
Concept explainers
Nutterco, Inc., produces two types of nut butter: peanut butter and cashew butter. Of the two, peanut butter is the more popular. Cashew butter is a specialty line using smaller jars and fewer jars per case. Data concerning the two products follow:
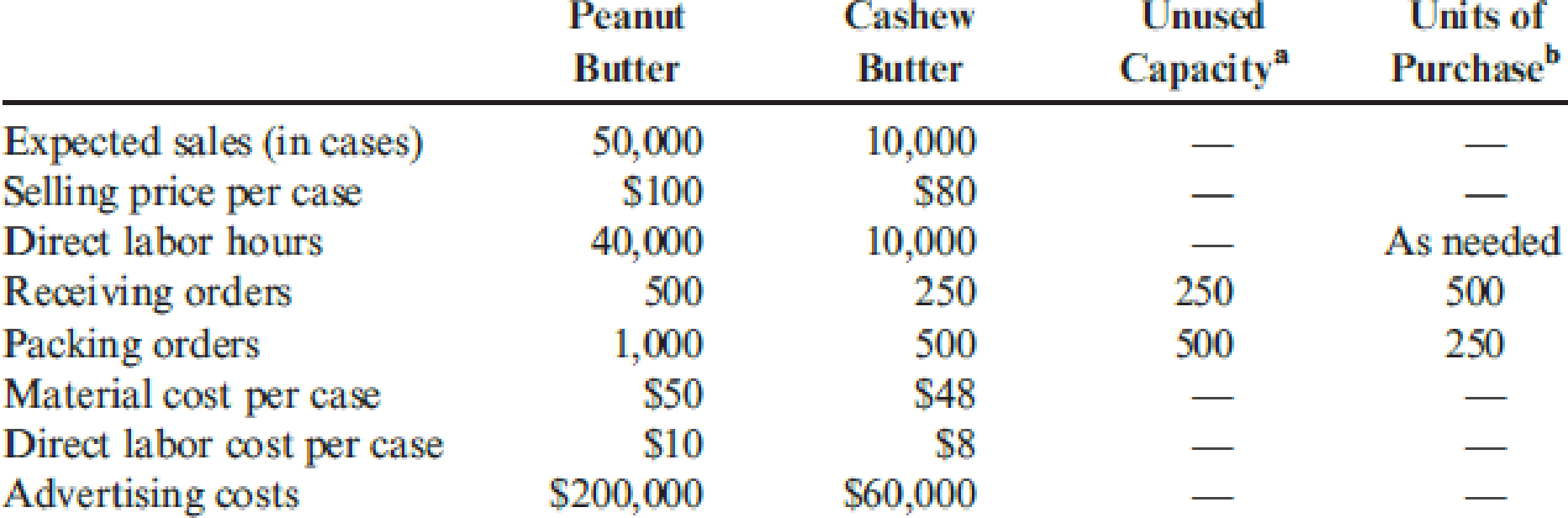
aPractical capacity less expected usage (all unused capacity is permanent).
bIn some cases, activity capacity must be purchased in steps (whole units). These steps are provided as necessary. The cost per step is the fixed activity rate multiplied by the step units. The fixed activity rate is the expected fixed activity costs divided by practical activity capacity.
Annual overhead costs are listed below. These costs are classified as fixed or variable with respect to the appropriate activity driver.
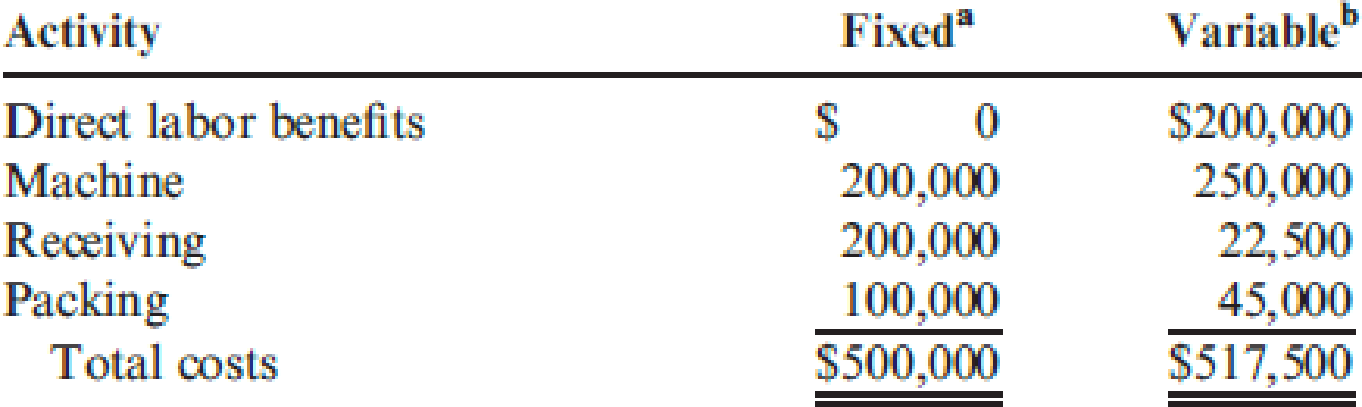
aCosts associated with practical activity capacity. The machine fixed costs are all
bThese costs are for the actual levels of the cost driver.
Required:
- 1. Prepare a traditional segmented income statement, using a unit-level overhead rate based on direct labor hours. Using this approach, determine whether the cashew butter product line should be kept or dropped.
- 2. Prepare an activity-based segmented income statement. Repeat the keep-or-drop analysis using an ABC approach.
1.
Prepare a traditional segmented income statement of company N, under a unit-level overhead rate and state whether the cashew butter product line should be kept or dropped.
Explanation of Solution
Tactical decision making: Tactical decision making is a process in which the company can choose the correct alternative based on the profitability. In tactical decision making, offer price of a product is compared with the normal selling price and offer price less than the normal selling price of product is considered as the idle capacity for decision making.
| Particulars | Peanut Butter (A) (1) | Cashew Butter (2) (B) |
Total |
| Revenues | $5,000,000 | $800,000 | $5,800,000 |
| Less: variable expenses | |||
| Direct materials | 2,500,000 | 480,000 | 2,980,000 |
| Direct labor | 500,000 | 80,000 | 580,000 |
| Variable overhead | 360,000 | 90,000 | 450,000 |
| Contribution margin | $1,640,000 | $150,000 | $1,790,000 |
| Less: Direct fixed expenses | $200,000 | $60,000 | $260,000 |
| Product margin | $1,440,000 | $90,000 | $1,530,000 |
| Less: Common fixed expenses | 567,500 (4) | ||
| Segment margin | $962,500 |
Table (1)
Working note (1):
Compute the amounts of revenues and expenses of Peanut Butter:
| Particulars | Costs per cases for Peanut butter (A) | Sales units (B) | Peanut Butter |
| Revenues | $100 | 50,000 | $5,000,000 |
| Less: variable expenses | |||
| Direct materials | $50 | 50,000 | $2,500,000 |
| Direct labor | $10 | 50,000 | 500,000 |
| Variable overhead | $9 (2) | 40,000 | 360,000 |
Table (2)
Working note (2):
Compute the variable overhead rate:
Working note (3):
Compute the amounts of revenues and expenses of Peanut Butter:
| Particulars | Costs per cases for cashew butter (A) | Sales units (B) | Cashew Butter |
| Revenues | $80 | 10,000 | $800,000 |
| Less: variable expenses | |||
| Direct materials | $48 | 10,000 | $480,000 |
| Direct labor | $8 | 10,000 | 80,000 |
| Variable overhead | $9 (2) | 10,000 | 90,000 |
Table (3)
Working note (4):
Compute the common fixed expenses:
Therefore, the company should not drop the cashew butter because the segment margin is positive.
2.
Prepare an activity-based segmented income statement of company N, under ABC approach and state whether the cashew butter product line should be kept or dropped.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare an activity-based segmented income statement of company N, under ABC approach and state whether the cashew butter product line should be kept or dropped as follows:
| Particulars | Peanut Butter (A) (1) | Cashew Butter (2) (B) | Total |
| Revenues | $5,000,000 | $800,000 | $5,800,000 |
| Less: variable expenses | |||
| Direct materials | 2,500,000 | 480,000 | 2,980,000 |
| Direct labor | 500,000 | 80,000 | 580,000 |
| Variable overhead | 360,000 | 90,000 | 450,000 |
| Contribution margin | $1,640,000 | $150,000 | $1,790,000 |
| Less: Traceable expenses | |||
| Advertising | $200,000 | $60,000 | $260,000 |
| Receiving | 115,000 (7) | 57,500 (8) | 172,500 |
| Packing | 80,000 (11) | 40,000 (12) | 120,000 |
| Product margin | $1, 245,000 | $(7,500) | $1,237,500 |
| Less: Unused activity expenses | 567,500 | ||
| Receiving (13) | 50,000 | ||
| Packing (14) | 25,000 | ||
| Less: Machine depreciation expenses | (200,000) | ||
| Segment margin | $962,500 |
Table (4)
From the above calculation it is clear that dropping the cashew butter line is better because the product margin of the cashew butter is showing a negative margin of $7,500.
Working note (5):
Compute the fixed receiving rate:
Working note (6):
Compute the variable receiving rate:
Working note (7):
Compute the receiving expenses of peanut butter:
Working note (8):
Compute the receiving expenses of cashew butter:
Working note (9):
Compute the fixed packaging rate:
Working note (10):
Compute the variable packaging rate:
Working note (11):
Compute the packaging expenses of peanut butter:
Working note (12):
Compute the packaging expenses of cashew butter:
Working note (13):
Compute the unused receiving expenses:
Working note (14):
Compute the unused packing expenses:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
- Busy-Bee Baking Company produces a variety of breads. The average price of a loaf of bread is 1. Costs are as follows: Other data: Required: 1. Compute the break-even point in units using conventional analysis. 2. Compute the break-even point in units using activity-based analysis. 3. Suppose that Busy-Bee could reduce the setup cost by 100 per setup and could reduce the number of maintenance hours needed to 1,000. How many units must be sold to break even in this case? (Round answer up to whole units.)arrow_forwardMabbut Company has the following departmental manufacturing layout for one of its plants: A consulting firm recommended a value stream with the following manufacturing cell: Required: 1. Calculate the total time it takes to produce a batch of 10 units using the traditional departmental manufacturing layout. 2. Using cellular manufacturing, how much time is saved producing the same batch of 10 units? Assuming the cell operates continuously, what is the production rate? Which process controls this production rate? 3. Assume the processing time of Welding is reduced to 6 minutes, while the times of the other processes stay the same. What is the production rate now, and how long will it take to produce a batch of 10 units if the cell is in a continuous production mode?arrow_forwardGumbrecht Company has the following departmental manufacturing layout for one of its plants: A consulting firm has recommended a value stream with the following manufacturing cell: Required: 1. Calculate the total time it takes to produce a batch of 20 units using the traditional departmental manufacturing layout. 2. Using cellular manufacturing, how much time is saved producing the same batch of 20 units? Assuming the cell operates continuously, what is the production rate? Which process controls this production rate? 3. Assume the processing time of Casting is reduced to 9 minutes, while the times of the other processes stay the same. What is the production rate now, and how long will it take to produce a batch of 20 units if the cell is in a continuous production mode?arrow_forward
- Ivanhoe Industries manufactures and sells three different models of wet-dry shop vacuum cleaners. Although the shop vacs vary in terms of quality and features, all are good sellers. Ivanhoe is currently operating at full capacity with limited machine time. Sales and production information relevant to each model is as follows: Product Economy Standard Deluxe Selling price $31.00 $53.20 $97.90 Variable costs and expenses $13.50 $18.00 $41.50 Machine hours required 0.50 0.80 1.60 Ignoring the machine time constraint, which single product should Ivanhoe Industries produce? Ivanhoe Industries should produce select a product . What is the contribution margin per unit of limited resource for each product? (Round answers to 2 decimal places, e.g. 15.75.) Model Contribution Margin…arrow_forwardMariah Enterprises makes a variety of consumer electronic products. Its camera manufacturing plant is considering choosing between two different processes, named Alpha and Beta, which can be used to make two component parts A and B. To make the correct decision, the managers would like to compare the labor and multifactor productivity of process Alpha with that of process Beta. The value of process output for component A and B are $175 and $140 per unit, respectively. The corresponding overhead costs are $6,000 and $5,000, respectively. Process Alpha Process Beta Product A B C D Output (units) 50 60 30 80 Labor ($) $1,200 $1,400 $1,000 $2,000 Material ($) $2,500 $3,000 $1,400 $3,500 a. Which process, Alpha or Beta, is more productive? b. What conclusions can you draw from your analysis?arrow_forwardRosehill Co. manufactures two types of toilet paper: Ultra-strong and Ultra-soft. Because of a recent shortage of chlorine-based bleach, a key ingredient needed for the two products, the company has to decide the optimal amount of each product to produce. Information related to the two products that use chlorine-based bleach are shown below: Ultra-strong Ultra-soft Selling price per case $100 $96 Variable cost per case $40 $44 Chlorine-based bleach required per case (in liters) 10 8 Maximum monthly demand (in cases) 500 700 Assume that Rosehill Co. only has 7,200 liters of Chlorine-based bleach available next month. To maximize the company’s contribution margin next month, how many cases of Ultra-strong and how many cases of Ultra-soft the company should produce? Multiple Choice a)300 cases of Ultra-strong and 400 cases of Ultra-soft b)500 cases of Ultra-strong and 275 cases of Ultra-soft c)500 cases of Ultra-strong and 700 cases…arrow_forward
- Dorina Company makes cases of canned dog food in batches of 1, 000 cases and sells each case for $15. The plant capacity is 50,000 cases; the company currently makes 40,000 cases. Doggie-Mart has offered to buy 1, 500 cases for $12 per case. Because product-level and facility level costs are unaffected by a special order, they are omitted. Required Complete the spreadsheet to calculate the contribution to income if the special order is accepted. Construct formulas so that the number of cases or the price could be changed and the new contribution would be automatically calculated. How would I put in Excel cell the "Number of Units for it to be 2000?arrow_forwardXYZ's Preserves currently makes jams and jellies and a variety of decorative jars used for packaging. An outside supplier has offered to supply all of the needed decorative jars for P2.00. For this make-or-buy decision, a cost analysis revealed the following avoidable unit costs for the decorative jars: Direct materials 1.06 Direct labor 0.08 Unit-related support costs 0.25 Batch-related support costs 0.24 Product-sustaining support costs 0.44 Facility-sustaining support costs 0.50 Total cost per jar 2.57 1. The net advantage (disadvantage) of accepting the supplier’s offer is? 2. The maximum price that XYZ's Preserves should be willing to pay for the decorative jars is?arrow_forwardThe Vera Molding company has two alternatives for meeting a customer requirement for 9,500 units of a specialty molding. If done in-house, fixed cost would be $518,000 with variable cost at $20 per unit. Alternative two is to outsource for a total cost of $90 per unit. What is the break-even quantity? Round your answer to the nearest whole number. units Should the firm make the 9,500 units in-house or outsource? Firm should produce the molding .arrow_forward
- A company is looking to launch a new product line, which requires new facilities to be used and at the moment has two planned products, called ‘Basic’ and ‘Super’. The cost per unit is planned as follows: Basic Super Direct materials £20 £24 Direct labour £14 £16 While using the absorption costing approach, the company uses machine hours as the basis to charge its production overheads. One unit of Basic will use 3 machine hours while one unit of Super will use 4 machine hours. The business sells these products at a price that gives a standard profit mark-up of 30% of full cost. For the coming year, the company expects to make and sell 8,000 units of Basic and 6,000 units of Super. If the company adopts the ABC approach, the details relating to the…arrow_forwardA company is looking to launch a new product line, which requires new facilities to be used and at the moment has two planned products, called ‘Basic’ and ‘Super’. The cost per unit is planned as follows: Basic Super Direct materials £20 £24 Direct labour £14 £16 While using the absorption costing approach, the company uses machine hours as the basis to charge its production overheads. One unit of Basic will use 3 machine hours while one unit of Super will use 4 machine hours. The business sells these products at a price that gives a standard profit mark-up of 30% of full cost. For the coming year, the company expects to make and sell 8,000 units of Basic and 6,000 units of Super. If the company adopts the ABC approach, the details relating to the…arrow_forwardA company is looking to launch a new product line, which requires new facilities to be used and at the moment has two planned products, called ‘Basic’ and ‘Super’. The cost per unit is planned as follows: Basic Super Direct materials £20 £24 Direct labour £14 £16 While using the absorption costing approach, the company uses machine hours as the basis to charge its production overheads. One unit of Basic will use 3 machine hours while one unit of Super will use 4 machine hours. The business sells these products at a price that gives a standard profit mark-up of 30% of full cost. For the coming year, the company expects to make and sell 8,000 units of Basic and 6,000 units of Super. If the company adopts the ABC approach, the details relating to the…arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning





