
Concept explainers
a)
Interpretation:
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with nitric acid is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
D-galactose is a monosaccharide molecule and it is sweet in taste as glucose. It is C-
Epimers are pair of stereoisoisomers which differ in configuration at one stereogenic center. In D-galactose molecule one terminal
Nitric acid has the chemical formula
a)
Answer to Problem 34P
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with nitric acid is given below,
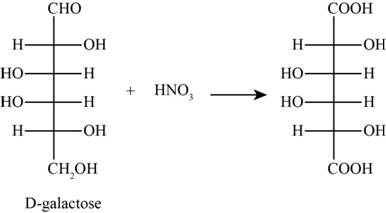
Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with nitric acid is as follows,

Figure 1
b)
Interpretation:
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with
Concept Introduction:
D-galactose is a monosaccharide molecule and it is sweet in taste as glucose. It is C-
Epimers are pair of stereoisoisomers which differ in configuration at one stereogenic center. In D-galactose molecule one terminal aldehydic and one terminal alcoholic group is present. The given ions
b)
Answer to Problem 34P
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with
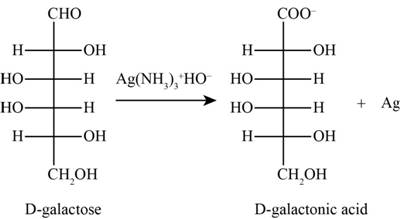
Figure 2
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with

Figure 2
The given ions
c)
Interpretation:
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with
Concept Introduction:
D-galactose is a monosaccharide molecule and it is sweet in taste as glucose. It is C-
Epimers are pair of stereoisoisomers which differ in configuration at one stereogenic center. In D-galactose molecule one terminal aldehydic and one terminal alcoholic group is present.
c)
Answer to Problem 34P
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with
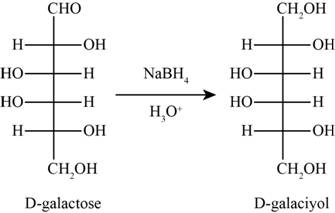
Figure 3
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with

Figure 3
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with
d)
Interpretation:
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with excess
Concept Introduction:
D-galactose is a monosaccharide molecule and it is sweet in taste as glucose. It is C-
d)
Answer to Problem 34P
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with excess
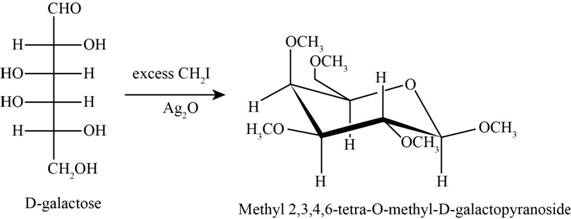
Figure 4
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with excess

Figure 4
e)
Interpretation:
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with
Concept Introduction:
D-galactose is a monosaccharide molecule and it is sweet in taste as glucose. It is C-
e)
Answer to Problem 34P
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with
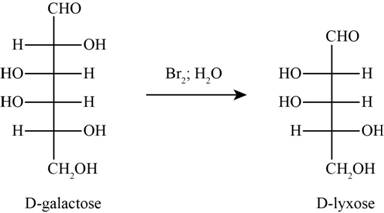
Figure 5
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with

Figure 5
f)
Interpretation:
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with ethanol
Concept Introduction:
D-galactose is a monosaccharide molecule and it is sweet in taste as glucose. It is C-
f)
Answer to Problem 34P
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with ethanol
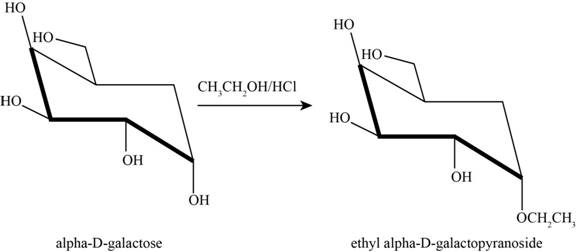
Figure 6
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with ethanol

Figure 6
g)
Interpretation:
The products obtained when D-galactose reacts with the given reactants are to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
D-galactose is a monosaccharide molecule and it is sweet in taste as glucose. It is C-
g)
Answer to Problem 34P
The products obtained when D-galactose reacts with the given reactants are shown in figure 7.
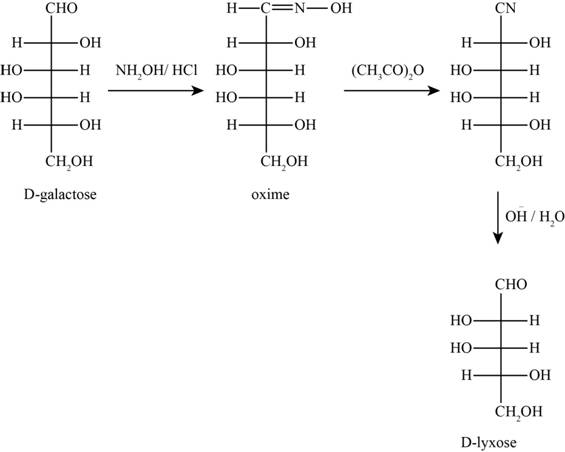
Figure 7
Explanation of Solution
The given reactants are hydroxylamine/trace acid, acetic anhydride/heat and
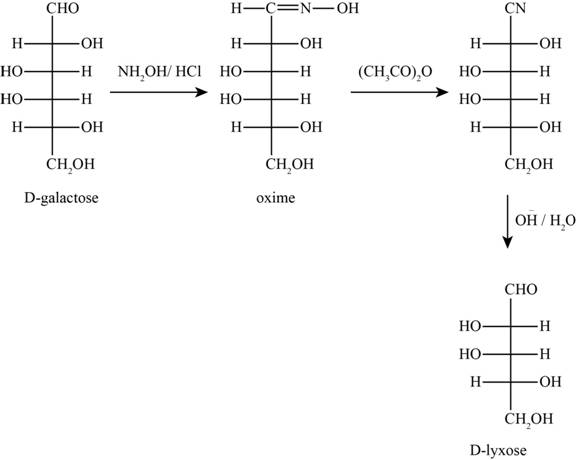
Figure 7
In the above reaction D-galactose first reacts with hydroxylamine in the presence of an acid, a compound of oxime is formed. Then it reacts with acetic anhydride with heat gives nitrile compound. Now, nitrile compound undergoes a reaction with base a compound D-Lyxose is formed.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Books a la Carte Plus Mastering Chemistry with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (8th Edition)
- What would be the product if D-mannose is reacted witha.. 1.) NH2OH then 2.) (CH3CO)2O, NaOCOCH3 then 3.)NaOCH3, then 4.)HNO3, H2O [note this is a consectutive reaction] b. oxidation using HNO3arrow_forwardPredict the products obtained when d-galactose reacts with each reagent.(a) Br2 and H2O (b) NaOH, H2O (c) CH3OH, H + (d) Ag(NH3) 2+ -OH(e) H2, Ni (f) excess Ac2O and pyridine (g) excess CH3 I, Ag2O (h) NaBH4(i) Br2, H2O, then H2O2 and Fe2(SO4)3 (j) (1) KCN/HCN; (2) H2, Pd/BaSO4; (3) H3O! (k) excess HIO42arrow_forwardWhen talking about the compound Gal(Beta 1-4) Glc, What carbon involved in glycoside bond? What isomerization? What anomeric still free?arrow_forward
- Consider the tetrasaccharide stachyose drawn below. Stachyose is found in white jasmine, soybeans, and lentils. Because humans cannot digest it, its consumption causes flatulence.a. Label all glycoside bonds.b. Classify each glycosidic linkage as α or β and use numbers to designate its location between two rings (e.g., 1→4-β).c. What products are formed when stachyose is hydrolyzed with H3O+?d. Is stachyose a reducing sugar?e. What product is formed when stachyose is treated with excess CH3I, Ag2O?f. What products are formed when the product in (e) is treated with H3O+?arrow_forwardDraw the products formed when α-D-galactose is treated with each reagent: i. CH3I (excess), Ag2O ii. CH3OH, H3O+ iii. NaOH, H2O iv. Br2, H2Oarrow_forwardD-glucose and L-glucose would be expected to show differences in which of the followingp roperties? (Answer the items as dif erent or not different) a. Solubility in an achiral solvent b. Density c. Melting point d. Solubility in a chiral solvent e. Freezing point f. Reaction with ethanol (achiral compound) g. Reaction with (+)-lactic acid (chiral compound)arrow_forward
- Consider the tetrasaccharide stachyose drawn below. Stachyose is found in white jasmine, soybeans, and lentils. Because humans cannot digest it, its consumption causes flatulence.a. Label all glycoside bonds.b. Classify each glycosidic linkage as αα or ββ and use numbers to designate its location between two rings (e.g., 1→→4-ββ)-c. What products are formed when stachyose is hydrolyzed with H33O++?d. Is stachyose a reducing sugar?e. What product is formed when stachyose is treated with excess CH33I, Ag22O?f. What products are formed when the product in (e) is treated with H33O++?arrow_forward17. .Draw the dash-wedge structure for the beta-furanose anomer of the L-ketohexose shown below.arrow_forwarda hexose if it has 6 C's, and so forth. ? Explainarrow_forward
- Like glucose, galactose mutarotates when it dissolves in water. The specific rotation ofa-d-galactopyranose is +150.7°, and that of the b anomer is +52.8°. When either ofthe pure anomers dissolves in water, the specific rotation gradually changes to +80.2°.Determine the percentages of the two anomers present at equilibrium.arrow_forwardReaction 6.2 shows the initial reaction of D-glucose with Cu2+ through Nelson’s test: a) What type of reaction occurs? Recall a property of D-glucose which allows the reaction to occur. b) Identify the other product aside from Cu2O.arrow_forwarda) Draw Haworth projections of both - and -anomers of D-fructose. Indicate which carbon is the anomeric carbon.b) Sucrose is a disaccharide made up of a molecule of D-fructose and D-glucose. Draw the structure of sucrose clearly indicating the linkage between the two monosaccharides and its biological significance.c) Tollen’s reagent is a very mild oxidizing agent which normally oxidize aldehydes but not ketones. However, both glucose and fructose give positive results with Tollen’s reagent and are classified as reducing sugars. Explain how fructose can also give positive results with Tollen’s reagent (illustrate using structures).arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

