
Concept explainers
Bacteriophage-Inspired Antibiotics Although bacteriophages have been infecting bacteria for billions of years, no mechanism, has evolved in bacteria to prevent the viruses from lysing the cell walls of their hosts. Now, scientists are targeting the same bacterial wall components that bacteriophages do. The goal is to develop antibiotics that bacteria will be less likely to develop resistance to.
FIGURE 20.22 shows the results of a study to test Epimerox, a new bacteriophage-inspired antibiotic, against Bacillus anthracis, the bacterial species that causes the disease anthrax.
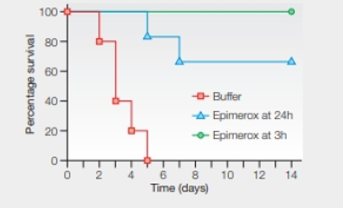
FIGURE 20.22 Effect of Epimerox on the survival of mice with anthrax. Mice were infected with the bacteria B. anthracis. One group of 15 then began receiving a drug-free buffer solution 3 hours later. Another 15 were treated with Epimerox beginning 3 hours after infection. A third group of 15was treated with Epimerox beginning 24 hours after infection.
How long did it take for all the mice that received the drug-free buffer alone to die? What function did this group play in the experiment?
To determine: The days taken for all the mice to receive the drug-free buffer alone and die.
Introduction: Scientists developed an investigational broad spectrum of an antibiotic compound called Epimerox that inhibits or blocks the activity of an enzyme called epimerase. Epimerase is an enzyme found in Bacillus anthracis that is required to synthesize a polysaccharide in their cell wall. It is also essential for bacterial growth and for receptor expression. Epimerase is used as a model to produce the drug Epimerox. The bacteriophage-lysin enzyme has the capability to specifically bind with epimerase of bacteria and cause cell lysis. Bacillus could not develop a resistant mechanism to prevent the viruses from lysing their host cell wall. This was the idea behind to produce an antibiotic epimerase that could be effective against Bacillus anthracis.
Explanation of Solution
In the given case study, scientists had conducted certain experiments to determine the action of the Epimerox drug. The experimental groups of mice were infected with the bacteria Bacillus anthracis. The mice were grouped into 15 member groups. The first set of mice began to receive drug-free buffer after three hours of infection. At the same time, another set was treated with Epimerox antibiotics. The third set of mice was treated with Epimerox after 24 hours of infection. They observed the survival rate of mice of different groups, and the results were plotted in a graph (Refer Fig 20.2) showing the time (days) of survival versus percentage of survival. Refer Fig 20.2, “Effect of Epimerox on the survival of mice with anthrax”, in the textbook. The graph shows that the group of mice that were injected with drug-free buffer solution died within five days of infection.
The group of mice that were injected with drug-free buffer solution died within five days of infection.
To determine: The role of drug-free buffer in the given experiment.
Introduction: Epimerox inhibits or blocks the activity of an enzyme called epimerase. Epimerase is an enzyme found in Bacillus anthracis that is required to synthesize a polysaccharide in their cell wall. It is also essential for bacterial growth and for receptor expression. Epimerase is used as a model to produce the drug Epimerox.
Explanation of Solution
A solution that will resist the pH change by the addition of either acid or base is called buffer. The buffers are important to maintain the pH of a solution. In the given experiment, drug-free buffer serves as a control group to check the efficiency of the drug Epimerox against the Bacillus anthracis in other groups.
The drug-free buffer served as the control group.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Biological Science
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (4th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology
- HersheyChase Experiments The graph shown in FIGURE 8.5 is reproduced from an original 1952 publication by Hershey and Chase. Bacteriophage were labeled with radioactive tracers and allowed 10 infect bacteria. The virusbacteria mixtures were then whirled in a blender to dislodge any viral components attached to the exterior of the bacteria. Afterward, radioactivity from the tracers was measured. FIGURE 8.5 Detail of Alfred Hershey and Martha Chases 1952 publication describing their experiments with bacteriophage. Infected bacteria refers to the percentage of bacteria that survived the blender. After 4 minutes in the blender, what percentage of each isotope was extracellular?arrow_forwardHersheyChase Experiments The graph shown in FIGURE 8.5 is reproduced from an original 1952 publication by Hershey and Chase. Bacteriophage were labeled with radioactive tracers and allowed 10 infect bacteria. The virusbacteria mixtures were then whirled in a blender to dislodge any viral components attached to the exterior of the bacteria. Afterward, radioactivity from the tracers was measured. FIGURE 8.5 Detail of Alfred Hershey and Martha Chases 1952 publication describing their experiments with bacteriophage. Infected bacteria refers to the percentage of bacteria that survived the blender. The extracellular concentration of which isotope increased the most with blending?arrow_forwardHersheyChase Experiments The graph shown in FIGURE 8.5 is reproduced from an original 1952 publication by Hershey and Chase. Bacteriophage were labeled with radioactive tracers and allowed 10 infect bacteria. The virusbacteria mixtures were then whirled in a blender to dislodge any viral components attached to the exterior of the bacteria. Afterward, radioactivity from the tracers was measured. FIGURE 8.5 Detail of Alfred Hershey and Martha Chases 1952 publication describing their experiments with bacteriophage. Infected bacteria refers to the percentage of bacteria that survived the blender. Before blending what percentage of each isotope. 35S and 32P, was extracellular (outside the bacteria)?arrow_forward
- Some mutations that occur in bacteria can cause the loss of phage receptors, and these bacteria become phage resistant. In order for a phage to infect the host bacterium, it is preferred that the cell wall is newly synthesized.why ?arrow_forwardMRSA has emerged as a serious infectious disease, with the first case of methicillin-resistant S. aureus being detected in 1961. Why are medical professionals so concerned when antibiotics exist that can kill MRSA? MRSA can transfer methicillin-resistance to other bacteria Patients are not treated with correct antibiotics rapidly enough to prevent serious illness MRSA could acquire additional antibiotic resistance genes from other bacteria to become a “super bug." All of the above.arrow_forwardWhich of these statements is true? An antibiotic is any substance produced by a organism that is antagonistic to the growth of prokaryotes An antibiotic is any substance produced by a prokaryote that is antagonistic to the growth of other viruses An antibiotic is any substance produced by a prokaryote that is antagonistic to the growth of eukaryotic cells An antibiotic is any substance produced by a prokaryote that prevents growth of the same prokaryote.arrow_forward
- Each species of bacteria has its own distinctive cell surface. Thecharacteristics of the cell surface play an important role in processessuch as conjugation and transduction. For example, certainstrains of E. coli have pili on their cell surface. These pili enableE. coli to conjugate with other E. coli and also enable certain bacteriophages (such as M13) to bind to the surface of the E. coli andgain entry into the cytoplasm. With these ideas in mind, explainwhich forms of genetic transfer (i.e., conjugation, transduction,and transformation) are more likely to occur between different speciesof bacteria. Discuss some of the potential consequences ofinterspecies genetic transfer.arrow_forwardReplication of many RNA viruses depends on RNA polymerase. The antiviral drug ribavirin does not inhibit the polymerase but instead increases its error rate. Explain how this affects the virus.arrow_forwardQuestion:- Transformation of host cells by several DNA viruses requires inactivation of the cellular proteins pRB, CKI ( cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor) and p53. give an example of how each of these cellular proteins can be inactivated by DNA viruses. ( one example/cellular protein)arrow_forward
- Fill in the blanks. The parentheses represent the choices for the blank. Scientists already knew that a special type of virus called a bacteriophage inserts genetic information into a bacterial cell in order to force the bacterial cell to make more bacteriophage viruses. What scientists did not know, however, was whether that genetic information is carried by the (proteins, DNA) covering the outside of the bacteriophage virus or by the (proteins, DNA) inside the bacteriophage virus.arrow_forwardConjugation: Diagram the process of conjugation in bacterial cells (using F plasmid transfer):a. In you diagram, label the parts of both the donor and recipient cell, draw an arrow, then show the resulting cells and their resulting phenotypes. Label any other special features needed for this process.arrow_forwardWe use Lysozyme to break down the cell wall in E.coli to lyse the cells. Why do we not use Lysozyme on mammalian cells?arrow_forward
 Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax

