
Concept explainers
Morrill Company produces two different types of gauges: a density gauge and a thickness gauge. The segmented income statement for a typical quarter follows.
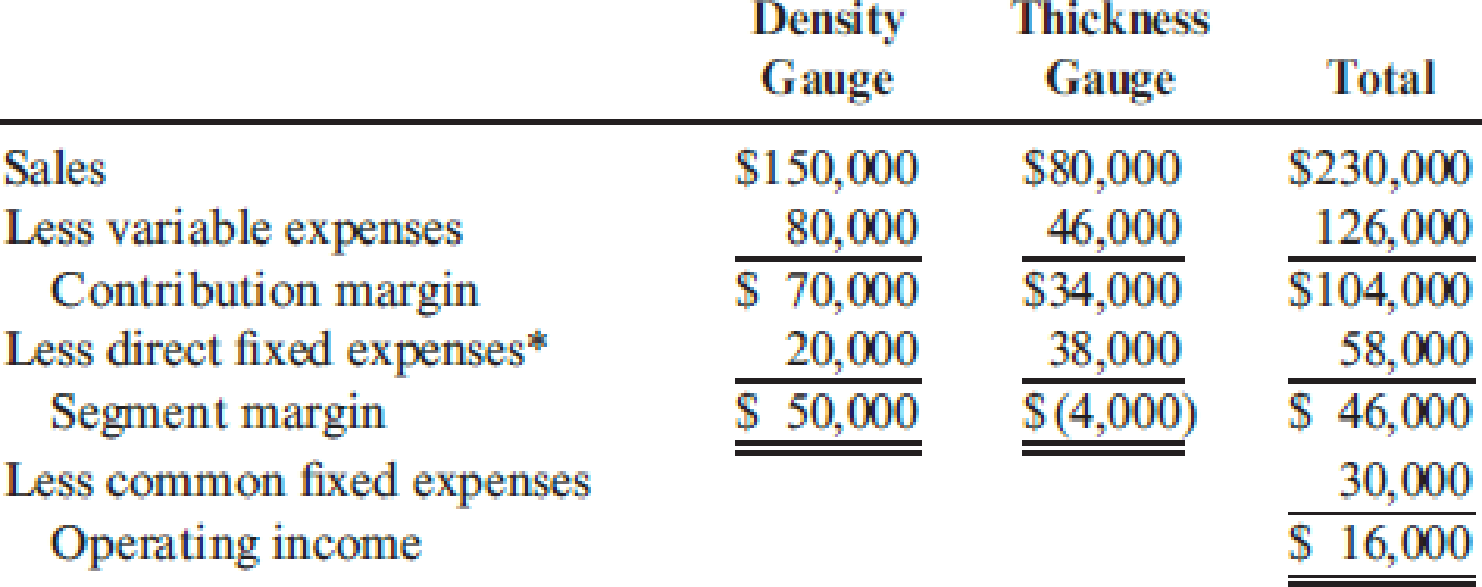
*Includes
The density gauge uses a subassembly that is purchased from an external supplier for $25 per unit. Each quarter, 2,000 subassemblies are purchased. All units produced are sold, and there are no ending inventories of subassemblies. Morrill is considering making the subassembly rather than buying it. Unit-level variable
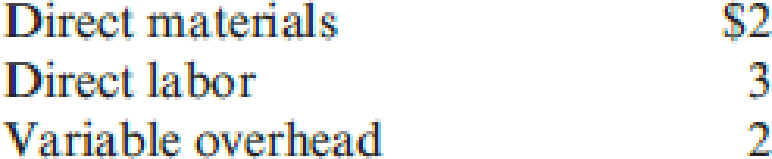
No significant non-unit-level costs are incurred.
Morrill is considering two alternatives to supply the productive capacity for the subassembly.
- 1. Lease the needed space and equipment at a cost of $27,000 per quarter for the space and $10,000 per quarter for a supervisor. There are no other fixed expenses.
- 2. Drop the thickness gauge. The equipment could be adapted with virtually no cost and the existing space utilized to produce the subassembly. The direct fixed expenses, including supervision, would be $38,000, $8,000 of which is depreciation on equipment. If the thickness gauge is dropped, sales of the density gauge will not be affected.
Required:
- 1. Should Morrill Company make or buy the subassembly? If it makes the subassembly, which alternative should be chosen? Explain and provide supporting computations.
- 2. Suppose that dropping the thickness gauge will decrease sales of the density gauge by 10 percent. What effect does this have on the decision?
- 3. Assume that dropping the thickness gauge decreases sales of the density gauge by 10 percent and that 2,800 subassemblies are required per quarter. As before, assume that there are no ending inventories of subassemblies and that all units produced are sold. Assume also that the per-unit sales price and variable costs are the same as in Requirement 1. Include the leasing alternative in your consideration. Now, what is the correct decision?
1.
Describe whether company M should make or buy the subassembly. Assume that the company has to choose the making decision, state the alternative that should be chosen and provide the supporting calculations.
Explanation of Solution
Tactical decision making: Tactical decision making is a process in which the company can choose the correct alternative based on the profitability. In tactical decision making, offer price of a product is compared with the normal selling price and offer price less than the normal selling price of product is considered as the idle capacity for decision making.
Indicate whether company M should make or buy the subassembly:
| Particulars | Lease and make | Buy |
| Purchase cost (1) | $0 | $50,000 |
| Variable manufacturing cost (2) | $14,000 | $0 |
| Lease expense | $27,000 | $0 |
| Supervisor salary | $10,000 | $0 |
| Total relevant cost | $51,000 | $51,000 |
Table (1)
If company has chosen the make decision, which alternative should be chosen:
| Particulars | Drop thickness gauge and make |
| Purchase cost (1) | $0 |
| Variable manufacturing cost (2) | $14,000 |
| Lost contribution margin | $34,000 |
| Total relevant cost | $48,000 |
Table (2)
Note: The direct fixed expense is same for all alternatives.
In this case, the company should choose the making decision because the subassembly would produce more income than the thickness gauge.
Working note (1):
Calculate the purchase cost of subassembly.
Working note (2):
Calculate the variable manufacturing cost.
2.
State the effect of the given decision; assume that dropping the thickness gauge decreases the sale of density gauge by 10%.
Explanation of Solution
State the effect of the decision if dropping in thickness gauge will decreases the sale of density gauge by 10% as follows:
| Particulars | Make | Buy |
| Lost sales for density gauge (3) | $15,000 | $0 |
| Cost of making component (4) | $12,600 | $0 |
| Less: Reduction of other variable costs (5) | ($3,000) | $0 |
| Purchase cost (1) | $34,000 | $50,000 |
| Total relevant cost | $58,600 | $50,000 |
Table (3)
If company is choose buy alternative, then the sales volume is not reduced and the same number of components would be needed for the production process.
Working note (3):
Calculate the lost sales for density gauge.
Working note (4):
Calculate the cost of making component.
Working note (5):
Calculate the other variable cost.
3.
Indicate the correct decision for the given situation.
Explanation of Solution
Indicate the correct decision for the given situation as follows:
| Particulars | Lease and make | Buy |
| Purchase cost (6) | $0 | $70,000 |
| Variable manufacturing cost (7) | $19,600 | $0 |
| Lease expense | $27,000 | $0 |
| Supervisor salary | $10,000 | $0 |
| Total relevant cost | $56,600 | $70,000 |
Table (4)
If the dropping the thickness gauge decreases the sales of density gauge by 10%:
| Particulars | Drop thickness gauge and make |
| Purchase cost | $0 |
| Lost sales from density gauge (3) | $15,000 |
| Variable manufacturing cost (8) | $17,640 |
| Less: Other variable cost (9) | ($1,000) |
| Lost contribution margin | $34,000 |
| Total relevant cost | $65,640 |
Table (5)
Note: The direct fixed expense is same for all alternatives.
In this case, the company should make the component because the total relevant cost of making decision ($56,600) is less than the buying decision ($70,000) and dropping the thickness gauges ($65,640).
Working note (6):
Calculate the purchase cost of subassembly.
Working note (7):
Calculate the variable manufacturing cost.
Working note (8):
Calculate the cost of making component.
Working note (9):
Calculate the other variable cost.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
- Materials used by the Instrument Division of Ziegler Inc. are currently purchased from outside suppliers at a cost of 1,350 per unit. However, the same materials are available from the Components Division. The Components Division has unused capacity and can produce the materials needed by the Instrument Division at a variable cost of 900 per unit. a. If a transfer price of 1,000 per unit is established and 75,000 units of materials are transferred, with no reduction in the Components Divisions current sales, how much would Ziegler Inc.s total operating income increase? b. How much would the Instrument Divisions operating income increase? c. How much would the Components Divisions operating income increase?arrow_forwardJonfran Company manufactures three different models of paper shredders including the waste container, which serves as the base. While the shredder heads are different for all three models, the waste container is the same. The number of waste containers that Jonfran will need during the following years is estimated as follows: The equipment used to manufacture the waste container must be replaced because it is broken and cannot be repaired. The new equipment would have a purchase price of 945,000 with terms of 2/10, n/30; the companys policy is to take all purchase discounts. The freight on the equipment would be 11,000, and installation costs would total 22,900. The equipment would be purchased in December 20x4 and placed into service on January 1, 20x5. It would have a five-year economic life and would be treated as three-year property under MACRS. This equipment is expected to have a salvage value of 12,000 at the end of its economic life in 20x9. The new equipment would be more efficient than the old equipment, resulting in a 25 percent reduction in both direct materials and variable overhead. The savings in direct materials would result in an additional one-time decrease in working capital requirements of 2,500, resulting from a reduction in direct material inventories. This working capital reduction would be recognized at the time of equipment acquisition. The old equipment is fully depreciated and is not included in the fixed overhead. The old equipment from the plant can be sold for a salvage amount of 1,500. Rather than replace the equipment, one of Jonfrans production managers has suggested that the waste containers be purchased. One supplier has quoted a price of 27 per container. This price is 8 less than Jonfrans current manufacturing cost, which is as follows: Jonfran uses a plantwide fixed overhead rate in its operations. If the waste containers are purchased outside, the salary and benefits of one supervisor, included in fixed overhead at 45,000, would be eliminated. There would be no other changes in the other cash and noncash items included in fixed overhead except depreciation on the new equipment. Jonfran is subject to a 40 percent tax rate. Management assumes that all cash flows occur at the end of the year and uses a 12 percent after-tax discount rate. Required: 1. Prepare a schedule of cash flows for the make alternative. Calculate the NPV of the make alternative. 2. Prepare a schedule of cash flows for the buy alternative. Calculate the NPV of the buy alternative. 3. Which should Jonfran domake or buy the containers? What qualitative factors should be considered? (CMA adapted)arrow_forwardVenezuela Oil Inc. transports crude oil to its refinery where it is processed into main products gasoline, kerosene, and diesel fuel, and by-product base oil. The base oil is sold at the split-off point for $1,000,000 of annual revenue, and the joint processing costs to get the crude oil to split-off are $10,000,000. Additional information includes: Required: Determine the allocation of joint costs using the net realizable value method, rounding the sales value percentages to the nearest tenth of a percent. (Hint: Reduce the amount of the joint costs to be allocated by the amount of the by-product revenue.)arrow_forward
- Ottis, Inc., uses 640,000 plastic housing units each year in its production of paper shredders. The cost of placing an order is 30. The cost of holding one unit of inventory for one year is 15.00. Currently, Ottis places 160 orders of 4,000 plastic housing units per year. Required: 1. Compute the economic order quantity. 2. Compute the ordering, carrying, and total costs for the EOQ. 3. How much money does using the EOQ policy save the company over the policy of purchasing 4,000 plastic housing units per order?arrow_forwardTaylor Company produces two industrial cleansers that use the same liquid chemical input: Pocolimpio and Maslimpio. Pocolimpio uses two quarts of the chemical for every unit produced, and Maslimpio uses five quarts. Currently, Taylor has 6,000 quarts of the material in inventory. All of the material is imported. For the coming year, Taylor plans to import 6,000 quarts to produce 1,000 units of Pocolimpio and 2,000 units of Maslimpio. The detail of each products unit contribution margin is as follows: Taylor Company has received word that the source of the material has been shut down by embargo. Consequently, the company will not be able to import the 6,000 quarts it planned to use in the coming years production. There is no other source of the material. Required: 1. Compute the total contribution margin that the company would earn if it could import the 6,000 quarts of the material. 2. Determine the optimal usage of the companys inventory of 6,000 quarts of the material. Compute the total contribution margin for the product mix that you recommend. 3. Assume that Pocolimpio uses three direct labor hours for every unit produced and that Maslimpio uses two hours. A total of 6,000 direct labor hours is available for the coming year. a. Formulate the linear programming problem faced by Taylor Company. To do so, you must derive mathematical expressions for the objective function and for the materials and labor constraints. b. Solve the linear programming problem using the graphical approach. c. Compute the total contribution margin produced by the optimal mix.arrow_forwardBienestar, Inc., has two plants that manufacture a line of wheelchairs. One is located in Kansas City, and the other in Tulsa. Each plant is set up as a profit center. During the past year, both plants sold their tilt wheelchair model for 1,620. Sales volume averages 20,000 units per year in each plant. Recently, the Kansas City plant reduced the price of the tilt model to 1,440. Discussion with the Kansas City manager revealed that the price reduction was possible because the plant had reduced its manufacturing and selling costs by reducing what was called non-value-added costs. The Kansas City manufacturing and selling costs for the tilt model were 1,260 per unit. The Kansas City manager offered to loan the Tulsa plant his cost accounting manager to help it achieve similar results. The Tulsa plant manager readily agreed, knowing that his plant must keep pacenot only with the Kansas City plant but also with competitors. A local competitor had also reduced its price on a similar model, and Tulsas marketing manager had indicated that the price must be matched or sales would drop dramatically. In fact, the marketing manager suggested that if the price were dropped to 1,404 by the end of the year, the plant could expand its share of the market by 20 percent. The plant manager agreed but insisted that the current profit per unit must be maintained. He also wants to know if the plant can at least match the 1,260 per-unit cost of the Kansas City plant and if the plant can achieve the cost reduction using the approach of the Kansas City plant. The plant controller and the Kansas City cost accounting manager have assembled the following data for the most recent year. The actual cost of inputs, their value-added (ideal) quantity levels, and the actual quantity levels are provided (for production of 20,000 units). Assume there is no difference between actual prices of activity units and standard prices. Required: 1. Calculate the target cost for expanding the Tulsa plants market share by 20 percent, assuming that the per-unit profitability is maintained as requested by the plant manager. 2. Calculate the non-value-added cost per unit. Assuming that non-value-added costs can be reduced to zero, can the Tulsa plant match the Kansas City per-unit cost? Can the target cost for expanding market share be achieved? What actions would you take if you were the plant manager? 3. Describe the role that benchmarking played in the effort of the Tulsa plant to protect and improve its competitive position.arrow_forward
- Dimitri Designs has capacity to produce 30,000 desk chairs per year and is currently selling all 30,000 for $240 each. Country Enterprises has approached Dimitri to buy 800 chairs for $210 each. Dimitris normal variable cost is $165 per chair, including $50 per unit in direct labor per chair. Dimitri can produce the special order on an overtime shift, which means that direct labor would be paid overtime at 150% of the normal pay rate. The annual fixed costs will be unaffected by the special order and the contract will not disrupt any of Dimitris other operations. What will be the impact on profits of accepting the order?arrow_forwardA company has prepared the following statistics regarding its production and sales at different capacity levels. Total costs: 1. At what point is break-even reached in sales dollars? In units? (Hint: Use the capacity level to determine the number of units.) 2. If the company is operating at 60% capacity, should it accept an offer from a customer to buy 10,000 units at 3 per unit?arrow_forwardAldovar Company produces a variety of chemicals. One division makes reagents for laboratories. The divisions projected income statement for the coming year is: Required: 1. Compute the contribution margin per unit, and calculate the break-even point in units. (Note: Round answer to the nearest unit.) Calculate the contribution margin ratio and use it to calculate the break-even sales revenue. (Note: Round contribution margin ratio to four decimal places, and round the break-even sales revenue to the nearest dollar.) 2. The divisional manager has decided to increase the advertising budget by 250,000. This will increase sales revenues by 1 million. By how much will operating income increase or decrease as a result of this action? 3. Suppose sales revenues exceed the estimated amount on the income statement by 1,500,000. Without preparing a new income statement, by how much are profits underestimated? 4. Compute the margin of safety based on the original income statement. 5. Compute the degree of operating leverage based on the original income statement. If sales revenues are 8% greater than expected, what is the percentage increase in operating income? (Note: Round operating leverage to two decimal places.)arrow_forward
- Bethany Company has just completed the first month of producing a new product but has not yet shipped any of this product. The product incurred variable manufacturing costs of 5,000,000, fixed manufacturing costs of 2,000,000, variable marketing costs of 1,000,000, and fixed marketing costs of 3,000,000. Under the variable costing concept, the inventory value of the new product would be: a. 5,000,000. b. 6,000,000. c. 8,000,000. d. 11,000,000.arrow_forwardMarkson and Sons leases a copy machine with terms that include a fixed fee each month plus acharge for each copy made. Markson made 9,000 copies and paid a total of $480 in January. In April, they paid $320 for 5,000 copies. What is the variable cost per copy if Markson uses the high-low method to analyze costs?arrow_forwardBolger and Co. manufactures large gaskets for the turbine industry. Bolgers per-unit sales price and variable costs for the current year are as follows: Bolgers total fixed costs aggregate to 360,000. Bolgers labor agreement is expiring at the end of the year, and management is concerned about the effects of a new labor agreement on its break-even point in units. The controller performed a sensitivity analysis to ascertain the estimated effect of a 10-per-unit direct labor increase and a 10,000 reduction in fixed costs. Based on these data, the break-even point would: a. decrease by 1,000 units. b. decrease by 125 units. c. increase by 375 units. d. increase by 500 units.arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





