
(a)
Interpretation:
Bond-line structure of the molecules should be drawn for the given IUPAC names.
Concept introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the parent chain.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with Cyclo.
The structure of a molecule can be drawn by analyzing the presence of prefix, suffix and root word in the given IUPAC name.
In bond-line structure the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms which are attached to that carbon atom are not to show, they are drawn as line segments. For acyclic carbon chains it draws as in a zig-zag fashion and for cyclic chains of carbon it draws as a cyclic polygon. For representing a heteroatom attached to the carbon, use a labelled line segment.
(a)
Answer to Problem 30PP
Answer
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To analyze the presence of prefix suffix and root name in the given IUPAC name and draw the bond- line structure of the molecule (a).
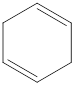
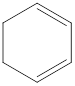
The given IUPAC name is 1,4-Cyclohexadiene.

The given IUPAC Name is 1, 4-Cyclohexadiene. In the IUPAC name 1,4 represents the position of substituents or functional group in the molecule. But no substituents presented in the name, so the 1,4 positions are locating the function groups.
The root word cyclohex indicates the molecule contains 6 carbons and the cyclo indicates the molecule is cyclic. The suffix ‘diene’ denotes the molecule is alkene and the number ‘1,4’just before the root name represent the positions of double bonds.
Therefore the bond- line structure of the molecule (a) is shown below.
(b)
Interpretation:
Bond-line structure of the molecules should be drawn for the given IUPAC names.
Concept introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the parent chain.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc. The position of this fictional group is represented just before the root name.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with Cyclo.
The structure of a molecule can be drawn by analyzing the presence of prefix, suffix and root word in the given IUPAC name.
In bond-line structure the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms which are attached to that carbon atom are not to show, they are drawn as line segments. For acyclic carbon chains it draws as in a zig-zag fashion and for cyclic chains of carbon it draws as a cyclic polygon. For representing a heteroatom attached to the carbon, use a labelled line segment.
(b)
Answer to Problem 30PP
Answer
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To analyze the presence of prefix suffix and root name in the given IUPAC name and draw the bond- line structure of the molecule (b).
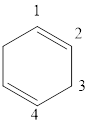
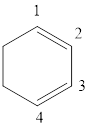
The given IUPAC name is 1, 3-Cyclohexadiene.

The given IUPAC Name is 1, 3-Cyclohexadiene. In the IUPAC name 1,3 represents the position of substituents or functional group in the molecule. But no substituents presented in the name, so the 1, 3 positions are locating the function groups.
The root word cyclohex, indicates the molecule contains 6 carbons and the cyclo indicates the molecule is cyclic, the suffix ‘diene’ denotes the molecule is alkene and the number ‘1,3’just before the root name represent the positions of double bonds.
Therefore the bond- line structure of the molecule (b) is shown below.
(c)
Interpretation:
Bond-line structure of the molecules should be drawn for the given IUPAC names.
Concept introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the parent chain.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc. The position of this fictional group is represented just before the root name.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with Cyclo.
The structure of a molecule can be drawn by analyzing the presence of prefix, suffix and root word in the given IUPAC name.
In bond-line structure the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms which are attached to that carbon atom are not to show, they are drawn as line segments. For acyclic carbon chains it draws as in a zig-zag fashion and for cyclic chains of carbon it draws as a cyclic polygon. For representing a heteroatom attached to the carbon, use a labelled line segment.
(c)
Answer to Problem 30PP
Answer
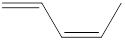
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To analyze the presence of prefix suffix and root name in the given IUPAC name and draw the bond- line structure of the molecule (c).
The given IUPAC name is (z)-1, 3-Pentadiene.

The given IUPAC Name is (z)-1, 3-Pentadiene.
In the IUPAC name 1, 3 represent the position of substituents or functional groups in the molecule. In the IUPAC name 1, 3 represent the position of substituents or functional group in the molecule. But no substituents presented in the name, so the 1,3 positions are locating the function groups.
The word pent indicates the molecule contains 5 carbons. The suffix ‘diene’ denotes the molecule is alkene and the number ‘1, 3’ just before the root name represents the positions of double bonds. The prefix ‘z’ is a stereo-descriptor for the double bond, which indicates the non-similar groups are attached to double bond on same sides.
Hence the bond- line structure for the given IUPAC name is
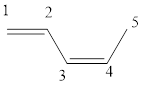
(d)
Interpretation:
Bond-line structure of the molecules should be drawn for the given IUPAC names.
Concept introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the parent chain.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc. The position of this fictional group is represented just before the root name.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with Cyclo.
The structure of a molecule can be drawn by analyzing the presence of prefix, suffix and root word in the given IUPAC name.
In bond-line structure the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms which are attached to that carbon atom are not to show, they are drawn as line segments. For acyclic carbon chains it draws as in a zig-zag fashion and for cyclic chains of carbon it draws as a cyclic polygon. For representing a heteroatom attached to the carbon, use a labelled line segment.
(d)
Answer to Problem 30PP
Answer
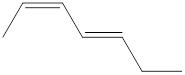
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To analyze the presence of prefix suffix and root name in the given IUPAC name and draw the bond- line structure of the molecule (d).
The given IUPAC name is (2Z, 4E)-Hepta-2,4-diene.

The given IUPAC Name is (2Z, 4E)-Hepta-2,4-diene.
The word Hepta indicates the molecule contains 7 carbons. The suffix ‘diene’ denotes the molecule is alkene and the number ‘2, 4’ just before the root name represents the positions of double bonds. The prefix ‘2Z,4E’ is the stereo-descriptor for the double bonds, which indicates the non-similar groups attached to 2-positioned double bond are on same sides and the non-similar groups attached to 4-positioned double bond are on opposite sides.
Hence the bond- line structure for the given IUPAC name is
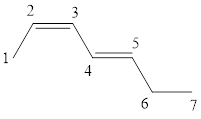
(e)
Interpretation:
Bond-line structure of the molecules should be drawn for the given IUPAC names.
Concept introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the parent chain.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc. The position of this fictional group is represented just before the root name.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with Cyclo.
The structure of a molecule can be drawn by analyzing the presence of prefix, suffix and root word in the given IUPAC name.
In bond-line structure the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms which are attached to that carbon atom are not to show, they are drawn as line segments. For acyclic carbon chains it draws as in a zig-zag fashion and for cyclic chains of carbon it draws as a cyclic polygon. For representing a heteroatom attached to the carbon, use a labelled line segment.
(e)
Answer to Problem 30PP
Answer
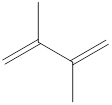
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To analyze the presence of prefix suffix and root name in the given IUPAC name and draw the bond- line structure of the molecule (e).
The given IUPAC name is 2, 3–Dimethyl-1, 3-butadiene.

The given IUPAC Name is 2, 3–Dimethyl-1, 3-butadiene.
In the IUPAC name 2, 3 represent the position of substituents in the molecule. Dimethyl is the prefix that indicates the presence of two methyl groups in the molecule.
The word but indicates the molecule contains 4 carbons. The suffix diene denotes the molecule is alkene and the number ‘2, 3’ just before the root name represents the positions of double bonds.
Hence the bond- line structure for the given IUPAC name is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





