
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305970939
Author: Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 17, Problem 17.8P
Refer to Problem 17.7 and Figure 17.16. Suppose a footing (1.5 m × 1.5 m) is constructed at a depth of 1 m.
a. Estimate the design values for N60 and
b. What is the net allowable load that the footing can carry? The maximum allowable 17.7 settlement is 25 mm. Use Eqs. (16.56) and (16.61).
Refer to the boring log shown in Figure 17.16. Estimate the average drained friction angle,
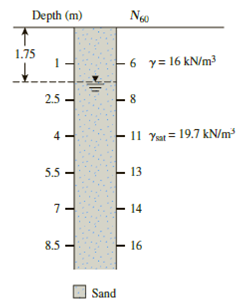
Figure 17.16
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
An embankment consists of clay fill for which c=25 kPa and angle of internal friction is 260 (from consolidated undrained test with pore pressure measurement) The weight of fill per unit volume is 18.64 kN/m3. Compute the effective stress in kPa at a depth of 20 m. If the pore pressure at this point is shown by a piezometer to be 180 kPa.
a. 62.5
b. 372.8
c. 192.8
d. 21.6
It is required to design a cantilever retaining wall to retain a 5.0 m high sandy backfill. The dimensions of the cantilever wall are shown in Figure 15.52 along with the soil properties. Check the stability with respect to sliding and overturning, based on the active earth pressures determined, usinga. Coulomb's earth pressure theory (δ' = 24°), andb. Rankine's earth pressure theory.The unit weight of concrete is 24 .0 kN/m3
Figure 2 shows the cross-section of a 7m-wide, 2.5m-deep excavation that will be used to build a large sewer line. The excavation is supported by sheet pile walls that extend through layers of sand layers. The friction angle of the sand 1 and sand 2 is 30° and 35°, respectively.
Explain your assumptions.
Draw the earth pressure diagrams (some of the earth pressures will be function of “d”, embedment depth).
Find the embedment depth “d” using the simplified method.
Find the maximum moment on the wall and minimum section modulus required.
Chapter 17 Solutions
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A shallow square foundation for a column is to be constructed. It must carry a net vertical load of 1000 kN. The soil supporting the foundation is sand. The standard penetration numbers (N60) obtained from field exploration are as follows: FIG. 17.15 The groundwater table is located at a depth of 12 m. The unit weight of soil above the water table is 15.7 kN/m3, and the saturated unit weight of soil below the water table is 18.8 kN/m3. Assume that the depth of the foundation will be 1.5 m and the tolerable settlement is 25 mm. Determine the size of the foundation.arrow_forwardThe table gives the standard penetration numbers determined from a sandy soil deposit in the field: Using Eq. (12.19), determine the variation of the peak soil friction angle, . Estimate an average value of for the design of a shallow foundation. Note: For depth greater than 6 m, the unit weight of soil is 18.55 kN/m3.arrow_forwardThe following is a sketch of the proposed embankment, calculate the addition of vertical stress (Bousinesq method / graph below) at the depths of points A and B. Assume the unit weight of the soil stockpile = 20 kN / m3.arrow_forward
- 1. The following is a sketch of the proposed embankment, calculate the addition of vertical stress (Bousinesq method / graph below) at the depths of points A and B. Assume the unit weight of the soil stockpile = 20 kN / m3. 2. Calculate the added vertical stress at points A and B as deep as Z = 8 m, under the rectangular loadarrow_forwardA cut slope of h= 7m was excavated in a saturated clay with a slope of angle beta = 45 degrees with the horizontal. The Previous explorations showed that a rock layer was located at a depth of 14 m. Given that, c = 60 kN/m² and unit weight = 17 kN / (m ^ 3) . Determine the factor of safety.arrow_forwardA vertical cut is to be made in a purely cohesive clay deposit (c'=30kPa, φ'=0deg, γ=16kN/m3). Find the maximum height of the cut which can be temporarily supported. From the stability chart, the stability number can be used as 0.261.arrow_forward
- An embankment consists of clay fill for which c=25 kPa and angle of internal friction is 260 9from consolidated undrained test with pore pressure measurement) The weight of fill per unit volume is 18.64 kN/m3. Compute the stress in kPa at depth of 20 m. Show free body diagram a.21.6 b.372.8 c.192.8 d.62.5arrow_forwardFollowing are the standard penetration numbers determined from a sandy soil in the field: Using Eq. (3.30), determine the variation of the peak soil friction angle, Φ'. Estimate an average value of Φ' for the design of a shallow foundation. (Note: For depth greater than 20 ft, the unit weight of soil is 118 lb/ft3.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305970939
Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305635180
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305081550
Author:Braja M. Das
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Types of Foundation in building construction in detail - Civil Engineering Videos; Author: Civil Engineers;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7sl4KuM4UIE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Types of Foundation || Foundation Engineering; Author: Civil Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AFLuAKGhanw;License: Standard Youtube License