
Concept explainers
Decide if the side chains of the amino acid residues in the following peptides are nonpolar or polar, and label the hydrophobic and hydrophilic end of each peptide.
- VLLFGEDEK
- RKVSFLGAA
(a)
Interpretation:
The polarity of the side chains of the amino acid residue in the given peptide should be determined and also label the hydrophilic and hydrophobic ends of the given peptide.
VLLFGEDEK
Concept Introduction:
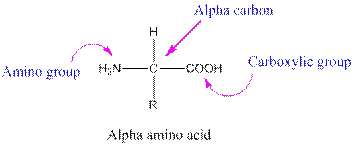
Amino acids are organic compounds containing two functional groups namely amino and carboxylic group. Amino group is attached to the alpha carbon, carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group making them alpha amino acids.
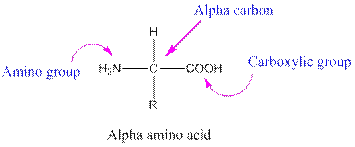
This table gives information about the polarity of the side chains:
| Name of Amino Acid | One-letter abbreviation | Structure | Side chain Polarity | Side chain |
| Alanine | A | 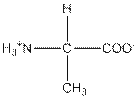 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Asparagine | N | 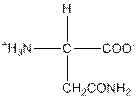 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Cysteine | C | 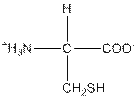 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Glutamine | Q | 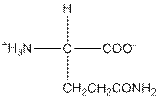 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Glycine | G | 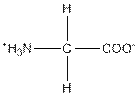 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Isoleucine | I | 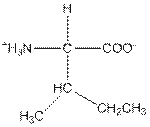 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Leucine | L | 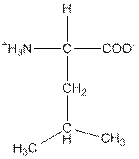 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Methionine | M | 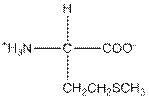 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Phenylalanine | F | 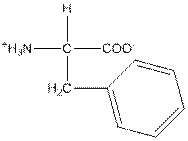 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Proline | P | 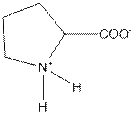 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Serine | S | 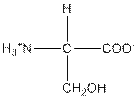 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Threonine | T | 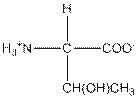 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Tryptophan | W | 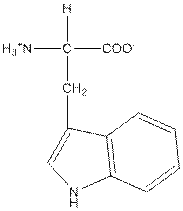 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Tyrosine | Y | 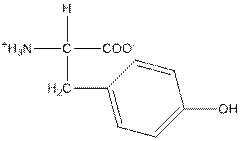 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Valine | V | 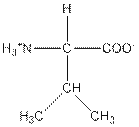 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Aspartic acid | D | 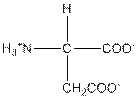 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Glutamic acid | E | 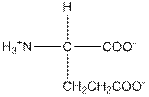 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Arginine | R | 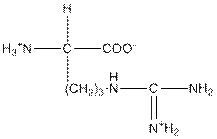 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Histidine | H | 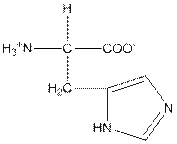 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Lysine | K | 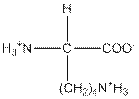 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
Answer to Problem 56P
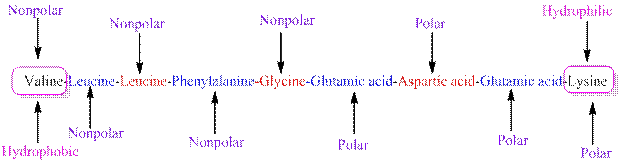
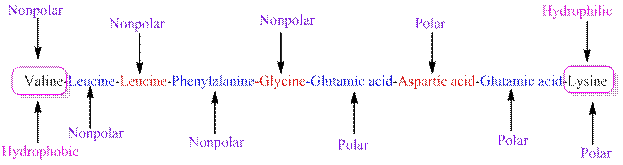
The polarity of the side chains of amino acids are shown along with hydrophobic and hydrophilic end of the given peptide 'VLLFGEDEK' as follows:
Explanation of Solution
Side chains of amino acids are non-polar because only carbon and hydrogen atoms are present having very small dipole moment and tends to repel water. That's why non-polar amino acids are hydrophobic in nature.
Side chains of amino acids are polar because these proteins have those toms which are capable of forming hydrogen bonds have very high dipole moment and tends to attract water. That's why polar amino acids are hydrophilic in nature.
From the table, the sequence of peptide contains the following amino acids:
V = Valine is a non-polar amino acid.
L = Leucine is a non-polar amino acid.
F = Phenylalanine is a non-polar amino acid.
G = Glycine is a non-polar amino acid.
E = Glutamic acid is a polar amino acid.
D = Aspartic acid is a polar amino acid.
K = Lysine is a polar amino acid.
From the given peptide sequence 'VLLFGEDEK', Valine present at the right end and Lysine present at the left end of the sequence.
Valine is a non-polar amino acid and hydrophobic in nature.
Lysine is a non-polar amino acid and hydrophilic in nature.
Hydrophobic and hydrophilic ends along with polar and non-polar amino acids are indicated in the given sequence as follows:
(b)
Interpretation:
The polarity of the side chains of the amino acid residue in the given peptide should be determined and also label the hydrophilic and hydrophobic ends of the given peptide.
RKYSFLGAA
Concept Introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds containing two functional groups namely amino and carboxylic group. Amino group is attached to the alpha carbon, carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group making them alpha amino acids.
Answer to Problem 56P
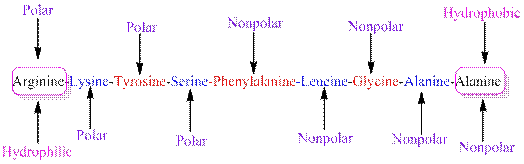
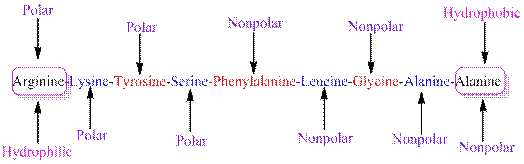
The polarity of the side chains of amino acids are shown along with hydrophobic and hydrophilic end of the given peptide 'RKYSFLGAA' as follows:
Explanation of Solution
Side chains of amino acids are non-polar because only carbon and hydrogen atoms are present having very small dipole moment and tends to repel water. That's why non-polar amino acids are hydrophobic in nature.
Side chains of amino acids are polar because these proteins have those toms which are capable of forming hydrogen bonds have very high dipole moment and tends to attract water. That's why polar amino acids are hydrophilic in nature.
From the table, the sequence of peptide 'RKYSFLGAA' contains the following amino acids:
R = Arginine is a polar amino acid.
K = Lysine is a polar amino acid.
Y = Tyrosine is a polar amino acid.
S = Serine acid is a polar amino acid.
F = Phenylalanine is a non-polar amino acid.
L = Leucine is a non-polar amino acid.
G = Glycine is a non-polar amino acid.
A = Alanine is a non-polar amino acid.
From the given peptide sequence 'RKYSFLGAA', Arginine present at the right end and Alanine present at the left end of the sequence.
Arginine is a polar amino acid and hydrophilic in nature.
Alanine is a non-polar amino acid and hydrophobic in nature.
Hydrophobic and hydrophilic ends along with polar and non-polar amino acids are indicated in the given sequence as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- Using both three- and one-letter codes for amino acids, write the structures of all possible peptides containing the following amino acids: (a) Val, Ser, Leu (b) Ser, Leu2, Proarrow_forward22-42 (a) How many atoms of the peptide bond lie in the same plane? (b) Which atoms are they?arrow_forwardDrawing Peptide Structures Draw the tripeptide that would result from cysteine attaching to the previous dipeptide on the acidic side.arrow_forward
- 22-28 A tetrapeptide is abbreviated as DPKH. Which amino acid is at the N-terminus, and which is at the C-terminus?arrow_forward22-71 Which amino acid side chain is most frequently involved in denaturation by reduction?arrow_forward22-35 Why is histidine considered a basic amino acid when the pKa of its side chain is 6.0?arrow_forward
- Identify the R group of the side chain in the following amino acids that results in the side-chain classification indicated in parentheses see Table 19.1: a. tyrosine neutral, polar b. glutamate acidic, polar c. methionine neutral, nonpolar d. histidine basic, polar e. cysteine neutral, polar f. valine neutral, nonpolararrow_forwardHow many of the -amino acids shown in Table 26-1 contain aromatic rings? How many contain sulfur? How many contain alcohols? How many contain hydrocarbon side chains?arrow_forwardComplete degradation of a protein into individual amino acids involves choose all that are correct: a. Removal of a water molecule from between two amino acids b. Addition of a water molecule between two amino acids c. A hydrolysis reaction d. The breaking of peptide linkagearrow_forward
- 22-64 If both cysteine residues on the B chain of insulin were changed to alanine residues, how would it affect the quaternary structure of insulin?arrow_forward22-16 Which amino acids in Table 22-1 have more than one stereocenter?arrow_forward22-61 Polyglutamic acid (a polypeptide chain made only of glutamic acid residues) has an a-helix conformation below pH 6.0 and a random-coil conformation above pH 6.0. What is the reason for this conformational change?arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning  General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,





