
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The molecular formula of peramivir should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Peramivir is an antiviral drug which is used in the treatment of influenza. It is a neuraminidase inhibitor which inhibits the transition state of the influenza so that it does not produce new viruses from the infected cells.
Molecular formula of a molecule represents the total number of atoms present in the molecule.
Answer to Problem 19.46P
C15 H28 N4 O4.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the molecule is as follows:
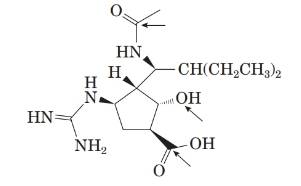
From the structure, the molecular formula of the compound is C15 H28 N4 O4.
(b)
Interpretation:
The
Concept Introduction:
Functional group of a compound represents its chemical properties. The most common organic functional groups are alcohol,
In amines, the alkyl group is attached to the nitrogen atom having 2 hydrogen atoms and one lone pair on it.
Depending on the number of alkyl groups attached to nitrogen atom, they are classified as primary (1 alkyl group), secondary (2 alkyl groups) and tertiary (3 alkyl groups).
In alcohols, the alkyl group is attached to a hydroxyl group. Similar to amines, depending on the number of alkyl groups they are classified as primary, secondary and tertiary.
Carboxylic acid, ketone and aldehyde have common carbonyl group which is attached to hydroxyl group in carboxylic group, hydrogen atom in aldehyde and two alkyl groups in ketone.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the molecule is as follows:
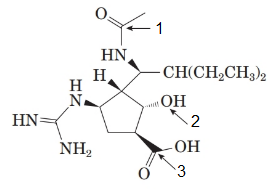
The labelled groups are as follows:
- Amide
- Alcohol
- Carboxylic acid
Here, nitrogen in the amide group and alcohol (hydroxyl group) both are secondary.
(c)
Interpretation:
The number of stereocenters present in peramivir should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Stereocentre or chiral centre is the carbon centre when four different groups attached to it. For a molecule with n stereocenters, the number of stereoisomers can be calculated using the following formula:
Answer to Problem 19.46P
5 stereocenters.
Explanation of Solution
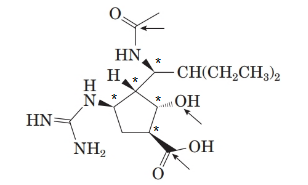
The structure of the molecule is as follows:
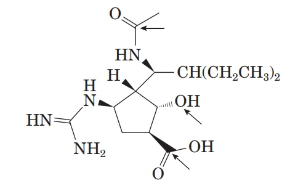
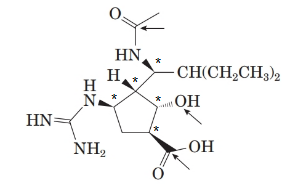
Stereocentre or chiral centre is the carbon centre when four different groups attached to it. All the stereocenters present in the compound are represented as follows:
(d)
Interpretation:
The maximum number of stereoisomers should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Stereocentre or chiral centre is the carbon centre when four different groups attached to it. For a molecule with n stereocenters, the number of stereoisomers can be calculated using the following formula:
Answer to Problem 19.46P
32 stereoisomers.
Explanation of Solution
The number of stereocenters in the compound is 5.
Thus, maximum number of stereoisomers can be calculated as follows:
Putting the value,
Thus, there are 32 stereoisomers in the molecule.
(e)
Interpretation:
The number of enantiomers and diastereomers of peramivir should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Enantiomers are two stereoisomers which are non-superimposable mirror image of each other. Two enantiomers of a compound have similar physical properties but the direction of rotation of polarized light is different. The interaction with the optical isomers of other compounds is also different for them.
Due to this, there are different biological effects of different enantiomers of a compound. Optical activity can be observed in pure enantiomers. They can be separated making use of a chiral agent.
Naturally, there is only one enantiomer possible for most of the chiral compounds which are biologically present. For example, glycine in amino acids.
Diastereomer.
They are stereoisomers which are not mirror image of each other. The following isomers comes under this category:
Meso compounds, E-Z isomers, cis-trans isomers etc.
They also have similar physical properties.
One should not confuse with the D- and L- notation of the isomers with commonly used d- and l- labelling.
(e)
Answer to Problem 19.46P
There are 12 enantiomers and 30 diastereomers of peramivir.
Explanation of Solution
For any molecule, number of enantiomers and diastereomers can be calculated as follows:
For even number of stereocenters, the number of enantiomers can be calculated as follows:
And, for odd number of stereocenters, the number of enantiomers can be calculated as follows:
Since, the number of stereocenters are 5, it follows the formula for odd.
Putting the value,
Thus, number of enantiomers will be 12.
Now, now of diastereomers can be calculated as follows:
Putting the value,
Thus, number of diastereomers will be 30.
(f)
Interpretation:
The stereocenter with R-Configuration should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Peramivir is an antiviral drug which is used in the treatment of influenza. It is a neuraminidase inhibitor which inhibits the transition state of the influenza so that it does not produce new viruses from the infected cells.
Answer to Problem 19.46P
The stereocenter with R-configuration is represented as follows:
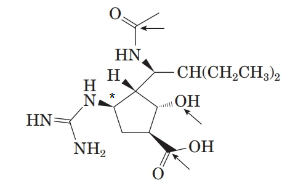
Explanation of Solution
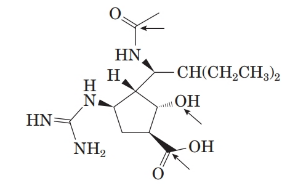
The structure of molecule is as follows:
There are 5 stereoisomers in the above molecule labelled as follows:
To name the molecule, the priory order for the atoms in ring will be:
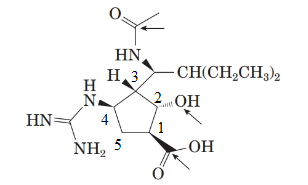
This is done by considering the functional group priority. Carboxylic acid gets the priority order one.
From the spectral data, chemical name of peramivir is ([1S, 2S, 3S, 4R]-3-[(1S)-1-(acetylamino)-2-ethylbutyl]-4-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]-2-hydroxy cyclopentane carboxylic acid. Thus, the stereocenter at 4th position in the 5 membered ring has the r configuration.
Therefore, the stereocenter with R-configuration is represented as follows:
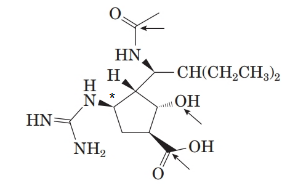
(g)
Interpretation:
The given molecules should be classified as identical, enantiomer, diastereomer and none of these.
Concept Introduction:
Enantiomers are two stereoisomers which are non-superimposable mirror image of each other. Two enantiomers of a compound have similar physical properties but the direction of rotation of polarized light is different. The interaction with the optical isomers of other compounds is also different for them.
Due to this, there are different biological effects of different enantiomers of a compound. Optical activity can be observed in pure enantiomers. They can be separated making use of a chiral agent.
Naturally, there is only one enantiomer possible for most of the chiral compounds which are biologically present. For example, glycine in amino acids.
Diastereomer.
They are stereoisomers which are not mirror image of each other. The following isomers comes under this category:
Meso compounds, E-Z isomers, cis-trans isomers etc.
They also have similar physical properties.
One should not confuse with the D- and L- notation of the isomers with commonly used d- and l- labelling.
Answer to Problem 19.46P
A- Identical.
B- Diastereomers.
C- Diastereomers.
D-Enantiomers.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the peramivir is as follows:
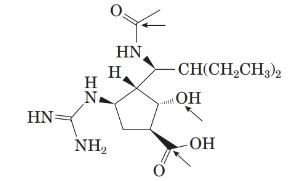
Comparing the molecular structure, A with the given structure of peramivir as follows:
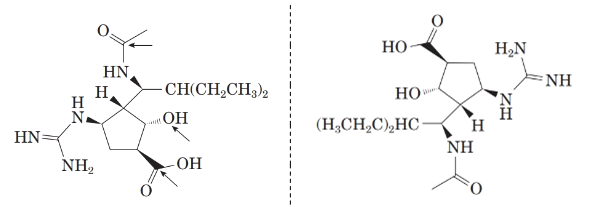
Both are not mirror image of each other. They are identical to each other. The second structure on the right-hand side formed by 180-degree rotation of the molecule given in left.
They are neither diastereomers nor enantiomers.
Now, comparing the molecular structure B with the given structure of peramivir as follows:
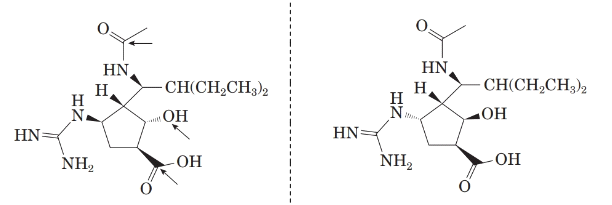
The molecules are not mirror image of each other. Thus, they are diastereomers.
Now, comparing the molecular structure C with the given structure of peramivir as follows:
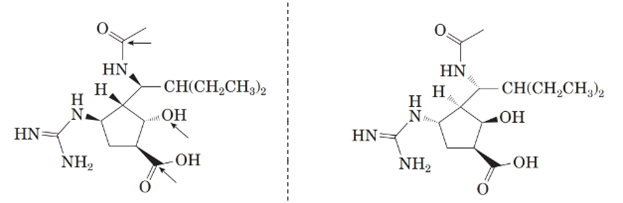
They are not mirror image of each other. The molecules are diastereomers.
Now, comparing the molecular structure D with the given structure of peramivir as follows:
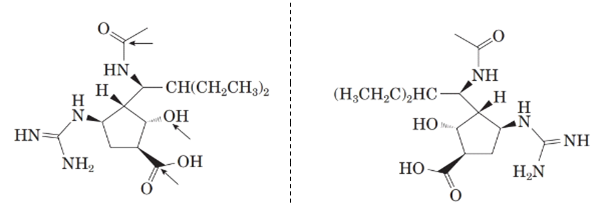
From the above figure, both the structures are mirror image of each other. Also, the mirror images are non-superimposable. Thus, they are enantiomers of each other.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- Complete the tables by providing the names of the functional groups corresponding to each letter. For any alcohol, alkyl halide, amide, or amine in the moleculeclassify it as 1, 2, or 3°Consider the functional groups in histrionicotoxi Classification: A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. Not applicablearrow_forwardAssume for the purposes of this problem that to be an alcohol (-ol) or an amine (-amine), the hydroxyl or amino group must be bonded to a tetrahedral (sp3 hybridized) carbon atom. Write the structural formula of a compound with an unbranched chain of four carbon atoms that is an: Q. Alkenolarrow_forward1. Do you think the benzoic acid will dissolve in water at room temperature? At a higher temperature? If not, how will you convert the substance into a water-soluble compound? 2. What is the importance of solubility in organic solvents? Can we use this property as a preliminary method of identifying the identity of unknown organic compounds? Explain in 1– 3 sentences.arrow_forward
- Write structural formulas for all ketones with the molecular formula C6H12O and give each its IUPAC name. Which of these ketones are chiral?arrow_forwardWould you expect 1-propanol to be soluble in water? Would you expect 1-heptanol to be soluble in water? Would either of them be more soluble in hexane than in water? Explain.arrow_forwardDuring the purification of banana oil, Isoamyl acetate, pentane is separated from the desired product by distillation. How is this possible?arrow_forward
- (a) Draw a skeletal structure of the anabolic steroid methenolone from the following description. Methenolone contains the tetracyclic steroid skeleton with a carbonyl group at C3, a hydroxyl at C17, a double bond between C1 and C2, and methyl groups bonded to C1, C10, and C13. (b) Add wedges and dashed wedges for all stereogenic centers with thefollowing information: the configuration at C10 is R, the configuration at C13 is S, the configuration at C17 is S, and all substituents at ring fusions are trans to each other. (c) Draw the structure of Primobolan, the product formed when methenolone is treated with CH3(CH2)5COCl and pyridine. Primobolan is an anabolic steroid that can be taken orally or by injection and has been used illegally by well-known Major League Baseball players.arrow_forwardConsider compound I below, which is structurally related to a natural product that was isolated from an extract of a Caribbean marine sponge (See J. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 6015). Answer the following questions about this compound ( Please Explain Answers) How primary alcohols are present? _________ How many secondary alcohols are present? _________ How many quaternary carbons are present? _______arrow_forwardIdentify the functional groups present in THC. Is the molecule likely to be hydrophilic or hydrophobic? Would you expect THC to build up in fatty tissues in the body, or would it be readily eliminated in the urine?arrow_forward
- Identify the functional groups in two drugs, atenolol and donepezil. Atenololis a β (beta) blocker, a drug used to treat hypertension (high bloodpressure), and donepezil (trade name Aricept) is used to treat mild tomoderate dementia associated with Alzheimer's disease.arrow_forwardComplete each of the following by supplying the missing product indicated by the question mark:arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
