
Concept explainers
The zinc-air battery shows much promise for electric cars because it is lightweight and rechargeable:
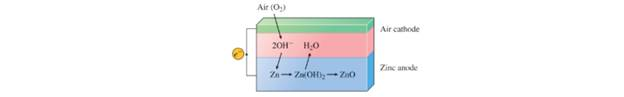
The net transformation is
Interpretation:
The half-reaction, the standard emf of battery, the emf under actual operating conditions, the energy density, and the volume of air essential to supply the battery every second is to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
The Nernst equation is the reduction potential of an electrochemical reaction to the standard electrode potential, temperature, and activities of the chemical species undergoing oxidation and reduction.
The Nernst equation is an important equation of electrochemistry. The equation is
Here,
The standard free energy change is the difference of the sum of standard free energy change of products and the sum of standard free energy change of reactants.
Answer to Problem 126AP
Solution:
(a)
The half-reaction is as follows:
The standard emf of battery is
(b)
The emf is
(c)
The energy density of Zn is
(d)
The volume of air essential to supply the battery every second is
Explanation of Solution
Given information: The given reaction is as follows:
The current is
a) The half-reaction at zinc-air electrode and the standard emf of the battery.
The half-reaction is as follows:
The standard emf is calculated with the help of
Here,
The standard free energy changes for the formation of
Substitute the values of standard Gibbs energy of formation of reactants and products in the equation above,
Thus, the standard free energy change
The standard emf of battery is calculated as follows:
Here,
Substitute the values of
Therefore, the standard emf of battery is
b) The emf under actual operating conditions when the partial pressure of oxygen is
The Nernst equation is as follows:
Substitute the values of
Therefore, the emf is
c) The energy density of zinc electrode.
The maximum energy obtained from the reaction is the free energy. The energy density of the zinc electrode is calculated with the help of free energy.
The energy density of the zinc electrode is calculated as follows:
Substitute the values of free energy
Therefore, the energy density is
d) The volume of air would need to be supplied to the battery every second.
The number of moles can be calculated with the help of charge as follows:
Here,
Substitute the values in the equation above:
Therefore, the number of moles is
In the balanced reaction,
Therefore, the number of moles of oxygen reduced by
The volume of oxygen at
Here,
Substitute the values of pressure, moles, temperature, and gas constant in the equation above,
Therefore, the volume of oxygen is
As the air is
The volume of air essential to supply the battery every second is calculated as follows:
Therefore, the volume of air essential to supply the battery every second is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Chemistry
- At 298 K, the solubility product constant for Pb(IO3)2 is 2.6 1013, and the standard reduction potential of the Pb2+(aq) to Pb(s) is 0.126 V. (a) Find the standard potential of the half-reaction Pb(IO3)2(s)+2ePb(s)+2IO3(aq) (Hint: The desired half-reaction is the sum of the equations for the solubility product and the reduction of Pb2+. Find G for these two reactions, and add them to find G for their sum. Convert the G to the potential of the desired half-reaction.) (b) Calculate the potential of the Pb/Pb(IO3)2 electrode in a 3.5 103 M solution of NaIO3.arrow_forwardWhat is the standard cell potential you would obtain from a cell at 25C using an electrode in which Hg22+(aq) is in contact with mercury metal and an electrode in which an aluminum strip dips into a solution of Al3+(aq)?arrow_forwardAt 298 K, the solubility product constant for PbC2O4 is 8.5 1010, and the standard reduction potential of the Pb2+(aq) to Pb(s) is 0.126 V. (a) Find the standard potential of the half-reaction PbC2O4(s)+2ePb(s)+C2O42(aq) (Hint: The desired half-reaction is the sum of the equations for the solubility product and the reduction of Pb2+. Find G for these two reactions and add them to find G for their sum. Convert the G to the potential of the desired half-reaction.) (b) Calculate the potential of the Pb/PbC2O4 electrode in a 0.025 M solution of Na2C2O4.arrow_forward
- A half-cell that consists of a copper wire in a 1.00 M Cu(NO3)2 solution is connected by a salt bridge to a solution that is 1.00 M in both Pu3+ and Pu4+, and contains an inert metal electrode. The voltage of the cell is 0.642 V, with the copper as the negative electrode. (a) Write the half-reactions and the overall equation for the spontaneous chemical reaction. (b) Use the standard potential of the copper half-reaction, with the voltage of the cell, to calculate the standard reduction potential for the plutonium half-reaction.arrow_forwardFor each of the reactions, calculate E from the table of standard potentials, and state whether the reaction is spontaneous as written or spontaneous in the reverse direction under standard conditions. (a) Zn(s)+Fe2+(aq)Zn2+(aq)+Fe(s) (b) AgCl(s)+Fe2+(aq)Ag(s)+Fe3+(aq)+Cl(aq) (c) Br2(l)+2Cl(aq)Cl2(g)+2Br(aq)arrow_forwardCalculate the cell potential of a cell operating with the following reaction at 25C, in which [Cr2O32] = 0.020 M, [I] = 0.015 M, [Cr3+] = 0.40 M, and [H+] = 0.60 M. Cr2O72(aq)+6I(aq)+14H+(aq)2Cr3+(aq)+3I2(s)+7H2O(l)arrow_forward
- For each reaction listed, determine its standard cell potential at 25 C and whether the reaction is spontaneous at standard conditions. (a) Mn(s)+Ni2+(aq)Mn2+(aq)+Ni(s) (b) 3Cu2+(aq)+2Al(s)2Al3+(aq)+3Cu(s) (c) Na(s)+LiNO3(aq)NaNO3(aq)+Li(s) (d) Ca(NO3)2(aq)+Ba(s)Ba(NO3)2(aq)+Ca(s)arrow_forwardCalculate the cell potential of a cell operating with the following reaction at 25C, in which [MnO4] = 0.010 M, [Br] = 0.010 M. [Mn2] = 0.15 M, and [H] = 1.0 M. 2MNO4(aq)+10Br(aq)+16H+(aq)2MN2(aq)+5Br2(l)+8H2O(l)arrow_forwardCalculate the standard cell potential of the following cell at 25C. Sn(s)Sn2+(aq)I2(aq)I(aq)arrow_forward
- You have 1.0 M solutions of Al(NO3)3 and AgNO3 along with Al and Ag electrodes to construct a voltaic cell. The salt bridge contains a saturated solution of KCl. Complete the picture associated with this problem by a writing the symbols of the elements and ions in the appropriate areas (both solutions and electrodes). b identifying the anode and cathode. c indicating the direction of electron flow through the external circuit. d indicating the cell potential (assume standard conditions, with no current flowing). e writing the appropriate half-reaction under each of the containers. f indicating the direction of ion flow in the salt bridge. g identifying the species undergoing oxidation and reduction. h writing the balanced overall reaction for the cell.arrow_forwardThe cell potential of the following cell at 25C is 0.480 V. ZnZn2+(1M)H+(testsolution)H2(1atm)Pt What is the pH of the test solution?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





