
Concept explainers
If one hydrogen in a hydrocarbon is replaced by a halogen
a. n-pentane
b. 2-methylbutane
c. 2,4-dimethylpentane
d. methylcyclobutane
(a)
Interpretation: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen atom in each of the given compound is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Concept introduction: Structural isomerism occurs when two compounds have same number of atoms but the spatial arrangement of the atoms is different from each other. If one hydrogen atom of a hydrocarbon is replaced by a halogen atom, the number of isomers that exists for the substituted compound depends on the number of types of hydrogen in the original hydrocarbon.
To determine: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen in n-pentane is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Answer to Problem 45E
Answer
Three isomers are obtained when one hydrogen atom of n-pentane is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The isomer is
The given compound n-pentane has five carbon atoms in the longest carbon chain. When hydrogen of first carbon of n-pentane is replaced by chlorine atom, then the isomer named
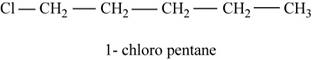
Figure 1
The isomer is
The given compound n-pentane has five carbon atoms in the longest carbon chain. When hydrogen of second carbon of n-pentane is replaced by chlorine atom, then the isomer named
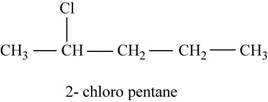
Figure 2
The parent chain contains five carbon atom and chlorine group is attached to second carbon.
The compound
The isomer is
The given compound n-pentane have five carbon atoms in the longest carbon chain. When hydrogen of third carbon of n-pentane is replaced by chlorine atom, then the isomer named
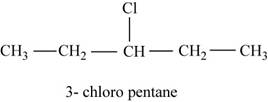
Figure 3
The compound
(b)
Interpretation: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen atom in each of the given compound is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Concept introduction: Structural isomerism occurs when two compounds have same number of atoms but the spatial arrangement of the atoms is different from each other. If one hydrogen atom of a hydrocarbon is replaced by a halogen atom, the number of isomers that exists for the substituted compound depends on the number of types of hydrogen in the original hydrocarbon.
To determine: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen atom in
Answer to Problem 45E
Answer
Nine isomers are obtained when one hydrogen of
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The isomer is
In the given compound,
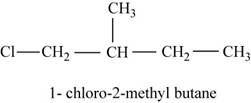
Figure 4
The isomer is
In the given compound,
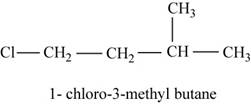
Figure 5
The isomer is
In the given compound,
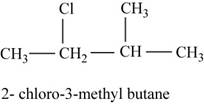
Figure 6
The isomer is
In the given compound,
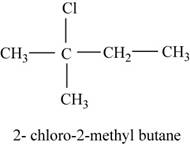
Figure 7
The isomer is
In the given compound,
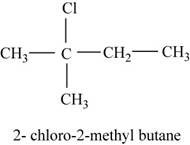
Figure 8
The isomer is
In the given compound,
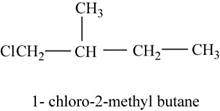
Figure 9
The isomer is
In the given compound,
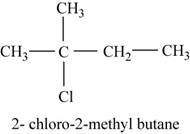
Figure 10
The isomer is
In the given compound,

Figure 11
The isomer is
In the given compound,

Figure 12
(c)
Interpretation: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen atom in each of the given compound is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Concept introduction: Structural isomerism occurs when two compounds have same number of atoms but the spatial arrangement of the atoms is different from each other. If one hydrogen atom of a hydrocarbon is replaced by a halogen atom, the number of isomers that exists for the substituted compound depends on the number of types of hydrogen in the original hydrocarbon.
To determine: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen in
Answer to Problem 45E
Answer
Two isomers are obtained when one hydrogen of
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The isomer is
The given compound
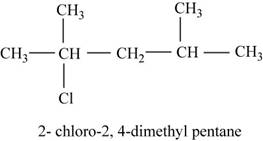
Figure 13
The isomer is
The given compound
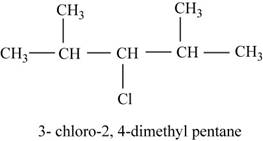
Figure 14
(d)
Interpretation: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen atom in each of the given compound is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Concept introduction: Structural isomerism occurs when two compounds have same number of atoms but the spatial arrangement of the atoms is different from each other. If one hydrogen atom of a hydrocarbon is replaced by a halogen atom, the number of isomers that exists for the substituted compound depends on the number of types of hydrogen in the original hydrocarbon.
To determine: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen in methylcyclobutane is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Answer to Problem 45E
Answer
Three isomers are obtained when one hydrogen of methylcyclobutane is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The isomer is
In the given compound methylcyclobutane, the ring of four carbon atoms is considered as the parent chain. Methyl group is attached at first carbon. When hydrogen of the methyl group is replaced by chlorine atom, then the isomer named
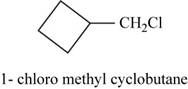
Figure 15
The isomer is
In the given compound methylcyclobutane, the ring of four carbon atoms is considered as the parent chain. Methyl group is attached at first carbon. When hydrogen of the second carbon of the ring is replaced by chlorine atom, then the isomer named
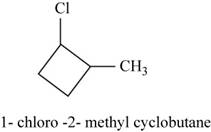
Figure 16
The isomer is
In the given compound methylcyclobutane, the ring of four carbon atoms is considered as the parent chain. Methyl group is attached at first carbon. When hydrogen of the third carbon of the ring is replaced by chlorine atom, then the isomer named
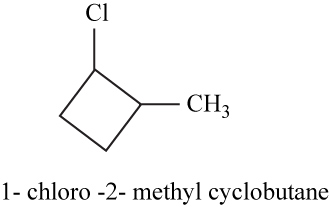
Figure 17
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
- What is the difference in bonding and in general molecular formula between an alkene and a cycloalkane with the same number of carbon atoms?arrow_forwardDistinguish between isomerism and resonance. Distinguish between structural and geometric isomerism. When writing the various structural isomers, the most difficult task is identifying which are different isomers and which are identical to a previously written structurethat is, which are compounds that differ only by the rotation of a carbon single bond. How do you distinguish between structural isomers and those that are identical? Alkenes and cycloalkanes are structural isomers of each other. Give an example of each using C4H8. Another common feature of alkenes and cycloalkanes is that both have restricted rotation about one or more bonds in the compound, so both can exhibit cis- trans isomerism. What is required for an alkene or cycloalkane to exhibit cis-trans isomerism? Explain the difference between cis and trans isomers. Alcohols and ethers are structural isomers of each other, as are aldehydes and ketones. Give an example of each to illustrate. Which functional group in Table 21-4 can be structural isomers of carboxylic acids? What is optical isomerism? What do you look for to determine whether an organic compound exhibits optical isomerism? 1-Bromo-1-chloroethane is optically active whereas 1-bromo-2-chloroethane is not optically active. Explain.arrow_forwardThe molecule 2-chloro-4-methylhexane is made by addition of HCl to an alkene. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction.arrow_forward
- Note the number of isomers for Butane and Octane. Why does the number of possible isomers go up with an increasing number of carbon atoms?arrow_forwardPetroleum products such as kerosene and gasoline are separated using fractional distillation. Each of them has their own properties and usage. Why can't we use one petroleum product as a substitute for the other when they are composed majority of alkanes?arrow_forwardAldehydes and ketones can be named in a systematic way by counting the number of carbon atoms (including the carbonyl carbon) that they contain. The name of the aldehyde or ketone is based on the hydrocarbon with the same number of carbon atoms. The ending -al for aldehyde or -one for ketone is added as appropriate. Draw the structural formulas for 3-methyl-2-butanone.arrow_forward
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





