitrogen donates a pair of electrons to hydrogen thus, making a salt. Thus, aqueous solutions of amines are basic in nature.
Hence, the statement is True.
(b)
Interpretation:
To check whether the statement, “
Concept Introduction:
Lewis acids are the ones which can accept a pair of electrons. Lewis bases are the ones which donate a pair of electrons. So, a substance which can donate a pair of electrons can be termed as a base.
Explanation of Solution
Aniline is the benzene ring that is attached to amine group. The lone pair of electrons present on the nitrogen atom is in conjugation with the aromatic ring. Thus, the lone pair of electrons is less available to donate to a proton. Hence, aniline is less basic in nature in comparison with methyl amine.
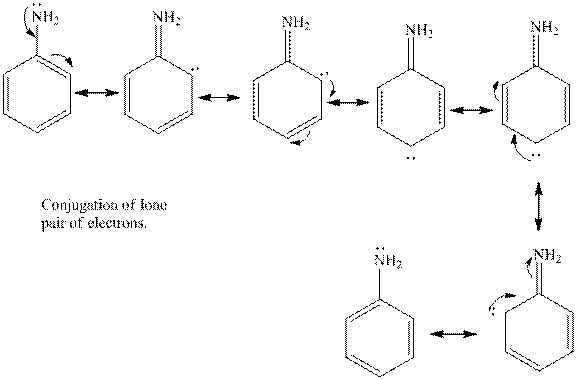
The cyclohexylamine is the one where the cyclohexyl ring is attached to the amine group. Hence, it is similar to an alkyl group attached to amine group. The alkyl groups are electron donating in nature due to inductive effect. Hence, the basicity of the amine nitrogen increases due to the attached cyclohexyl ring. Hence, the compound is more basic.
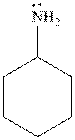
Thus, cyclohexylamine is more basic than aniline. Hence, aromatic amines are weaker bases than aliphatic amines.
The given statement is True.
(c)
Interpretation:
To check whether the statement, “Aliphatic amines are stronger bases than inorganic bases such as NaOH and KOH” is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
Generally, the strength of a base is compared on the basis that how readily the base produces the hydroxide ion. This can be either by releasing the hydroxide ion which they readily have and may be because they take hydrogen ions from the water and thus they can produce hydroxide ion.
Explanation of Solution
Generally, the strength of a base is compared on the basis that how readily the base produces the hydroxide ion. This can be either by releasing the hydroxide ion which they readily have and may be because they take hydrogen ions from the water and thus they can produce hydroxide ion.
NaOH and KOH are the acids which readily give hydroxide ions when added to water. They dissociate completely. The reaction is not reversible and hence, they are strong acids.
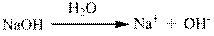
Aliphatic amines with general formula

Hence, the statement is False.
(d)
Interpretation:
To check whether the statement, “Water insoluble amines react with strong aqueous acids such as HCl to form water soluble salts” is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
Water has a property to ionize salts. This property helps in dissolution of salts in water.
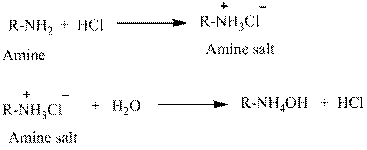
Explanation of Solution
Water is an universal solvent. Its polarity and many other aspects make it an unique solvent. It also has the property to ionize. This property makes salts to be easily dissolved in water. For this reason, amines which are usually insoluble in water are made soluble by converting into hydrochloride salts.
(e)
Interpretation:
To check whether the statement, “If the pH of an aqueous solution of a primary aliphatic amine is adjusted to pH 2.0 by the addition of concentrated HCl, the amine will be present in solution almost entirely as its conjugate acid” is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
The nature of the compound depends on its similarity of the chemical environment. The balance of a reaction is according to Le Chatlier’s principle.
Explanation of Solution
The general formula of amines is
Let us consider its reaction with water.

The reactant amine is basic in nature, and the conjugate acid is the product. Given that pH is 2.0. That means, it is on the acidic side. As the acidic environment is present, the species that will present is the amine salt.
Hence, the statement is True.
(f)
Interpretation:
To check whether the statement, “If the pH of an aqueous solution of a primary aliphatic amine is adjusted to pH 10.0 by the addition of NaOH, the amine will be present in solution almost entirely as the free base” is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
The nature of the compound depends on its similarity of the chemical environment. The balance of a reaction is according to Le Chatlier’s principle.
Explanation of Solution
The general formula of amines is
Let us consider its reaction with water.

The reactant amine is basic in nature, and the conjugate acid is the product. Given that pH is 10.0 by addition of NaOH. That means, the pH is on the basic side which is because of the added NaOH. As the basic environment is present, the species that will present is the basic amine.
Hence, the statement is True.
(g)
Interpretation:
To check whether the statement, “For a primary amine, the concentrations of salt and basic amine will be equal when the pH of the solution is equal to the pKb of the amine” is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
The nature of the compound depends on its similarity of the chemical environment. The balance of a reaction is according to Le Chatlier’s principle.
Explanation of Solution
The general formula of amines is
Let us consider its reaction with water.

The reactant amine is basic in nature, and the conjugate acid is the product. At certain pH such as pKb the system is at equilibrium. pKb is the equilibrium dissociation constant pH. That means, the pH is so supporting that the forward and reverse reactions are at equal rate. That means, there will be forward and reverse reactions but that is not noticeable because they are at equal rate.
Hence, at this pH, the concentrations of salt and the basic salt will be equal. Hence, the statement is True.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- 16-15 There are eight primary amines with the molecular formula C5H13N. (a) Name and draw a structural formula for each amine. (b > Which of these amines are chiral?arrow_forward8 (Chemical Connections 19C) Once it has been opened, and particularly if it has been left open to the air, a bottle of aspirin may develop a vinegar-like odor. Explain how this might happen.arrow_forward18-48 4-Aminobenzoic acid is prepared from benzoic acid by the following two steps. Show reagents and experimental conditions to bring about each step.arrow_forward
- 16-13 Classify each amino group as primary, secondary, or tertiary and as aliphatic or aromatic. Serotonin (a neurotransmitter) Diphenhydramine (the hydrochloride salt is the antihistamine Benadryl) Lysine (an amino acid)arrow_forward18-28 Arrange these compounds in order of increasing acidity: benzoic acid, benzyl alcohol, phenol.arrow_forward17-35 Suppose that you take a bottle of benzaldehyde (a liquid, bp 179°C) from a shelf and find a white solid in the bottom of the bottle. The solid turns litmus red; that is, it is acidic. Yet aldehydes are neutral compounds. How can you explain these observations?arrow_forward
- 7 What type of structural feature do the anhydrides of phosphoric acid have in common with carboxylic acids?arrow_forward16-35 (Chemical Connections 16B ) What is an alkaloid? Are all alkaloids basic to litmus?arrow_forward8 In Chapter 22, we will discuss a class of compounds called amino acids, so named because they contain both an amino group and a carboxyl group. Following is a structural formula for the amino acid alanine. What would you expect to be the major form of alanine present in aqueous solution (a) at pH 2.0, (b) at pH 5—6, and (c) at pH 11.0? Explain.arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
