
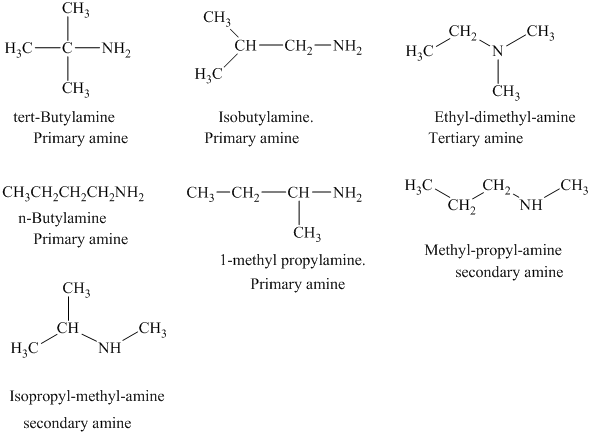
Interpretation:
The structural formulas for all the
Concept introduction:
If the molecular formula of two compounds is same but their atoms are connected in different ways, they are known as constitutional or structural isomers.
In primary amines, the nitrogen atom is connected to two hydrogen atoms. In secondary amines, the nitrogen atom is connected to one hydrogen atom and tertiary amines have no hydrogen atom connected to the nitrogen atom.
Answer to Problem 23P
Solution:
The structural formulas for all the amines of molecular formula
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular formula is

In each of the above isomer, the functional group is amine group. Therefore, the suffix used while naming the isomer is amine. On the basis of the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the nitrogen, the given isomers are classified as primary, secondary, and tertiary amine.
The structural formulas for all the seven isomeric amines possible for the molecular formula
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY W/CONNECT
- Predict the major products formed when the following amines undergo exhaustivemethylation, treatment with Ag2O, and heating.N-ethylpiperidinearrow_forwardDefine the simplest method to synthesize an amine ?arrow_forwardAcetaminophen is an analgesic marketed under the brand name Tylenol, among others. Draw the amine that results from the base hydrolysis of acetaminophen.arrow_forward
- What carboxylic acid and amine are needed to synthesize the pain reliever phenacetin? Phenacetin was once a component of the over-the-counter pain reliever APC (aspirin, phenacetin, caffeine), but it is no longer used because of its kidney toxicity.arrow_forwardDraw structural formulas for the three secondary amines with the molecular formula C4H11N.arrow_forwardWrite equations for the hydrolysis of these amides in concentrated aqueous HCl. Show all products as they exist in aqueous HCl and the number of moles of HCl required for hydrolysis of each amidearrow_forward
- Draw a structural formula for each amine and amine derivative. (a) N,N-Dimethylaniline (b) Triethylamine (c) tert-Butylamine (d) 1,4-Benzenediamine (e) 4-Aminobutanoic acid (f) (R)-2-Butanamine (g) Benzylamine (h) trans-2-Aminocyclohexanol (i) 1-Phenyl-2-propanamine (amphetamine) (j) Lithium diisopropylamide (LDA) (k) Benzyltrimethylammonium hydroxide (Triton B)arrow_forwardWhich type of amine is (s)-methamphetamine? a) a primary aliphatic amine b) a primary aromatic amine c) a secondary aliphatic amine d) a secondary aromatic aminearrow_forward* The compound CH3CH2NH2 is classified as a A) primary amine. B) secondary amine. C) tertiary amine. D) quaternary amine. E) hydrated amine. * Which of the following compounds is an amine? A) (CH3CH2)2NH B) CH3CH2CH2CH2CO2CH3 C) CH3CH2CH2CH2-O-CH2CH2CH3 D) CH3CH=O E) CH3COCH3arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole




