
Concept explainers
Answer Problem 17.29 for the following dinucleotide.
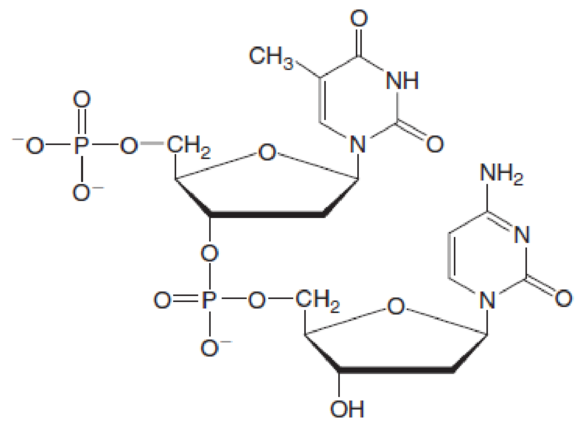
(a)
Interpretation:
Bases present in the below dinucleotide has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
The skeleton structure of base in nucleic acid generally consists of a nitrogen atom in it. There are two types of bases that are pyrimidine base and purine base.
(a) Pyrimidine base consists of one ring and is present in uracil (U), cytosine (C), and thymine (T).
(b) Purine base consists of two rings and is present in adenine (A) and guanine (G).
Explanation of Solution
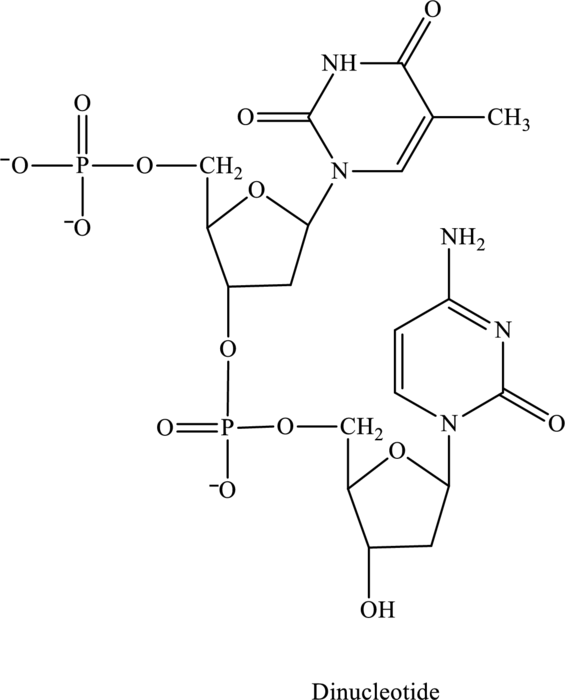
The given structure contains two nucleotides that are nucleotide 1 and nucleotide 2 and is drawn as follows:
Nucleotide 1 contains a base with one ring in it thus is a pyrimidine base. Therefore, the name of base is thymine. Whereas nucleotide 2 contains a base with one ring in it thus is a pyrimidine base. Therefore, the name of base is cytosine.
(b)
Interpretation:
The
Concept Introduction:
Nucleotide is defined as basic unit for formation of nucleic acid that is essential for completion of metabolic reactions in body. The three basic components of nucleotide are as follows:
1 Nitrogen-containing base
2 Pentose sugar
3 Phosphate group
Dinucleotide is a polymer that is composed of two nucleotide units either of DNA or RNA that is bonded to each other through a covalent bond.
Explanation of Solution
Phosphate group is attached to
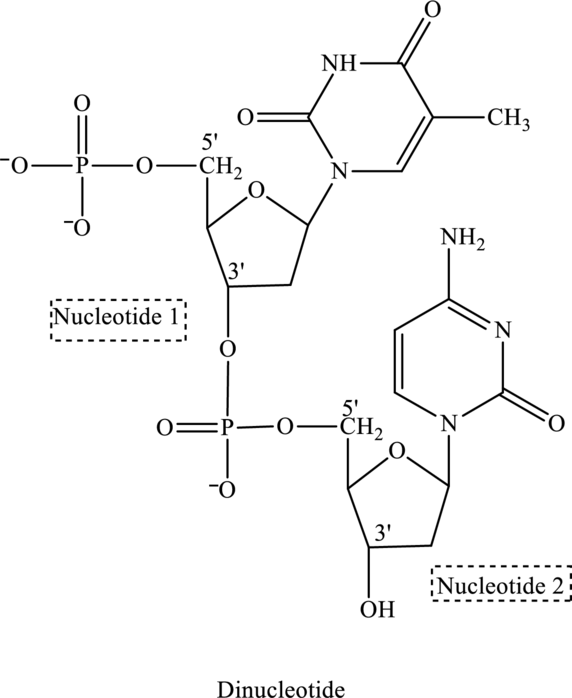
(c)
Interpretation:
Three or four letter abbreviation of below dinucleotide has to be identified.
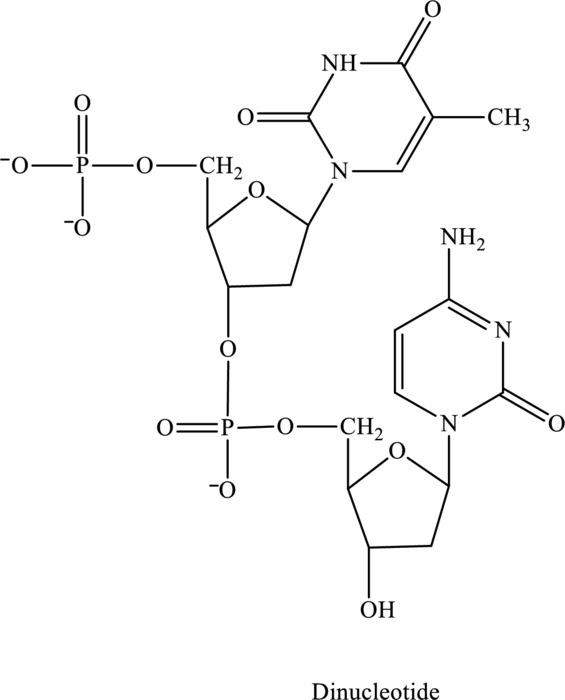
Concept Introduction:
Nucleotides are named accordingly as follows:
1 Identify the type of sugar unit attached is ribose or deoxyribose. If in the structure of nucleoside there is
2 Identify the name of the different nitrogen bases present in the molecule. There are two types of bases that are pyrimidine base and purine base.
(a) Pyrimidine base consists of one ring and is present in uracil, cytosine, and thymine.
(b) Purine base consists of two rings and is present in adenine and guanine.
3 Nucleosides with pyrimidine bases end with the suffix
4 Identify the number of carbon atom to which phosphate group is attached. The prefix is added as mono, di or tri for numbers of phosphate groups present in the nucleotide.
Abbreviation is assigned with respect to the type of sugar. For ribose sugar, 3 letter abbreviation is used and for deoxyribose sugar, 4 letter abbreviation is used followed by d as a prefix.
Explanation of Solution
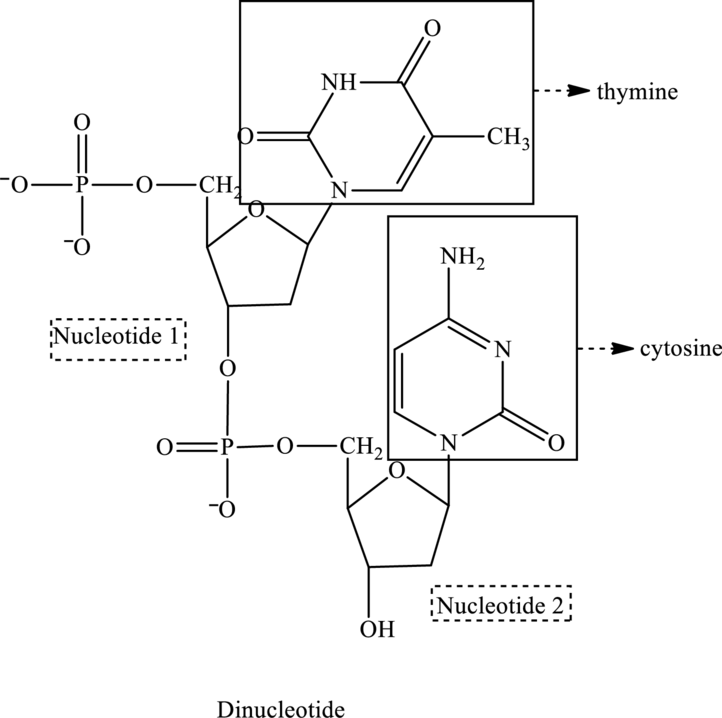
In the below structure of dinucleotide, base, phosphate group and monosaccharide are labeled as follows:
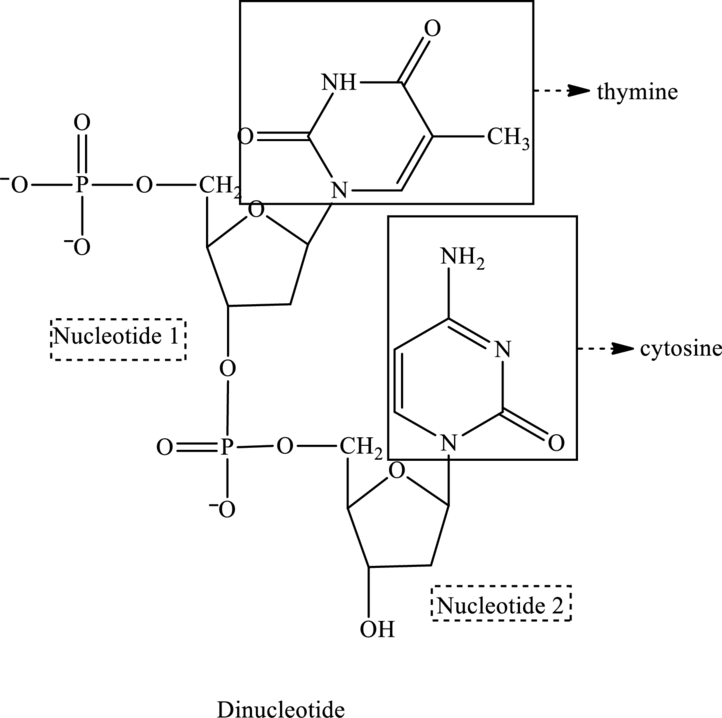
For nucleotide 1:
Name of nucleotide is assigned as follows:
1 There is no
2 It contains one ring, therefore, it is a pyrimidine base called thymine and suffix used is
3. Phosphate group is attached to
Hence, the name of the given nucleotide is
For nucleotide 2
Name of nucleotide is assigned as follows:
1 There is no
2 It contains one ring therefore is a pyrimidine base called cytosine and suffix used is
3. Phosphate group is attached to
Hence, the name of the given nucleotide is
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether the below nucleotide is ribonucleotide or deoxyribonucleotide has to be explained.
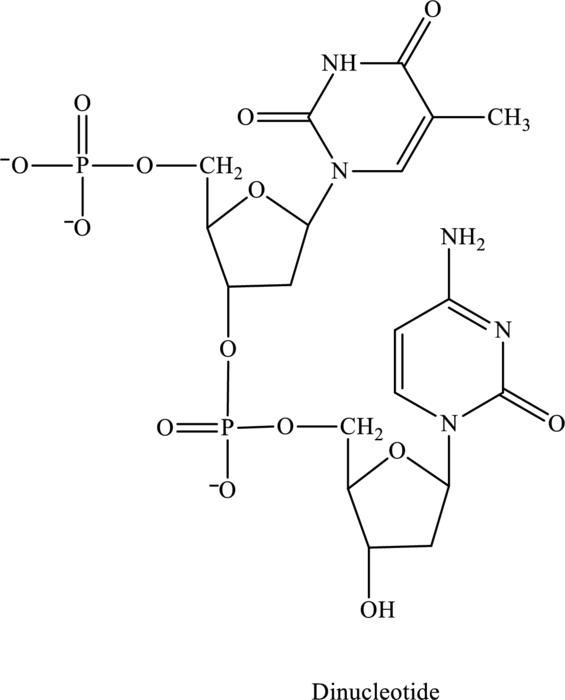
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (c).
Explanation of Solution
Since in the structure of dinucleotide both the nucleotide does not contain an
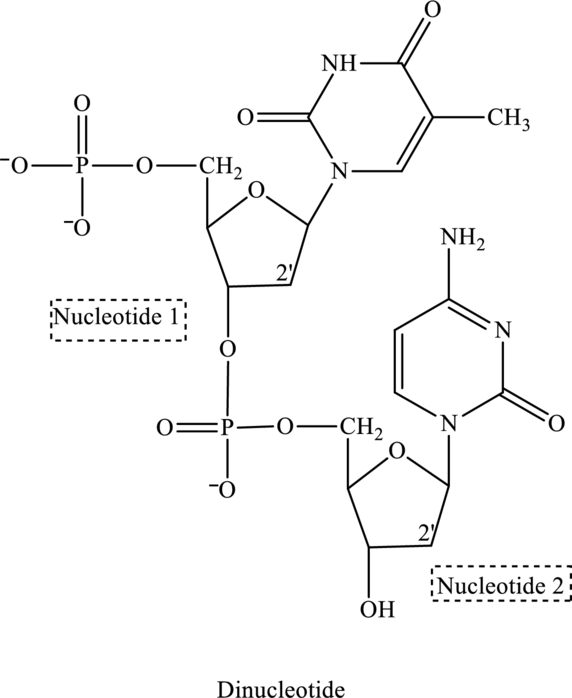
(e)
Interpretation:
Name of the below dinucleotide has to be identified.
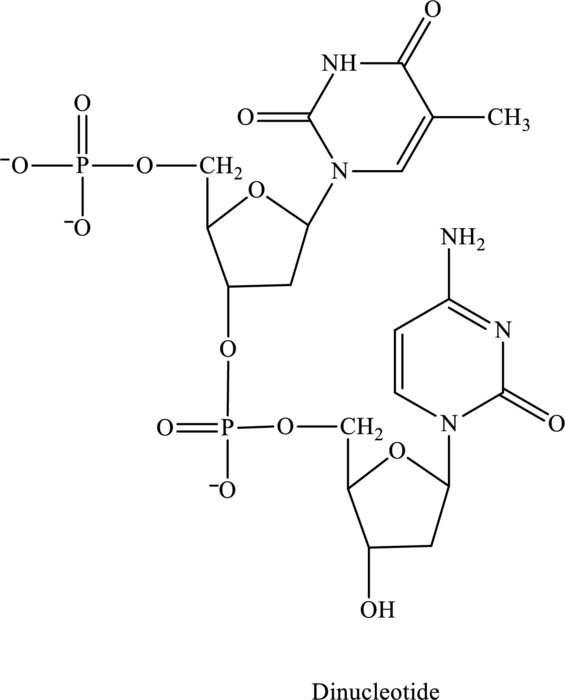
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (c).
Explanation of Solution
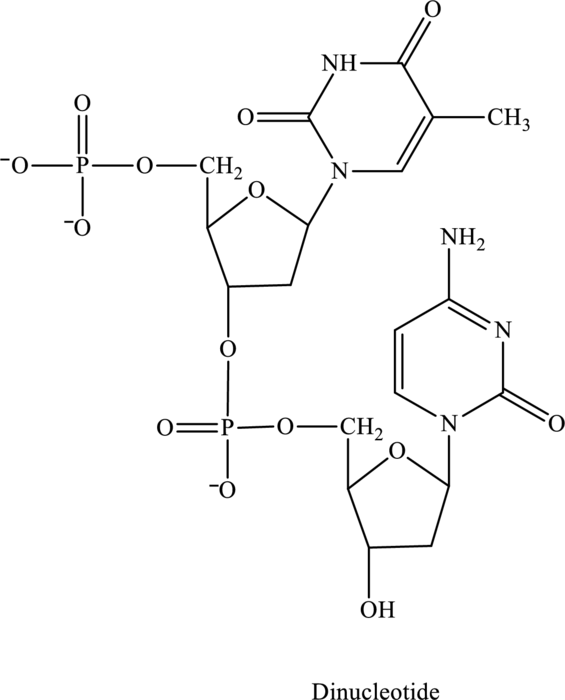
The given structure contains two nucleotides that are nucleotide 1 and nucleotide 2 and is drawn as follows:
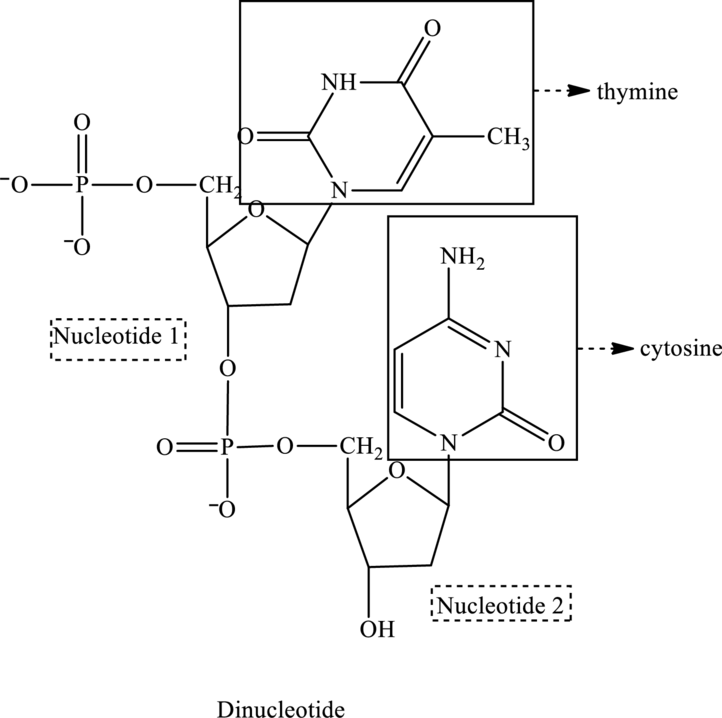
For nucleotide 1:
Name of nucleotide is assigned as follows:
1 There is no
2 It contains one ring, therefore, it is a pyrimidine base called thymine and suffix used is
3. Phosphate group is attached to
Hence, the name of the given nucleotide is
For nucleotide 2:
Name of nucleotide is assigned as follows:
1 There is no
2 It contains one ring, therefore, it is a pyrimidine base called cytosine and suffix used is
3. Phosphate group is attached to
Hence, the name of the given nucleotide is
Therefore, the name of the dinucleotide is TC.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Principles of General, Organic, Biological Chemistry
- Show the steps involved in a laboratory synthesis of the DNA fragment with the sequence CTAG.arrow_forwardGive the sequence of the following tetrapeptide:arrow_forwardOne of the steps in the biosynthesis of a nucleotide called inosine monophosphate is the formation of aminoimidazole ribonucleotide from formylglycinamidine ribonucleotide. Propose a mechanism.arrow_forward
- What is the base sequence in the original DNA strand on which the mRNA sequence in Problem 28-9 was made?arrow_forwardThe -chain of hemoglobin is a protein that contains 146 amino acids residues. What minimum number of nucleotides must be present in a strand of mRNA that is coded for this protein?arrow_forward25-66 Can dATP Serve as a source for a primer?arrow_forward
- pslease help.with,part.Carrow_forwardA random-sequence polyribonucleotide produced by polynucleotide phosphorylase, with CDP and ADP in a 5:1 molar ratio stimulated the incorporation of proline, histidine, threonine, glutamine, asparagine, and lysine in a cell-free translation system in the following proportions: 100, 23.4, 20, 3.3, 3.3, and 1.0, respectively. What does this experiment reveal about the nucleotide composition of coding triplets for these six amino acids?arrow_forwardWhy is peptide synthesis carried out from C terminus to N terminus using dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC)? Can you illustrate the explanation with a mechanism/drawing?arrow_forward
- You want to incorporate an unnatural amino acid (not one of the 20 ‘normal’ amino acids) into a protein of interest. What steps would have to be taken in order to successfully incorporate this into the protein. Assume you already have the ‘Wild type’ gene in a plasmid expression vector. (Hint: remember the central dogma DNA>mRNA>tRNA-> Protein)arrow_forwardAn enhancer element is a region of ________ and can______ transcription. A. DNA; activate B. RNA; activate C. RNA; repress D. DNA; repressarrow_forwardCarbohydrate rxn with excess acetic anhydridearrow_forward

 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


