
A cylinder
(a)
The total drag force
Answer to Problem 17.1PP
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Diameter, d =
Velocity, v =
Length, l =
Formula used:
v is velocity
A is area
d is diameter
Calculation:
For water
Conclusion:
The total drag force on a cylinder when moving through water is calculated as
(b)
The total drag force
Answer to Problem 17.1PP
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Diameter, d =
Velocity, v =
Length, l =
Formula used:
v is velocity
A is area
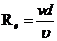
d is diameter
Calculation:
For air,
Conclusion:
The total drag force on a cylinder when moving through water is calculated as
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Applied Fluid Mechanics: Global Edition
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Fundamentals of Aerodynamics
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics
Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design (McGraw-Hill Series in Mechanical Engineering)
DeGarmo's Materials and Processes in Manufacturing
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
- fluid mechanics explain the effect of aerodynamic drag and lift on aerofoilsarrow_forwardQ6. Two large fixed parallel planes are 12 mm apart. The space between the surfaces is filled with oil of viscosity 0.972 N.s / m². A flat thin plate 0.25 m² area moves through the oil at a velocity of 0.3 m / s. Calculate the drag force: (1) When the plate is equidistant from both the planes, and (ii) When the thin plate is at a distance of 4 mm from one of the plane surfaces.arrow_forwardA propeller-driven aircraft has an in-flight weight of 4,105 lb (equivalent to a mass of 1,862 kg) and is cruising at a true airspeed of 120 kts. The lift-to-drag ratio of the aircraft is 8.2. If the propeller efficiency, ηp, is 0.8, then how much brake power is required for flight? Work through this problem in both USC and SI units.arrow_forward
- Name some applications in which a large drag is desired.arrow_forwardWe are testing a flat plate of length L = 1.125 m and width W = 0.225 m in a stream of air flowing with a velocity of 20 m/s. In test case 1, the air is flowing parallel to L and in test case 2 air is flowing parallel to W. Find: What portion of the boundary layer flow is laminar in each case? What is the highest laminar boundary layer thickness in each case? Assuming the flow is entirely turbulent over the plate, calculate the drag force in both test cases Take air density as 1.2 kg/m3 and its viscosity as μ=18×10−6μ=18×10−6 N.s/m2.arrow_forwardThe lift on a spinning circular cylinder in a freestream with a velocity of 30 m/s and at standard sea level conditions is 6 N/m of span. Calculate the circulation around the cylinderarrow_forward
- A 2.4-in-diameter smooth ball rotating at 500 rpm is dropped in a water stream at 60°F flowing at 4 ft/s. Determine the lift and the drag force acting on the ball when it is first dropped in the water.arrow_forwardFor a new sailboat, a designer wants to determine the drag force that may be expected at a given speed. To do so, she places a model of the proposed hull in a test channel and uses three cables to keep its bow on the centerline of the channel. Dynamometer readings indicate that for a given speed, the tension is 40 lb in cable AB and 60 lb in cable AE. Determine the drag force exerted on the hull and the tension in cable AC.arrow_forwardSolve Parts A-C and label Them QUESTION: Suppose you buy a 3 x 7-ft sheet of plywood and put it on your roof rack. You drive home at 45 mi/h. Part A - If the board is perfectly aligned with the airflow, how thick is the boundary layer at the end of the board? Part B - Estimate the drag on the sheet of plywood if the boundary layer remains laminar? Part C - Estimate the drag on the sheet of plywood if the boundary layer is turbulent (assume the wood is smooth) and compare the result to that of the laminar boundary layer case. HINT - 3 X 7-ft sheet of plywood and put it on your roof rack. You drive home at 45 mi/h.arrow_forward
- Compute for the lift force acting on a wing with an area of 56 sq. ft., velocity of 75 ft/s at an altitude of 5000 ft. Cl of the wing is 0.75. Calculate the drag of a certain wing with an area of 20 sq. meters , velocity of 75 m/s at an altitude of 2000m . Cd of the wing is 0.05. Compute for the drag of a rectangular wing with a chord of 4.5 ft and a span of 16 ft. if the dynamic pressure 80 psi. Cd of the wing is 0.030.arrow_forwardThe wing of the Fairchild Republic A-10A twin-jet close-support airplane is approximately rectangular with a wingspan (the length perpendicular to the flow direction) of 17.5 m and a chord (the length parallel to the flow direction) of 3 m. The airplane is flying at standard sea level with a velocity of 200 m/s. Assume the wing is approximated by a flat plate and incompressible flow. If the critical Reynolds number for transition is 106, calculate the skin friction drag for the wing. Use turbulent drag as 2830 N. (Round the final answer to the nearest whole number.)arrow_forward1. Describe the flow phenomenon and mechanism of suddencontraction and sudden expansion shown in demonstration board.2. What are the advantages and the disadvantages of the multi-elementairfoil?3. Make a comparison of the airflow between an infinite wing and afinite wing.4. Sketch the forces on a Ping Pang ball when it is stable in an air jet.arrow_forward
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
