
Concept explainers
Good Scent, Inc., produces two colognes: Rose and Violet. Of the two, Rose is more popular. Data concerning the two products follow:
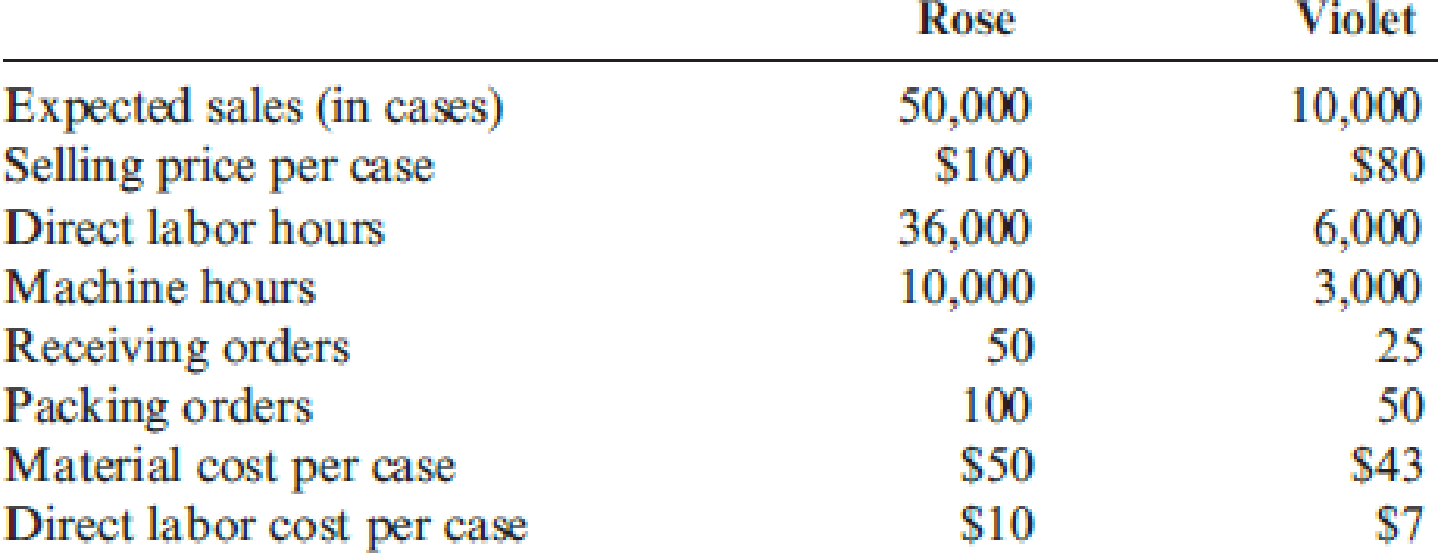
The company uses a conventional costing system and assigns overhead costs to products using direct labor hours. Annual overhead costs follow. They are classified as fixed or variable with respect to direct labor hours.
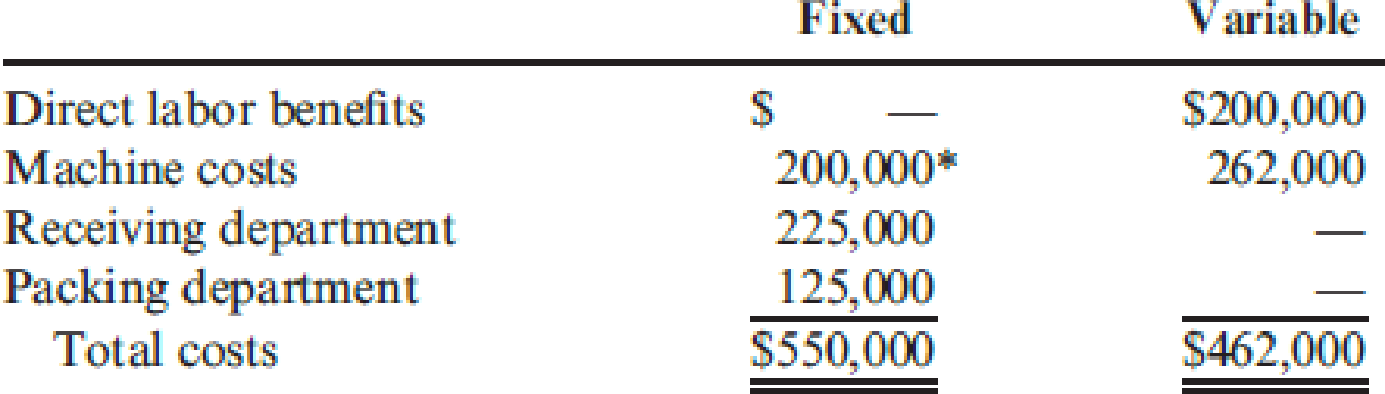
Required:
- 1. Using the conventional approach, compute the number of cases of Rose and the number of cases of Violet that must be sold for the company to break even.
- 2. Using an activity-based approach, compute the number of cases of each product that must be sold for the company to break even.
1.
Ascertain the break-even point using the conventional approach.
Explanation of Solution
Contribution Margin Ratio: The contribution margin ratio shows the amount of difference in the actual sales value and the variable expenses in percentage. This margin indicates that percentage which is available for sale above the fixed costs and the profit. The formula for variable cost ratio is shown below:
Break-Even Point: The break-even point refers to the point of sales at which the firm neither earns a profit nor suffers a loss. It is also known as the point of sales or sales value at which the firm recovers the entire cost of fixed and variable nature.
Break-Even in sales revenue: The break-even in sales revenue refers to the sales volume required to cover the fixed and variable costs and left out with neither profit nor loss.
Compute the package contribution margin units:
| Input | Price (A) | Unit Variable cost (B) | Unit Contribution margin | Sales Mix (D) |
Package Unit Contribution margin |
| Rose | $100.00 | $67.92 | $32.08 | 5 | $160.40 |
| Violet | $80.00 | $56.60 | $23.40 | 1 | $23.40 |
| Package Total | $183.80 |
Table (1)
Compute the break-even packages:
The number of break-even packages is 2,992.
Compute the break-even for Rose:
The number of break-even for Rose is 14,960.
Compute the break-even for Violet:
The number of break-even for Violet is 2,992.
Working Notes:
Compute the unit variable cost for rose:
The variable cost per unit for rose is $67.92.
Compute the unit variable cost for violet:
The variable cost per unit for violet is $56.60.
2.
Compute the break-even point and the incremental profit using the activity based costing.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the unit-based variable cost per unit:
| Particulars | Rose | Violet |
| Unit-based variable costs: | ||
| Prime costs | $60.00 | $50.00 |
| Benefits | $3.43 | $2.86 |
| Machine costs | $4.03 | $6.05 |
| Total | $67.46 | $58.91 |
| Sales Mix | ||
| Package Cost | $337.30 | $58.91 |
Table (2)
Compute the total package cost:
The total package cost is $396.21 (X1).
Compute the benefits cost per unit for rose:
The benefits cost per unit for rose is $3.43.
Compute the benefits cost per unit for violet:
The benefits cost per unit for violet is $2.86.
Compute the unit machine cost for rose:
The machine cost per unit for rose is $4.03.
Compute the unit machine cost for violet:
The machine cost per unit for violet is $6.05.
Compute the non-unit-based variable overhead cost per unit:
| Particulars | Calculations | Amount ($) |
| Non-unit-based variable costs: | ||
| Receiving (X2) | $3,000 | |
| Packing (X3) | $833.33 | |
Table (2)
Compute the sales and variable cost per unit:
| Particulars | Calculations | Amount ($) |
| Sales | $580.00 | |
| Variable cost | $396.20 | |
| Contribution margin | $183.80 |
Table (2)
CVP analysis:
Let,
X1 = Number of packages
X2 = Number of receiving orders
X3 = Number of packing orders
The number of break-even packages is 2,992.
Compute the break-even for Rose:
The number of break-even for Rose is 14,960.
Compute the break-even for Violet:
The number of break-even for Violet is 2,992.
Thus, the break-even point for Roses and Violets are same under both the requirements.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
- Evans, Inc., has a unit-based costing system. Evanss Miami plant produces 10 different electronic products. The demand for each product is about the same. Although they differ in complexity, each product uses about the same labor time and materials. The plant has used direct labor hours for years to assign overhead to products. To help design engineers understand the assumed cost relationships, the Cost Accounting Department developed the following cost equation. (The equation describes the relationship between total manufacturing costs and direct labor hours; the equation is supported by a coefficient of determination of 60 percent.) Y=5,000,000+30X,whereX=directlaborhours The variable rate of 30 is broken down as follows: Because of competitive pressures, product engineering was given the charge to redesign products to reduce the total cost of manufacturing. Using the above cost relationships, product engineering adopted the strategy of redesigning to reduce direct labor content. As each design was completed, an engineering change order was cut, triggering a series of events such as design approval, vendor selection, bill of materials update, redrawing of schematic, test runs, changes in setup procedures, development of new inspection procedures, and so on. After one year of design changes, the normal volume of direct labor was reduced from 250,000 hours to 200,000 hours, with the same number of products being produced. Although each product differs in its labor content, the redesign efforts reduced the labor content for all products. On average, the labor content per unit of product dropped from 1.25 hours per unit to one hour per unit. Fixed overhead, however, increased from 5,000,000 to 6,600,000 per year. Suppose that a consultant was hired to explain the increase in fixed overhead costs. The consultants study revealed that the 30 per hour rate captured the unit-level variable costs; however, the cost behavior of other activities was quite different. For example, setting up equipment is a step-fixed cost, where each step is 2,000 setup hours, costing 90,000. The study also revealed that the cost of receiving goods is a function of the number of different components. This activity has a variable cost of 2,000 per component type and a fixed cost that follows a step-cost pattern. The step is defined by 20 components with a cost of 50,000 per step. Assume also that the consultant indicated that the design adopted by the engineers increased the demand for setups from 20,000 setup hours to 40,000 setup hours and the number of different components from 100 to 250. The demand for other non-unit-level activities remained unchanged. The consultant also recommended that management take a look at a rejected design for its products. This rejected design increased direct labor content from 250,000 hours to 260,000 hours, decreased the demand for setups from 20,000 hours to 10,000 hours, and decreased the demand for purchasing from 100 component types to 75 component types, while the demand for all other activities remained unchanged. Required: 1. Using normal volume, compute the manufacturing cost per labor hour before the year of design changes. What is the cost per unit of an average product? 2. Using normal volume after the one year of design changes, compute the manufacturing cost per hour. What is the cost per unit of an average product? 3. Before considering the consultants study, what do you think is the most likely explanation for the failure of the design changes to reduce manufacturing costs? Now use the information from the consultants study to explain the increase in the average cost per unit of product. What changes would you suggest to improve Evanss efforts to reduce costs? 4. Explain why the consultant recommended a second look at a rejected design. Provide computational support. What does this tell you about the strategic importance of cost management?arrow_forwardLarsen, Inc., produces two types of electronic parts and has provided the following data: There are four activities: machining, setting up, testing, and purchasing. Required: 1. Calculate the activity consumption ratios for each product. 2. Calculate the consumption ratios for the plantwide rate (direct labor hours). When compared with the activity ratios, what can you say about the relative accuracy of a plantwide rate? Which product is undercosted? 3. What if the machine hours were used for the plantwide rate? Would this remove the cost distortion of a plantwide rate?arrow_forwardThe Chocolate Baker specializes in chocolate baked goods. The firm has long assessed the profitability of a product line by comparing revenues to the cost of goods sold. However, Barry White, the firms new accountant, wants to use an activity-based costing system that takes into consideration the cost of the delivery person. Following are activity and cost information relating to two of Chocolate Bakers major products: Using activity-based costing, which of the following statements is correct? a. The muffins are 2,000 more profitable. b. The cheesecakes are 75 more profitable. c. The muffins are 1,925 more profitable. d. The muffins have a higher profitability as a percentage of sales and, therefore, are more advantageous.arrow_forward
- Geneva, Inc., makes two products, X and Y, that require allocation of indirect manufacturing costs. The following data were compiled by the accountants before making any allocations: The total cost of purchasing and receiving parts used in manufacturing is 60,000. The company uses a job-costing system with a single indirect cost rate. Under this system, allocated costs were 48,000 and 12,000 for X and Y, respectively. If an activity-based system is used, what would be the allocated costs for each product?arrow_forwardAbernathy, Inc., produces two different generators and is concerned about their quality. The company has identified the following quality activities and costs associated with the two products: Required: 1. Calculate the quality cost per unit for each product, and break this unit cost into quality cost categories. Which of the two seems to have the lowest quality? 2. How might a manager use the unit quality cost information?arrow_forwardSilven Company has identified the following overhead activities, costs, and activity drivers for the coming year: Silven produces two models of cell phones with the following expected activity demands: 1. Determine the total overhead assigned to each product using the four activity drivers. 2. Determine the total overhead assigned to each model using the two most expensive activities. The costs of the two relatively inexpensive activities are allocated to the two expensive activities in proportion to their costs. 3. Using ABC as the benchmark, calculate the percentage error and comment on the accuracy of the reduced system. Explain why this approach may be desirable.arrow_forward
- Medical Tape makes two products: Generic and Label. It estimates it will produce 423,694 units of Generic and 652,200 of Label, and the overhead for each of its cost pools is as follows: It has also estimated the activities for each cost driver as follows: How much is the overhead allocated to each unit of Generic and Label?arrow_forwardMott Company recently implemented a JIT manufacturing system. After one year of operation, Heidi Burrows, president of the company, wanted to compare product cost under the JIT system with product cost under the old system. Motts two products are weed eaters and lawn edgers. The unit prime costs under the old system are as follows: Under the old manufacturing system, the company operated three service centers and two production departments. Overhead was applied using departmental overhead rates. The direct overhead costs associated with each department for the year preceding the installation of JIT are as follows: Under the old system, the overhead costs of the service departments were allocated directly to the producing departments and then to the products passing through them. (Both products passed through each producing department.) The overhead rate for the Machining Department was based on machine hours, and the overhead rate for assembly was based on direct labor hours. During the last year of operations for the old system, the Machining Department used 80,000 machine hours, and the Assembly Department used 20,000 direct labor hours. Each weed eater required 1.0 machine hour in Machining and 0.25 direct labor hour in Assembly. Each lawn edger required 2.0 machine hours in Machining and 0.5 hour in Assembly. Bases for allocation of the service costs are as follows: Upon implementing JIT, a manufacturing cell for each product was created to replace the departmental structure. Each cell occupied 40,000 square feet. Maintenance and materials handling were both decentralized to the cell level. Essentially, cell workers were trained to operate the machines in each cell, assemble the components, maintain the machines, and move the partially completed units from one point to the next within the cell. During the first year of the JIT system, the company produced and sold 20,000 weed eaters and 30,000 lawn edgers. This output was identical to that for the last year of operations under the old system. The following costs have been assigned to the manufacturing cells: Required: 1. Compute the unit cost for each product under the old manufacturing system. 2. Compute the unit cost for each product under the JIT system. 3. Which of the unit costs is more accurate? Explain. Include in your explanation a discussion of how the computational approaches differ. 4. Calculate the decrease in overhead costs under JIT, and provide some possible reasons that explain the decrease.arrow_forwardThe chief executive officer of Acadia, Inc. attended a conference in which one of the sessions was devoted to variable costing. The CEO was impressed by the presentation and has asked that the following data of Acadia, Inc. be used to prepare comparative statements using variable costing and the companys absorption costing. The data follow: The factory produced 80,000 units during the period, and 70,000 units were sold for 700,000. 1. Prepare an income statement using variable costing. 2. Prepare an income statement using absorption costing. (Round unit costs to three decimal places.)arrow_forward
- Grundvig Manufacturing produces several types of bolts used in aircraft. The bolts are produced in batches and grouped into three product families. Because the product families are used in different kinds of aircraft, customers also can be grouped into three categories, corresponding to the product family that they purchase. The number of units sold to each customer class is the same. The selling prices for the three product families range from 0.50 to 0.80 per unit. Historically, the costs of order entry, processing, and handling were expensed and not traced to individual customer groups. These costs are not trivial and totaled 9,000,000 for the most recent year. Recently, the company started emphasizing a cost reduction strategy with an emphasis on creating a competitive advantage. Upon investigation, management discovered that order-filling costs were driven by the number of customer orders processed with the following cost behavior: Step-fixed cost component: 50,000 per step (2,000 orders define a step) Variable cost component: 20 per order Grundvig currently has sufficient steps to process 200,000 orders. The expected customer orders for the year total 200,000. The expected usage of the order-filling activity and the average size of an order by customer category follow: As a result of cost behavior analysis, the marketing manager recommended the imposition of a charge per customer order. The charge was implemented by adding the cost per order to the price of each order (computed by using the projected ordering costs and expected orders). This ordering cost was then reduced as the size of the order increased and was eliminated as the order size reached 2,000 units. Within a short period of communicating this new price information to customers, the average order size for all three product families increased to 2,000 units. Required: 1. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Grundvig traditionally has expensed order-filling costs. What is the most likely reason for this practice? 2. Calculate the cost per order for each customer category. (Note: Round to two decimal places.) 3. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Calculate the reduction in order-filling costs produced by the change in pricing strategy (assuming that resource spending is reduced as much as possible and that the total units sold remain unchanged). Explain how exploiting customer activity information produced this cost reduction. Would any other internal activities benefit from this pricing strategy?arrow_forwardYoung Company is beginning operations and is considering three alternatives to allocate manufacturing overhead to individual units produced. Young can use a plantwide rate, departmental rates, or activity-based costing. Young will produce many types of products in its single plant, and not all products will be processed through all departments. In which one of the following independent situations would reported net income for the first year be the same regardless of which overhead allocation method had been selected? a. All production costs approach those costs that were budgeted. b. The sales mix does not vary from the mix that was budgeted. c. All manufacturing overhead is a fixed cost. d. All ending inventory balances are zero.arrow_forwardDK manufactures three products, W, X and Y. Each product uses the same materials and the same type of direct labour but in different quantities. The company currently uses a cost plus basis to determine the selling price of its products. This is based on full cost using an overhead absorption rate per direct labour hour. However, the managing director is concerned that the company may be losing sales because of its approach to setting prices. He thinks that a marginal costing approach may be more appropriate, particularly since the workforce is guaranteed a minimum weekly wage and has a three month notice period. Required: a) Given the managing director’s concern about DK’s approach to setting selling prices, discuss the advantages and disadvantages of marginal cost plus pricing AND total cost-plus pricing.arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning





