
(a)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the principal organic product formed when Butanal is reacted with.
Tollen’s reagent should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Tollen’s regent is reacts with the
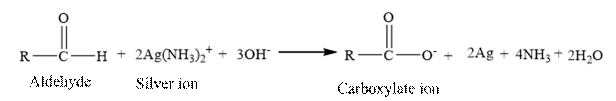
Butanal is an aldehyde. The structure of Butanal is as follows.
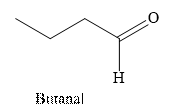
(b)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the principal organic product formed when Benzaldehyde is reacted with Tollen’s reagent should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Tollen’s regent is reacts with the aldehyde group of a compound. The carbonyl group acts as a reducing agent and reduces the silver ion of the Tollen’s regent to silver metal.
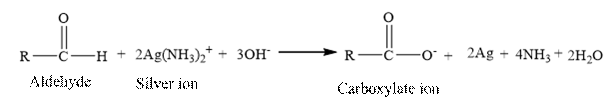
Benzaldehyde is an aldehyde. The structure of benzaldehyde is as follows.
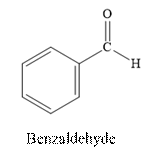
(c)
Interpretation:
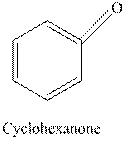
The structural formula for the principal organic product formed when cyclohexanone is reacted with Tollen’s reagent should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Tollen’s regent is reacts with the aldehyde group of a compound. The carbonyl group acts as a reducing agent and reduces the silver ion of the Tollen’s regent to silver metal.
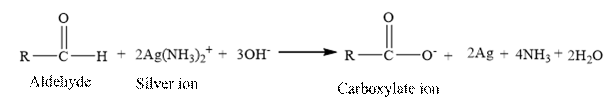
Cyclohexanone is a
(d)
Interpretation:
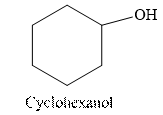
The structural formula for the principal organic product formed when cyclohexanol is treated with Tollen’s reagent.
Concept Introduction:
Tollen’s regent is reacts with the aldehyde group of a compound. The carbonyl group acts as a reducing agent and reduces the silver ion of the Tollen’s regent to silver metal.
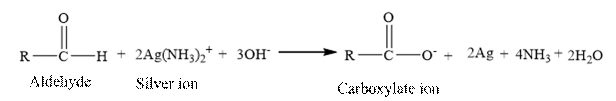
Cyclohexanol is an alcohol. The structure of cyclohexanol is as follows.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 17 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- 17-70 What simple chemical test could you use to distinguish between the members of each pair of com pounds? Tell what you would do, what you would expect to observe, and how you would interpret your experimental observation. (a) Benzaldehyde and cyclohexanone (b) Acetaldehyde and acetonearrow_forward17-29 Why can’t two molecules of acetone form a hydrogen bond with each other?arrow_forward17-47 What is the characteristic structural feature of a hemiacetal? Of an acetal?arrow_forward
- 17-11 What is the difference in structure between an aromatic aldehyde and an aliphatic aldehyde?arrow_forward18-18 Propanoic acid and methyl acetate are constitutional isomers, and both are liquids at room temperature. One of these compounds has a boiling point of 141°C; the other has a boiling point of 57°C. Which compound has which boiling point? Explain.arrow_forward16-28 Following is the structural formula of metformin, the hydrochloride salt of which is marketed as the antidiabetic medication Glucophage. Metformin was introduced into clinical practice in the United States in 1995 for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. More than 25 million prescriptions for this drug were written in 2000, making it the most commonly prescribed brand-name diabetes medication in the nation. NH NH H3(\ 3 N N Nh2ch3 h Metformin Complete the Lewis structure for metformin, showing all valence electrons. Which nitrogen is the most likely site of protonation? Draw the structural formula of Glucophage.arrow_forward
- 17-3 1 Draw a structural formula for the principal organic product formed when each compound is treated with K2Cr2O7/H2SO4. If there is no reaction, say so. (a) Butanal (b) Benzaldehyde (c) Cyclohexanone (d) Cyclohexanolarrow_forward17-67 Draw structural formulas for these compounds. (a) 1-Chloro-2-propanone (b) 3-Hydroxybutanal (c) 4-Hydroxy-4-methyl-2-pentanone (d) 3-Methyl-3-phenylbutanal (e) 1,3-Cyclohexanedione (f) 5-Hydroxyhexanalarrow_forward17-34 Explain why liquid aldehydes are often stored under an atmosphere of nitrogen rather than in air.arrow_forward
- 17-33 What simple chemical test could you use to distinguish between the members of each pair of com pounds? Tell what you would do, what you would expect to observe, and how you would interpret your experimental observation. (a) Pentanal and 2-pentanone (b) 2-Pentanone and 2-pentanolarrow_forward17-72 The following molecule is an enediol; each carbon of the double bond carries an —OH group. Draw structural formulas for the hydroxyketone and the a-hydroxyaldehyde with which this enediol is in equilibrium.arrow_forward16-13 Classify each amino group as primary, secondary, or tertiary and as aliphatic or aromatic. Serotonin (a neurotransmitter) Diphenhydramine (the hydrochloride salt is the antihistamine Benadryl) Lysine (an amino acid)arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
