
Concept explainers
A thin plate moves between two parallel, horizontal, stationary flat surfaces at a constant velocity of 5 m/s. The two stationary surfaces are spaced 4 cm apart, and the medium between them is filled with oil whose viscosity is
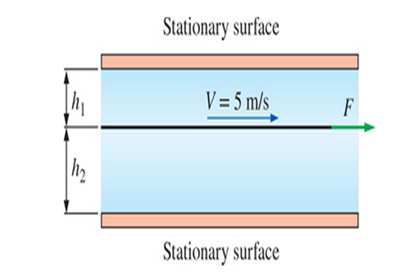
FIGURE P247
The force required maintain motion at
The force on the plate at
Answer to Problem 87P
The force required maintain motion at
The force on the plate at
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The moving velocity of the thin plate is
Write the expression for area of the plate.
Here the length of the plate is
Write the expression for shear force acting on the upper side of the plate.
Here, force acting on the upper side of the plate is
Write the expression for shear force acting on the lower side of the plate.
Here, shear force acting on the lower side of the plate is
Write the expression for force required to maintain the motion
Here force required to maintain the motion is
Write the expression for shear force acting on the upper side of the plate.
Here, force acting on the upper side of the plate is
Write the expression for shear force acting on the lower side of the plate.
Write the expression for force required to maintain the motion
Calculation:
Write the height of the plate from upper surface when the plate is between the mid of the surfaces.
Here, height of the plate from upper surface is
Write the height of the plate from bottom surface when the plate is between the mid of the surfaces.
Here, height of the plate from bottom surface is
Write the height of the plate from upper surface.
Here, the height of the plate from upper surface is
Write the height of the plate from bottom surface.
Here, the height of the plate from bottom surface is
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The force required maintain motion at
The force on the plate at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
- Two plates each having an area of 5 m^2 are 77 mm apart. The plate on top is fixed while the plate located at the bottom is pulled using a force equal to 26 N resulting in a constant velocity of 45 cm/s. Determine the viscosity of the fluid filling the space in between the two plates.arrow_forwardThe viscosity of a fluid is to be measured by a viscometer constructed of two 5-ft-long concentric cylinders. The inner diameter of the outer cylinder is 6 in, and the gap between the two cylinders is 0.035 in. The outer cylinder is rotated at 250 rpm, and the torque is measured to be 1.2 lbf⋅ft. Determine the viscosity of the fluidarrow_forwardA thin plate moves between two parallel, horizontal, stationary flat surfaces at a constant velocity of 5 m/s. The two stationary surfaces are spaced 4 cm apart, and the medium between them is filled with oil whose viscosity is 0.9 N⋅s/m2. The part of the plate immersed in oil at any given time is 2-m long and 0.5-m wide. If the plate moves through the mid-plane between the surfaces, determine the force required to maintain this motion. What would your response be if the plate was 1 cm from the bottom surface (h2) and 3 cm from the top surface (h1)?arrow_forward
- A plate separated by 0.5mm from a fixed plate moves at 0.50 m/s under a force per unit area of 4.0 N/m^2. Determine the viscosity of the fluid between the plates. Answer in mPaarrow_forwardThe space between two parallel plates 5 mm apart is filled with crude oil. A force of 2 N is required to drag the upper plate at a constant velocity of 0.8 m/s. The lower plate is stationary. The area of the upper plate is 0.09 m2 . Determine: () The dynamic viscosity, and (i the kinematic viscosity of the oil in stokes I the specific gravity of oil s 0.9,arrow_forwardTwo large planes are parallel to each other and are inclined at 30°V to the horizontal with the space between them filled with a fluid of viscosity 20cP. A small thin plate of 0.125m square slides parallel and midway between the planes and reaches a constant velocity of 2m/s. The weight of the plate is 1N. Determine the distance between the plates.arrow_forward
- Under what conditions can a moving body of fluid be treated as a rigid body?arrow_forwardaerodynamics: Determine the difference between the total pressure of an aircraft flying at sea level, and an aircraft flying at 5KM? Both have a velocity of 100m/s.arrow_forwardIgnoring any losses, estimate how much energy (in units of Btu) is required to raise the temperature of water in a 75-gallon hot-water tank from 60°F to 110°F.arrow_forward
- The figure below represents a cylinder C i (d = 11 cm) that is inside a hollow cylinder (d = 11.1 cm). The inner cylinder, with a mass of 30 kg and a length of 25 cm (L), is subjected to a pressure P of 50 kPa at its bottom, rising at a constant speed of 2.5 m/s. a) Determine the dynamic viscosity of the lubricating oil that must be placed in the space between the piston and the cylinder; b) Determine the kinematic viscosity knowing that it consists of a mixture of 3 L of oil A (specific mass of 880 kg/m 3 ) and 2200 mL of oil B (specific mass of 940 kg/m 3 ). Data: g = 9.81 m/s 2arrow_forwardDetermine the pressure difference between the inside and outside of the 0.1 mm diameter air bublle in a liquid if the surface tension at the air-liquid interface is 0.075 N/m. Express your answer in 3 decimal places and in kPa.arrow_forwardAn oil is contained between 2 identical parallel plates of 2m2area each. The top plate is pulled tothe left (-x direction) with a force of 0.33N at a velocity of 0.3 m/s. The bottom plate is pulled in theopposite direction with a force of 0.11N at a velocity of 0.1 m/s. The plates are 5mm apart. Whatis the viscosity of the oil in cP?arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





