
a)

Interpretation:
The major product(s) obtainable from sulfonation of fluorobenzene is/are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The substituents attached to the ring have a strong influence on the incoming electrophile. Electron releasing substituent groups, except halogens, activate the ring and direct the incoming electrophile to the o- and p- positions. Halogens are o- and p- directors but they deactivate the ring. Electron withdrawing substituent groups deactivate the ring and direct the incoming electrophile to the m- position.
To predict:
The major products obtainable from sulfonation of fluorobenzene.
Answer to Problem 51AP
The major products obtainable from sulfonation of fluorobenzene are o-flurobenzenesulfonic acid and p- flurobenzenesulfonic acid.
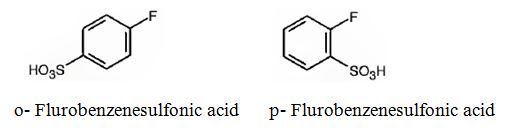
Explanation of Solution
Fluorine attached to an aromatic ring is an o- and p- directing deactivating group. Hence it directs the electrophile, SO3H+ to these positions.
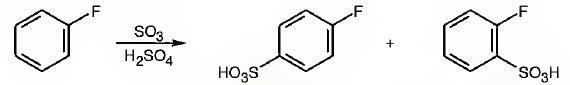
The major products obtainable from sulfonation of fluorobenzene are o-flurobenzenesulfonic acid and p- flurobenzenesulfonic acid.

b)
Interpretation:
The major product(s) obtainable from sulfonation of m-bromophenol is/are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Electrophilic substitution of disubstituted benzenes follows three simple rules. (i) If the directing influence of both the substituents reinforce each other, a single product results. (ii) If the directing influences of both the substituent groups oppose each other, the most powerful activating group among them has the dominant influence but usually a mixture of products results. (iii) In meta disubstituted compounds, further substitution in between the groups occurs only rarely, due to steric reasons.
To predict:
The major product(s) obtainable from sulfonation of m-bromophenol.
Answer to Problem 51AP
The major products produced during the sulfonation of m-bromophenol are 2-bromo-4-hydroxybenzenesulfonicacid (I) and 4-bromo-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonicacid (II).
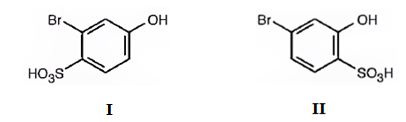
Explanation of Solution
The Br is an ortho and para directing and deactivating group while -OH group is also an ortho and para directing and highly activating group. Hence the -OH group decides the position at which the electrophilic substitution reaction will occur. The electrophile, SO3H+, enters into the ortho and para positions with respect to -OH group to produce 2-bromo-4-hydroxybenzenesulfonicacid (I) and 4-bromo-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonicacid (II).
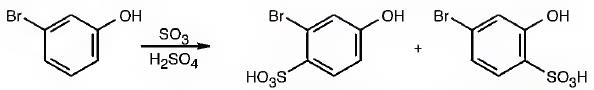
The major products produced during the sulfonation of m-bromophenol are 2-bromo-4-hydroxybenzenesulfonicacid (I) and 4-bromo-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonicacid (II).

c)
Interpretation:
The major product(s) obtainable from sulfonation of m-dichlorobenzene is/are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Electrophilic substitution of disubstituted benzenes follows three simple rules. (i) If the directing influence of both the substituents reinforce each other, a single product results. (ii) If the directing influences of both the substituent groups oppose each other, the most powerful activating group among them has the dominant influence but usually a mixture of products results. (iii) In meta disubstituted compounds, further substitution in between the groups occurs only rarely, due to steric reasons.
To predict:
The major product(s) obtainable from sulfonation of m-dichlorobenzene.
Answer to Problem 51AP
The major product produced during the sulfonation of m-dichlorobenzene is 2,4-dichlorobenzenesulfonicacid.
Explanation of Solution
In electrophilic substitution reactions, Cl is an ortho and para directing and deactivating group. Hence the electrophile, SO3H+, can enter into the ortho and para positions with respect to both Cl atoms. The ortho position in between the two Cl atoms is not favored for steric reasons. Hence the SO3H gets substituted in the p-position to a Cl which happens to be the ortho position to another Cl to yield 2,4-dichlorobenzenesulfonicacid.
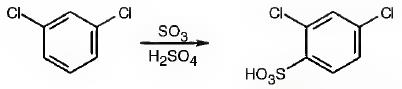
The major product produced during the sulfonation of m-dichlorobenzene is 2,4-dichlorobenzenesulfonicacid(I).

d)

Interpretation:
The major product(s) obtainable from sulfonation of 2,4-dibromophenol is/are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Electrophilic substitution of di and trisubstituted benzenes follows three simple rules. (i) If the directing influence of both the substituents reinforce each other, a single product results. (ii) If the directing influences of both the substituent groups oppose each other, the most powerful activating group among them has the dominant influence but usually a mixture of products results. (iii) In meta disubstituted compounds, further substitution in between the groups occurs only rarely, due to steric reasons.
To predict:
The major product(s) obtainable from sulfonation of 2,4-dibromophenol.
Answer to Problem 51AP
The major product produced during the sulfonation of 2,4-dibromophenol is 3,5-dibromo-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonicacid.
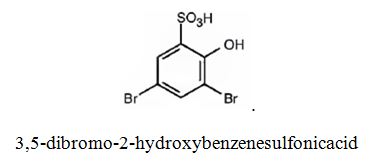
Explanation of Solution
In aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions Br is an ortho and para directing and deactivating group while –OH group also though ortho and para directing is a highly activating group. Hence the –OH group decides the position at which the electrophilic substitution reaction will occur. The electrophile, SO3H+, enters into the ortho and para positions with respect to –OH group. The para position and one ortho position to –OH are blocked by substituents. Hence the SO3H+ enters into the another ortho position to –OH group available to produce 3,5-dibromo-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonicacid.
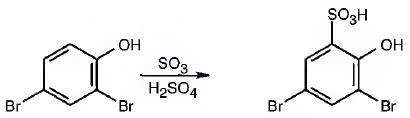
The major product produced during the sulfonation of 2,4-dibromophenol is 3,5-dibromo-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonicacid.

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- When 2-methyl-2, 5-pentanediol is treated with sulfuric acid, dehydration occurs and 2, 2-dimethyltetrahydrofuran is formed. Suggest a mechanism for this reaction. Which of the two oxygen atoms is most likely to be eliminated, and why?arrow_forwardAmines are converted into alkenes by a two-step process called Hofmann elimination. SN2 reaction of the amine with an excess of CH3I in the first step yields an intermediate that undergoes E2 reaction when treated with silver oxide as base. Pentylamine, for example, yields 1-pentene. Propose a structure for the intermediate, and explain why it readily undergoes elimination.arrow_forwardA. In the synthesis of 1-bromobutane, what is the inorganic by-product left in the reaction flask following the distillation? Why was the bromoalkane the bottom layer in the separatory funnel? B. Predict the product when 1-methylcyclohexanol reacts with H2SO4 and KBr. Show the mechanism.arrow_forward
- When A is reacted with hot aqueous NaOH, a compound B of molecular formula C8H11NO is produced. With this information, write the correct structure of B and propose the reaction mechanism (step by step, with the correct use of arrows) to obtain B.arrow_forwardWhen 5-bromo-1-pentanol is treated with sodium hydride in diethyl ether, the product is analyzed to be C5H10O. Propose a likely structure for this product, suggesting a reasonable mechanistic pathway for its formationarrow_forwardWhen 2,2-dibromo-1-phenylpropane is heated overnight with sodium amide at 150 °C, the major product (after addition of water) is a different foul-smelling compound of formula C9H8. Propose a structure for this product, and give a mechanism to account for its formation.arrow_forward
- The following sequence of steps converts (R)-2-octanol to (S)-2-octanol. Propose structural formulas for intermediates A and B, specify the configuration of each, and account for the inversion of configuration in this sequence.arrow_forwardThe treatment of (CH3)2C=CHCH2Br with H2O forms B (molecular formulaC5H10O) as one of the products. Determine the structure of B from its 1H NMR and IR spectra.arrow_forwardThe treatment of (CH3)2C=CHCH2Br with H2O forms B (molecular formula C5H10O) as one of the products. Determine the structure of B from its 1H NMR and IR spectra.arrow_forward
- A solution of acetone [(CH3)2C=O] in ethanol (CH3CH2OH) in the presence of a trace of acid was allowed to stand for several days, and a new compound of molecular formula C7H16O2 was formed. The IR spectrum showed only one major peak in the functional group region around 3000 cm−1, and the 1H NMR spectrum is given here. What is the structure of the product?arrow_forwarda)Write the SN2 reaction mechanism between iodobutane with sodium hydroxide, NaOH. b)Predict the products and show the SN1 reaction mechanism that occurs with 2-iodo-2- methylpropane in aqueous sodium hydroxide, NaOH.arrow_forwardWhen 1,4-dibromobutane was treated with excess ethanamine at propanone, the main product had the molecular formula C6H13N. Deduce the structure of this product by proposing a mechanism for the reaction.arrow_forward
 EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


