
Concept explainers
Suppose a chloride ion and a sodium ion are separated by a center—center distance of 5 Å. Is
the interaction energy (the energy required to pull them infinitely far apart) predicted to be larger if the medium between them is water, or if it is n-pentane? (See Table 2.5)
If Ca2+, Na+ and F¯ each have ionic radii ~1.16. Which ionic bond is stronger: Ca-F or Na-F? If Ca2+ is often bound on the surface of a protein by
Table 2.5 Important properties of liquid water compared with those of n-pentane, a nonpolar,
Nonhydrogen-bonding liquida
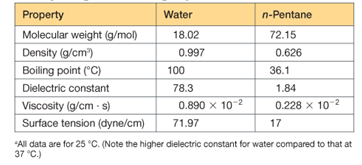
Interpretation:
Interaction energy will be more in which of the given ion pairs must be predicted. The stronger ionic bond must be predicted among the given ionic compounds. In which of the given pH the interaction between
Concept introduction:
Ionic interaction depends on Columbic interaction which depends on the charge of ions and distance by which those ions are separated. It aslo depends on the dielectric constant of the medium and the viscosity of the medium. The ionic bond is stronger when the size of the ions is small, charge in ions is high. Lattice energy depends on Columbic interaction. The bond between
Answer to Problem 1P
The interaction energy between sodium ion and chlorine ion will be larger in case of n-pentane.
Explanation of Solution
The interaction of ion pair will be more in case of n-pentane.
This is because the dielectric constant of n-pentane is
Now,
This is because of Columbic interaction
where
As calcium ion has the double charge of sodium ion so
The
This is because at pH greater than
So, the best pH is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (8th Edition)
Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)
Biological Science
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
- 3. a) An aqueous solution is 3.50% by mass potassium bromide, KBr, and has a density of 1.02 g/mL. The molality of potassium bromide in the solution is _________m. b)An aqueous solution of magnesium nitrate has a concentration of 0.474 molal. The percent by mass of magnesium nitrate in the solution is _________%. c)An aqueous solution of cobalt(II) bromide has a concentration of 0.153 molal. The percent by mass of cobalt(II) bromide in the solution is _________%.arrow_forwardHow many grams of glucose (C6H2O6 molecular mass =180daltons) would be present in one liter of a 1M (molar) solution of glucose?arrow_forwardA solution contains 2.2 x 10 -3 M in Cu2+ and 0.33 M in LiCN. If the Kf for Cu(CN)42- is 1.0 x 1025 , how much copper ion remains at equilibrium?arrow_forward
- At 39.9ºC, a solution of ethanol (XetOH = 0.9006, P * etOH = 130.4 Torr) and isooctane (P * iso = 43.9 Torr) forms a vapor phase with YetOH = 0.6667. The total pressure is 185.9 a. Calculate the activity and the activity coefficient of each component.b. Calculate the total pressure the solution would have if it were ideal.c. Comparing the ideal pressure to the actual pressure, what does this indicate about the molecular interactions?arrow_forwardThe amino acid alanine has two isomers, α-alanine and β-alanine. When equal masses of these two compounds are dissolved in equal amounts of a solvent, the solution of α-alanine freezes at the lowest temperature. Which form, α-alanine or β-alanine, has the larger equilibrium constant for ionization (HX ⇌ H+ + X−) ?arrow_forwardAn unknown mixture is known to contain only Ba(OH)2 (MW=171.34 g/mole) and NaOH (MW=40.0 g/mole). If the mixture is known to contain 45% by mass NaOH, and 8.0 grams of the mixture is dissolved completely in 50.0 ml of solution, answer the following. c).If 10.0 ml of a 0.2 M solution of Na2SO4 was added to the 50.0 ml solution, what would be the final concentration of Na+ in solution.arrow_forward
- Assuming equal concentrations of conjugate base and acid, which one of the following mixtures is suitable for making a buffer solution with an optimum pH of 7.4–7.6? NaOCl / HOCl (K a = 3.2 × 10 –8) NH 3 / NH 4Cl (K a = 5.6 × 10 –10) NaNO 2 / HNO 2 (K a = 4.5 × 10 –4) NaCl / HCl CH 3COONa / CH 3COOH (K a = 1.8 × 10 –5)arrow_forwardA solution with a density of 0.876 g>mL contains 5.0 g of toluene 1C7H82 and 225 g of benzene. Calculate the molarity of the solution.arrow_forwardThe much-abused drug cocaine is an alkaloid. Alkaloids are noted for their bitter taste, an indication of their basic properties. Cocaine, C17H21O4N, is soluble in water to the extent of 0.17g/100mL solution, and a saturated solution has a pH = 10.08. What is the value of Kb for cocaine?arrow_forward
- In a 0.1000 M acetic acid solution at 25 degrees celsius , the acid ionizes to the extent of about 1.34 %. Since each molecule of acetic acid which ionizes produces 1 H+ ion and 1 C2H3O2- ion, the concentration in the solution are: HC2H3O2 < -----------> H+ + C2H3O2-arrow_forwardAcetic acid is the principal ingredient in vinegar as shown; that's why it tastes sour. At equilibrium, a solution contains [CH3CO2H] = 0.0787 M and [H3 O+] = [CH3 CO2−] = 0.00118 M. What is the value of Ka for acetic acid?arrow_forwardA solution with a pH of 6 has a ____ difference in H ion concentration than a solution with a pH of 10. If a solution has a concentration of 10^-7 OH ions, how many H ions does it have?arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON





