
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to given IUPAC name of a compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
1. When the ring is mono-substituted, then there is no need of numbering.
2. When the ring is substituted with same substituents, then numbering to one substituent is given and for other substituent, numbering proceed from clockwise or anticlockwise such that it gets lower number.
3. When the ring is substituted with different substituents, then the numbering is done on the basis of priority.
4. Substituents on benzene ring is also indicated using ortho, meta, para prefix. The prefix ortho is used when substituents are on adjacent carbon, meta is used when substituents are separated by one carbon atom, para is used when substituents are across each other in benzene ring.
Answer to Problem 17.4P
The structure corresponding to given compound is,
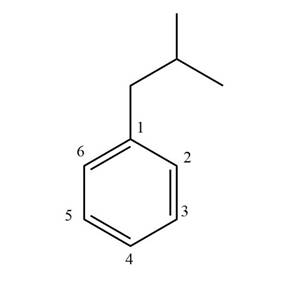
Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
The IUPAC name of the compound is isobutyl benzene. The parent ring is benzene.
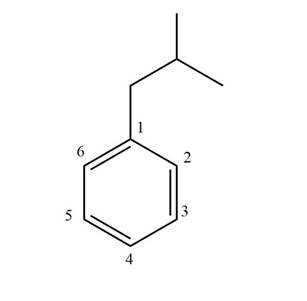
Figure 1
The structure corresponding to given compound is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to given IUPAC name of a compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic way of naming the organic compounds. The basic principles of IUPAC naming for benzene derivatives are:
1. When the ring is mono-substituted, then there is no need of numbering.
2. When the ring is substituted with same substituents, then numbering to one substituent is given and for other substituent, numbering proceed from clockwise or anticlockwise such that it gets lower number.
3. When the ring is substituted with different substituents, then the numbering is done on the basis of priority.
4. Substituents on benzene ring is also indicated using ortho, meta, para prefix. The prefix ortho is used when substituents are on adjacent carbon, meta is used when substituents are separated by one carbon atom, para is used when substituents are across each other in benzene ring.
Answer to Problem 17.4P
The structure corresponding to given compound is,
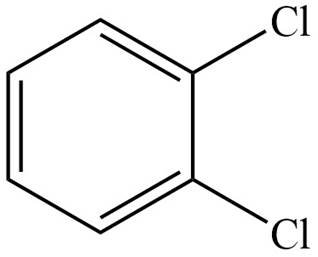
Figure 2
Explanation of Solution
The IUPAC name of the compound is

Figure 2
The structure corresponding to given compound is shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to given IUPAC name of a compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic way of naming the organic compounds. The basic principles of IUPAC naming for benzene derivatives are:
1. When the ring is mono-substituted, then there is no need of numbering.
2. When the ring is substituted with same substituents, then numbering to one substituent is given and for other substituent, numbering proceed from clockwise or anticlockwise such that it gets lower number.
3. When the ring is substituted with different substituents, then the numbering is done on the basis of priority.
4. Substituents on benzene ring is also indicated using ortho, meta, para prefix. The prefix ortho is used when substituents are on adjacent carbon, meta is used when substituents are separated by one carbon atom, para is used when substituents are across each other in benzene ring.
Answer to Problem 17.4P
The structure corresponding to given compound is,
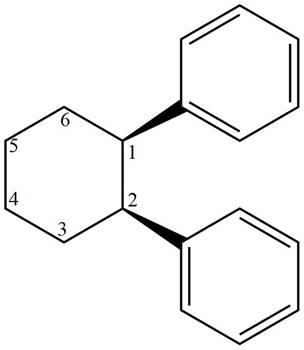
Figure 3
Explanation of Solution
The IUPAC name of the compound is

Figure 3
The structure corresponding to given compound is shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to given IUPAC name of a compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic way of naming the organic compounds. The basic principles of IUPAC naming for benzene derivatives are:
1. When the ring is mono-substituted, then there is no need of numbering.
2. When the ring is substituted with same substituents, then numbering to one substituent is given and for other substituent, numbering proceed from clockwise or anticlockwise such that it gets lower number.
3. When the ring is substituted with different substituents, then the numbering is done on the basis of priority.
4. Substituents on benzene ring is also indicated using ortho, meta, para prefix. The prefix ortho is used when substituents are on adjacent carbon, meta is used when substituents are separated by one carbon atom, para is used when substituents are across each other in benzene ring.
Answer to Problem 17.4P
The structure corresponding to given compound is,
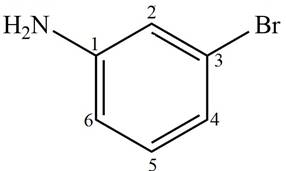
Figure 4
Explanation of Solution
The IUPAC name of the compound is

Figure 4
The structure corresponding to given compound is shown in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to given IUPAC name of a compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic way of naming the organic compounds. The basic principles of IUPAC naming for benzene derivatives are:
1. When the ring is mono-substituted, then there is no need of numbering.
2. When the ring is substituted with same substituents, then numbering to one substituent is given and for other substituent, numbering proceed from clockwise or anticlockwise such that it gets lower number.
3. When the ring is substituted with different substituents, then the numbering is done on the basis of priority.
4. Substituents on benzene ring is also indicated using ortho, meta, para prefix. The prefix ortho is used when substituents are on adjacent carbon, meta is used when substituents are separated by one carbon atom, para is used when substituents are across each other in benzene ring.
Answer to Problem 17.4P
The structure corresponding to given compound is,
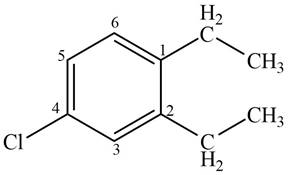
Figure 5
Explanation of Solution
The IUPAC name of the compound is

Figure 5
The structure corresponding to given compound is shown in Figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to given IUPAC name of a compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic way of naming the organic compounds. The basic principles of IUPAC naming for benzene derivatives are:
1. When the ring is mono-substituted, then there is no need of numbering.
2. When the ring is substituted with same substituents, then numbering to one substituent is given and for other substituent, numbering proceed from clockwise or anticlockwise such that it gets lower number.
3. When the ring is substituted with different substituents, then the numbering is done on the basis of priority.
4. Substituents on benzene ring is also indicated using ortho, meta, para prefix. The prefix ortho is used when substituents are on adjacent carbon, meta is used when substituents are separated by one carbon atom, para is used when substituents are across each other in benzene ring.
Answer to Problem 17.4P
The structure corresponding to given compound is,
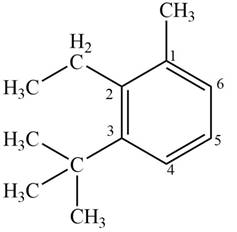
Figure 6
Explanation of Solution
The IUPAC name of the compound is
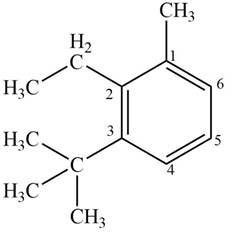
Figure 6
The structure corresponding to given compound is shown in Figure 6.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- a. Draw the structures and give the common and systematic names for alkynes with molecular formula C7H12. Ignore stereosiomers. (Hint: There are 14.) b. How many would there be if stereoisomers are included?arrow_forwardReaction of 2-methylpropene with CH3OH in the presence of H2SO4 catalyst yieldsmethyl tert-butyl ether, CH3OC(CH3)3, by a mechanism analogous to that of acid- catalyzed alkene hydration. Write the mechanism, using curved arrows for each step.arrow_forwardDraw structures corresponding to the following names: (a) 3, 3-Dimethyl-4-octyne (b) 3-Ethyl-5-methyl-1, 6, 8-decatriyne (c) 2, 2, 5, 5-Tetramethyl-3-hexyne (d) 3, 4-Dimethylcyclodecyne (e) 3, 5-Heptadien-1-yne (f) 3-Chloro-4, 4-dimethyl-1-nonen-6-yne (g) 3-sec-Butyl-1-heptyne (h) 5-tert-Buty1-2-methyl-3-octynearrow_forward
- a) When (Z)-3-methylhex-3-ene undergoes hydroboration–oxidation, two isomeric products are formed. Give their structures, and label each asymmetric carbon atom as (R) or (S). What is the relationship between these isomers?arrow_forward1) (S)-2-butanol reacts with potassium dichromate (K2CrO4) in aqueous sulfuric acid to give A (C4H8O). Treatment of A with ethylmagnesium bromide in anhydrous ether gives B (C6H14O). Draw the structure of B. 2)arrow_forwardCompound A (C11H23Br) is a secondary alkyl halide. On being heated with a solution of sodium ethoxide in ethanol, compound A yielded a mixture of two alkenes B and C, each having molecular formula C11H22. Catalytic hydrogenation of the major isomer B or the minor isomer C gave only 3,5-diethylheptane. Draw structures for compounds A, B, and C consistent with these observations.arrow_forward
- 4. Compound A has the formula C 8H 8. It reacts rapidly with KMnO 4 to give CO 2 and a carboxylic acid, B (C 7H 6O 2), but reacts with only 1 molar equivalent of H 2 on catalytic hydrogenation over a palladium catalyst. On hydrogenation under conditions that reduce aromatic rings, 4, equivalents of H 2 are taken up and hydrocarbon C (C 8H 16) is produced. What are the structures of A, B, and C.arrow_forward5. Compound A, C 10H 18O, undergoes reaction with dilute H 2SO 4 at 50 °C to yield a mixture of two alkenes, C 10H 16. The major alkene B, gives only cyclopentanone after ozone treatment followed by reduction with zinc in acetic acid. Which of the following reactions are correct.arrow_forwardWrite the structure of the compound E,E-2,4-Hexadien-1-ol and label each non-equivalent carbon with a letter, A,B,C..arrow_forward
- Heating compound X with aqueous formaldehyde forms Y (C17H23NO), which has been converted to a mixture of lupinine and epilupinine, alkaloids isolated from lupin, a perennial ornamental plant commonly seen on the roadside in parts of Alaska. Identify Y and explain how it is formed.arrow_forwardUnknown B: Soluble in water Bubbles upon contact with 5% NaHCO3 and forms a homogenous solutionWhat functional group is most likely present in the sample?arrow_forwardAlcohol A (C10H18O) is converted to a mixture of alkenes B and C on being heated with potassium hydrogen sulfate (KHSO4). Catalytic hydrogenation of B and C yields the same product. Assuming that dehydration of alcohol A proceeds without rearrangement, deduce the structures of alcohol A and alkene C.arrow_forward
