
Concept explainers
Entries and schedules for unfinished jobs and completed jobs
Kurtz Fencing Inc. uses a
- A. Materials purchased on account, $45,000.
- B. Materials requisitioned and factory labor used:
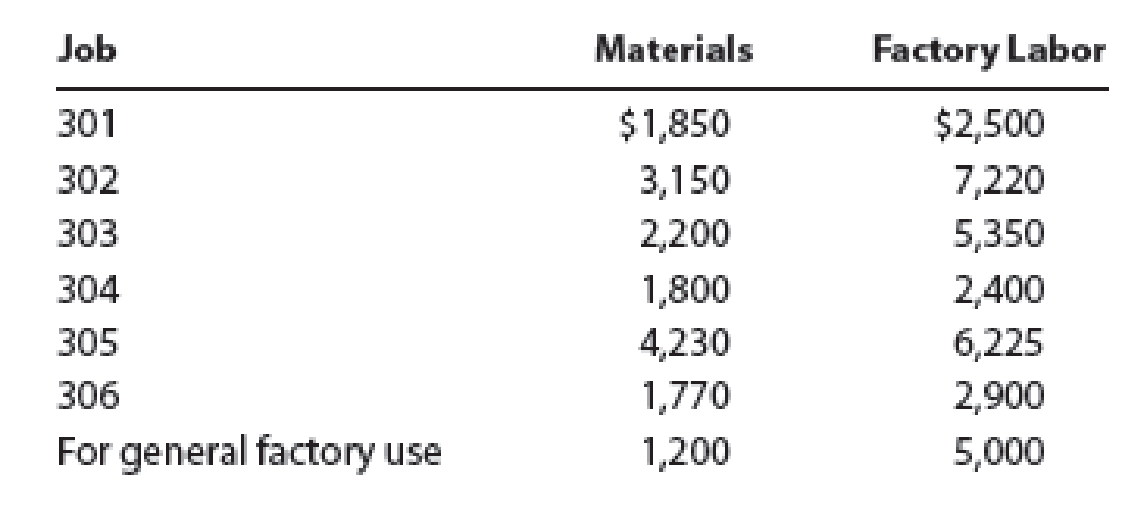
- C.
Factory overhead costs incurred on account, $1,800. - D.
Depreciation of machinery and equipment, $2,500. - E. The factory overhead rate is $30 per machine hour. Machine hours used:
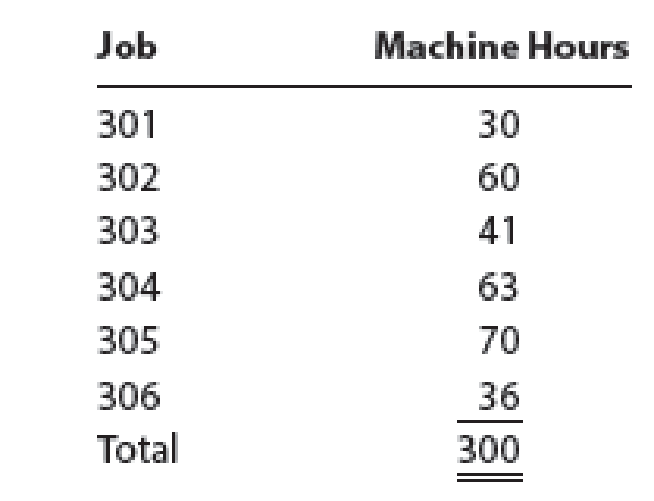
- F. Jobs completed: 301, 302, 303, and 305.
- G. Jobs were shipped and customers were billed as follows: Job 301, $8,500; Job 302, $16,150; Job 303, $13,400.
Instructions
- 1.
Journalize the entries to record the summarized operations. - 2.
Post the appropriate entries to T accounts for Work in Process and Finished Goods, using the identifying letters as transaction codes. Insert memo account balances as of the end of the month. - 3. Prepare a schedule of unfinished jobs to support the balance in the work in process account.
- 4. Prepare a schedule of completed jobs on hand to support the balance in the finished goods account.
(1)
Prepare the journal entries to record summarized operations.
Explanation of Solution
Job order costing
Job order cost system provides a separate record of each particular quantity of product that passes through the factory. Each quantity that is manufactured in the business is known as job. Job order costing is used when the products produced are significantly different from each other.
The journal entries of operations of Company KF is as follows:
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| a | Materials | 45,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | 45,000 | ||
| (Record materials purchased) | |||
| b | Work in processTable (2) | 15,000 | |
| Factory overhead | 1,200 | ||
| Materials | 16,200 | ||
| (Record material requisitioned to jobs) | |||
| Work in processTable (2) | 26,595 | ||
| Factory overhead | 5,000 | ||
| Wages payable | 31,595 | ||
| (Record factory labor used in production) | |||
| c | Factory overhead | 1,800 | |
| Accounts payable | 1,800 | ||
| (Record factory overhead cost incurred on account) | |||
| d | Factory overhead | 2,500 | |
| Accumulated depreciation – Machinery & Equipment | 2,500 | ||
| (Record depreciation on account) | |||
| e | Work in process | 9,000 | |
| Factory overhead(300 hours × $30) | 9,000 | ||
| (Record overhead applied to jobs) | |||
| f | Finished goodsTable (3) | 38,755 | |
| Work in process | 38,755 | ||
| (Record completion of job) | |||
| g | Accounts Receivable | 38,050 | |
| Sales | 38,050 | ||
| (Record sales on account) | |||
| h | Cost of goods sold Table (4) | 26,200 | |
| Finished goods | 26,200 | ||
| (Record cost of goods sold) |
Table (1)
Justification:
- a) The material is purchased on account. In regard to this, the material account is debited (Increased) and Accounts Payable is a liability and it is credited (Increased).
- b) The materials are requisitioned to jobs which includes direct and indirect cost. In regard to this, Work in process account is debited (Increased), Factory overhead account is debited (Increased), Material account is credited (Decreased), and Wages payable account is credited (Increased).
- c) The factory overhead costs are incurred on account. In regard to this, Factory overhead account is debited (Increased), and Accounts payable account is a liability and is credited (Increased).
- d) Depreciation on machinery is recorded. In regard to this, Factory overhead account is debited (Increased), and Accumulated depreciation – Machinery account is a contra asset and is credited (Increased).
- e) Factory overhead cost is applied to jobs. The work in process account is debited (Increased) and factory overhead account is credited (Decreased).
- f) The jobs are completed in the process. Finished goods account is debited (Increased) and Work in process account is credited (Decreased).
- g) Goods sold on account. Accounts receivable is an asset and is debited (Increased) and Sales affects stockholders’ equity and is credited (Increased).
- h) The cost of goods sold is recorded. Cost of goods sold account is debited (Increased), and finished goods account is credited (Decreased).
Working notes:
The material requisitioned to jobs is calculated as follows:
| Job | Directmaterials | Directlabor |
| 301 | 1,850 | 2,500 |
| 302 | 3,150 | 7,220 |
| 303 | 2,200 | 5,350 |
| 304 | 1,800 | 2,400 |
| 305 | 4,230 | 6,225 |
| 306 | 1,770 | 2,900 |
| 15,000 | 26,595 |
Table (2)
Compute the cost of jobs finished as follows:
| Job | Directmaterials | Directlabor | Factory overhead | Total |
| 301 | 1,850 | 2,500 | 900 | 5,250 |
| 302 | 3,150 | 7,220 | 1,800 | 12,170 |
| 303 | 2,200 | 5,350 | 1,230 | 8,780 |
| 305 | 4,230 | 6,225 | 2,100 | 12,555 |
| 38,755 |
Table (3)
Compute the cost of goods sold as follows:
| Job | Amount ($) |
| 301 | 5,250 |
| 302 | 12,170 |
| 303 | 8,780 |
| 26,200 |
Table (4)
(2)
Prepare the appropriate T-accounts for work in process and finished goods account.
Explanation of Solution
The T-account is prepared as follows:
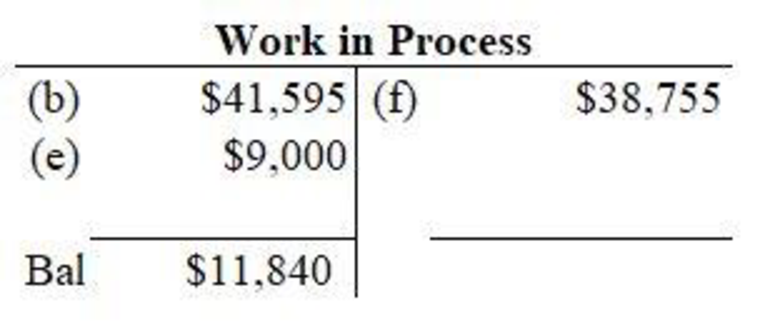
Figure (1)
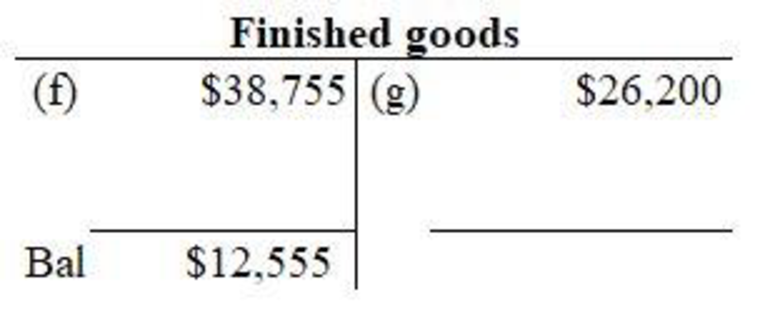
Figure (2)
In the work in process account, materials requisitioned for jobs is debited, application of factory overhead to jobs is debited and jobs that are completed are credited. Then, closing balance of work in process is determined.
In finished goods account, Jobs that are completed are debited and sale of goods is credited. Then, closing balance of finished goods is determined.
(3)
Prepare the schedule of unfinished jobs to support the balance in the work in process account.
Explanation of Solution
The schedule of unfinished jobs is prepared as follows:
| Job | Directmaterials ($) | Directlabor ($) | Factory overhead ($) | Total($) |
| No. 304 | 1,800 | 2,400 | 1,890 | 6,090 |
| No. 306 | 1,770 | 2,900 | 1,080 | 5,750 |
| Balance of work in process, Jan 30 | 11,840 |
Table (5)
The unfinished jobs are Job 304 and Job 306. The direct material cost, direct labor cost and factory overhead cost consists of jobs cost. The total of uncompleted jobs constitutes balance of work in process as on January 30.
(4)
Prepare a schedule of completed jobs to support the balance in the work in process account.
Explanation of Solution
The schedule of completed jobs is prepared as follows:
| Job | Directmaterials($) | Directlabor($) | Factory overhead($) | Total($) |
| No. 305 (Finished goods, January 30) | 4,230 | 6,225 | 2,100 | 12,555 |
Table (6)
The completed job is Job 305. The direct material cost, direct labor cost and factory overhead cost consists of jobs cost. The total of completed jobs constitutes balance of finished goods as on January 30.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Managerial Accounting
- Entries and schedules for unfinished jobs and completed jobs Hildreth Company uses a job order cost system. The following data summarize the operations related to production for April, the first month of operations: A. Materials purchased on account, 147,000. B. Materials requisitioned and factory labor used: C. Factory overhead costs incurred on account, 6,000. D. Depreciation of machinery and equipment, 4,100. E. The factory overhead rate is 40 per machine hour. Machine hours used: F. Jobs completed: 101, 102, 103, and 105. G. Jobs were shipped and customers were billed as follows: Job 101, 62,900; Job 102, 80,700; Job 105, 45,500. Instructions 1. Journalize the entries to record the summarized operations. 2. Post the appropriate entries to T accounts for Work in Process and Finished Goods, using the identifying letters as transaction codes. Insert memo account balances as of the end of the month. 3. Prepare a schedule of unfinished jobs to support the balance in the work in process account. 4. Prepare a schedule of completed jobs on hand to support the balance in the finished goods account.arrow_forwardLorrimer Company has a job-order cost system. The following debits (credits) appeared in the Work-in-Process account for the month of June. During the month of June, direct labor totaled 30,000 and 24,000 of overhead was applied to production. Finished Goods was debited 100,000 during June. Lorrimer Company applies overhead at a predetermined rate of 80% of direct labor cost. Job number 83, the only job still in process at the end of June, has been charged with manufacturing overhead of 3,400. What was the amount of direct materials charged to Job number 83? a. 3,400 b. 4,250 c. 8,350 d. 7,580arrow_forwardTerrills Transmissions uses a job order cost system. A partial list of the accounts being maintained by the company, with their balances as of November 1, follows: The following transactions were completed during November: a. Materials purchases on account during the month, 74,000. b. Materials requisitioned during the month: 1. Direct materials, 57,000. 2. Indirect materials, 11,000. c. Direct materials returned by factory to storeroom during the month, 1,100. d. Materials returned to vendors during the month prior to payment, 2,500. e. Payments to vendors during the month, 68,500. Required: 1. Prepare general journal entries for each of the transactions. 2. Post the general journal entries to T-accounts. 3. Balance the accounts and report the balances of November 30 for the following: a. Cash b. Materials c. Accounts Payablearrow_forward
- JOB ORDER COSTING TRANSACTIONS Stonestreet Enterprises makes garage doors. During the month of February, the company had four job orders: 205, 206, 207, and 208. Overhead was applied at predetermined rates, while actual factory overhead was recorded as incurred. All four jobs were completed. (a) Purchased raw materials on account, 44,000. (b) Issued direct materials to production: (c) Issued indirect materials to production, 5,700. (d) Incurred direct labor costs: (e) Charged indirect labor to production, 3,400. (f) Paid electricity, heating oil, and repair bills for the factory and charged to production, 5,300. (g) Applied factory overhead to each of the jobs using a predetermined factory over-head rate as follows: (h) Finished Job Nos. 205-208 and transferred to the finished goods inventory account as products L, M, N, and O, respectively. (i) Sold products L, M, N, and O, on account, for 21,000, 20,300, 19,000, and 20,500, respectively. REQUIRED 1. Prepare general journal entries to record transactions (a) through (i). Make compound entries for (b), (d), and (g), with separate debits for each job. 2. Post the entries to the work in process and finished goods T accounts only.arrow_forwardJOB ORDER COSTING TRANSACTIONS Stonestreet Enterprises makes garage doors. During the month of February, the company had four job orders: 205, 206, 207, and 208. Overhead was applied at predetermined rates, while actual factory overhead was recorded as incurred. All four jobs were completed. (a) Purchased raw materials on account, 44,000. (b) Issued direct materials to production: (c) Issued indirect materials to production, 5,700. (d) Incurred direct labor costs: (e) Charged indirect labor to production, 3,400. (f) Paid electricity, heating oil, and repair bills for the factory and charged to production, 5,300. (g) Applied factory overhead to each of the jobs using a predetermined factory overhead rate as follows: (h) Finished Job Nos. 205208 and transferred to the finished goods inventory account as products L, M, N, and O. (i) Sold products L, M, N, and O, on account, for 21,000, 20,300, 19,000, and 20,500, respectively. REQUIRED 1. Prepare general journal entries to record transactions (a) through (i). 2. Post the entries to the work in process and finished goods accounts only.arrow_forwardJOURNAL ENTRIES FOR MATERIAL, LABOR, AND OVERHEAD Eto Manufacturing had the following transactions during the month: (a) Purchased raw materials on account, 70,000. (b) Issued direct materials to Job No. 300, 25,000. (c) Issued indirect materials to production, 10,000. (d) Paid biweekly payroll and charged direct labor to Job No. 300, 8,000. (e) Paid biweekly payroll and charged indirect labor to production, 3,000. (f) Issued direct materials to Job No. 301, 20,000. (g) Issued indirect materials to production, 4,000. (h) Paid miscellaneous factory overhead charges, 6,000. (i) Paid biweekly payroll and charged direct labor to Job No. 301, 10,000. (j) Paid biweekly payroll and charged indirect labor to production, 2,000. REQUIRED Prepare general journal entries for transactions (a) through (j).arrow_forward
- Entries for costs in a job order cost system Royal Technology Company uses a job order cost system. The following data summarize the operations related to production for March: A. Materials purchased on account, 770,000. B. Materials requisitioned, 680,000, of which 75,800 was for general factory use. C. Factory labor used, 756,000, of which 182,000 was indirect. D. Other costs incurred on account for factory overhead, 245,000; selling expenses, 171,500; and administrative expenses, 110,600. E. Prepaid expenses expired for factory overhead were 24,500; for selling expenses, 28,420; and for administrative expenses, 16,660. F. Depreciation of factory equipment was 49,500; of office equipment, 61,800; and of office building, 14,900. G. Factory overhead costs applied to jobs, 568,500. H. Jobs completed, 1,500,000. I. Cost of goods sold, 1,375,000. Instruction Journalize the entries to record the summarized operations.arrow_forwardJOB ORDER COSTING TRANSACTIONS D K Enterprises makes wicker baskets. During the month of August, the company had four job orders: 501, 502, 503, and 504. Overhead was applied at predetermined rates, while actual factory overhead was recorded as incurred. All four jobs were completed. (a) Purchased raw materials on account, 44,000. (b) Issued direct materials to production: (c) Issued indirect materials to production, 5,000. (d) Incurred direct labor costs: (e) Charged indirect labor to production, 3,300. (f) Paid electricity, heating oil, and repair bills for the factory and charged to production, 5,200. (g) Applied factory overhead to each of the jobs using a predetermined factory overhead rate as follows: (h) Finished Job Nos. 501-504 and transferred to the finished goods inventory account as products W, X, Y, and Z, respectively. (i) Sold products W, X, Y, and Z for 17,500, 18,000, 16,900, and 19,000, respectively. REQUIRED 1. Prepare general journal entries to record transactions (a) through (i). Make compound entries for (b), (d), and (g), with separate debits for each job. 2. Post the entries to the work in process and finished goods T accounts only.arrow_forwardChannel Products Inc. uses the job order cost system of accounting. The following is a list of the jobs completed during March, showing the charges for materials issued to production and for direct labor. Assume that factory overhead is applied on the basis of direct labor costs and that the predetermined rate is 200%. Required: Compute the amount of overhead to be added to the cost of each job completed during the month. Compute the total cost of each job completed during the month. Compute the total cost of producing all the jobs finished during the month.arrow_forward
- (Appendix 4A) Journal Entries, Job Costs The following transactions occurred during the month of April for Nelson Company: a. Purchased materials costing 4,610 on account. b. Requisitioned materials totaling 4,800 for use in production, 3,170 for Job 518 and the remainder for Job 519. c. Recorded 65 hours of direct labor on Job 518 and 90 hours on Job 519 for the month. Direct laborers are paid at the rate of 14 per hour. d. Applied overhead using a plantwide rate of 6.20 per direct labor hour. e. Incurred and paid in cash actual overhead for the month of 973. f. Completed and transferred Job 518 to Finished Goods. g. Sold on account Job 517, which had been completed and transferred to Finished Goods in March, for cost (2,770) plus 25%. Required: 1. Prepare journal entries for Transactions a through e. 2. Prepare job-order cost sheets for Jobs 518 and 519. Prepare journal entries for Transactions f and g. (Note: Round to the nearest dollar.) 3. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured for April. Assume that the beginning balance in the raw materials account was 1,025 and that the beginning balance in the work-in-process account was zero.arrow_forwardDuring the month, Job Arch2 used specialized machinery for 350 hours and incurred $700 in utilities on account. $400 in factory depreciation expense, and $200 in property tax on the factory. Prepare journal entries for the following: A. Record the expenses incurred. B. Record the allocation of overhead at the predetermined rate of $1.50 per machine hour.arrow_forwardApplying factory overhead Bergan Company estimates that total factory overhead costs will be 620,000 for the year. Direct labor hours are estimated to be 80,000. For Bergan Company, (A) determine the predetermined factory overhead rate using direct labor hours as the activity base, (B) determine the amount of factory overhead applied to Jobs 200 and 305 in May using the data on direct labor hours from BE 16-2, and (C) prepare the journal entry to apply factory overhead to both jobs in May according to the predetermined overhead rate.arrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning





