
Concept explainers
(a)
Show that in case of heavy damping
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Since
The expression for the differential equation of over damping as follows:
Differentiate the above equation with respect to ‘t’.
Since the body is released with no initial velocity.
Substitute 0 for t,
Substitute 0 for t,
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Apply boundary condition.
For
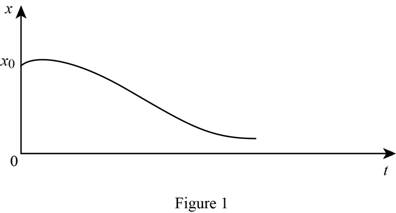
As
Thus the positive answer for the ‘t’ greater than 0 for the equation (4) cannot exist because the exponential (e) is increased to positive power be less than one which is not possible. Hence, the value of x is not becomes zero.
Show the graph of x versus t for the above solution as Figure (1).
(b)
Show that in case of heavy damping
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Since the body is started from O with arbitrary initial velocity.
Substitute 0 for t, 0 for x and
Substitute 0 for t, 0 for x, and
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Apply boundary condition.
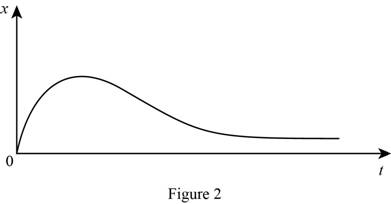
For
For
Show the graph of x versus t for the above solution as Figure (2).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- A simplified model of a washing machine is shown. A bundle of wet clothes forms a weight wb of 20 lb in the machine and causes a rotating unbalance. The rotating weight is 40 lb (including wb) and the radius of the washer basket e is 9 in. Knowing the washer has an equivalent spring constant k = 70 lb/ft and damping ratio and during the spin cycle the drum rotates at 250 rpm, determine the amplitude of the motion and the magnitude of the force transmitted to the sides of the washing machine.arrow_forwardA weight of 32 pounds is suspended from a spring with a modulus of 5 lb/ft. From equilibrium position, the weight is pulled down 4 inches below and then released. Given that the damping force in pounds is numerically equal to four times the instantaneous velocity, what is the position of the weight after sec.arrow_forwardA spring, with a 54 lb/in spring constant, is mounted on a vertical wall to support a 64.4 lb mass. At t=0 and an initial velocity of 9 in/sec. to the left, the mass is released from a position 2 inches to the right of the equilibrium position. Determine: a. Angular frequencyarrow_forward
- A body vibrating with viscous damping makes five complete oscillations per second, and in 10 cycles its amplitude diminishes by 1/5 of the orginal value. Determine the logarithmic decrement and the damping ratio.arrow_forwardFor a steady-state vibration with damping under a harmonic force, show that the mechanical energy dissipated per cycle by the dashpot is where is the coefficient of damping, xm is the amplitude of the motion, and wf is the circular frequency of the harmonic force.arrow_forwardA spring-mass-damper system has a mass of 80 kg suspended from a spring having stiffness of 1000 N/m and a viscous damper with a damping coefficient of 80 N-s/m. If the mass is subjected to a periodic disturbing force of 50 N at an undamped natural frequency, determine (i) The undamped natural frequency. (ii) The damped natural frequency. (iii) The amplitude of forced vibration of mass. (iv) The phase difference.arrow_forward
- Given a 75 percent isolation, and a damping ratio of 8 percent, determine the maximum spring rate of an isolator for a 60 kg dryer, that runs at 1500 rpm.arrow_forwardvibrating body with viscous damping makes 10 complete oscillations per second, and in 50 cycles diminishes to 20 percent. Determine the damped natural frequency, logarithmic decrement and the damping ratio.arrow_forwardA machine of mass 30 kg is placed on an elastic foundation. A sinusoidal force of magnitude 28 N is applied to the machine. A frequency sweep reveals that the maximum steady-state amplitude of 1.3 mm occurs when the period of response is 0.22 sec. Determine the equivalent stiffness and damping ratio of the foundation.arrow_forward
- The barrel of a field gun weighs 1500 lb and is returned into firing position after recoil by a recuperator of constant c=1100 1b.s/ft Determine (a) the constant k that should be used for the recuperator to return the barrel into firing position in the shortest possible time without any oscillation, (b) the time needed for the barrel to move back two-thirds of the way from its maximum-recoil position to its firing position.arrow_forward1. Explain_why_the_natural_frequency_measurements_should_better_reflect_the_system’s_true_undamped natural_frequency_(and_therefore_correlate_better_with_calculated_values)_than_the_frequency_of_oscillation measurements. 2. For_a Linear Spring-Mass System, Torsional Spring-Mass System, and Simple Pendulum System: identify_the_necessary_measurements_required_to_identify_the_natural_frequency_and the damping_ratio_for_the_linear_SMD_and_the_simple_pendulum.arrow_forward(a) A mass suspended from a helical spring of stiffness s, is displaced by a distance x from its equilibrium position and allowed to vibrate. Show that the motion is simple harmonic. (b) A vertical helical spring having a stiffness of 1540 N/m is clamped at its upper end and carries a mass of 20 kg attached to the lower end. The mass is displaced vertically through a distance of 120 mm and released. Find : 1. Frequency of oscillation ; 2. Maximum velocity reached ; 3. Maximum acceleration; and 4. Maximum value of the inertia force on the mass. (c) A machine of mass 75 kg is mounted on springs and is fitted with a dashpot to damp out vibrations. There are three springs each of stiffness 10 N/mm and it is found that the amplitude of vibration diminishes from 38.4 mm to 6.4 mm in two complete oscillations. Assuming that the damping force varies as the velocity, determine : 1. the resistance of the dashpot at unit velocity ; 2. the ratio of the frequency of the damped vibration to the…arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





