
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To identify the substances ATP, CoA–SH,
Concept introduction: The sum of various
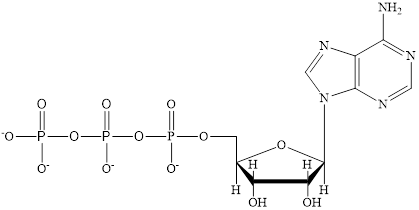
ATP is a
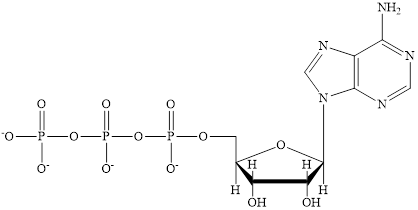
Coenzyme A (CoA) is a coenzyme which is utilized in various metabolic reactions. The functions of coenzyme A include oxidation of pyruvate in the citric cycle and fatty acid oxidation. The structure of Coenzyme A (CoA) is:
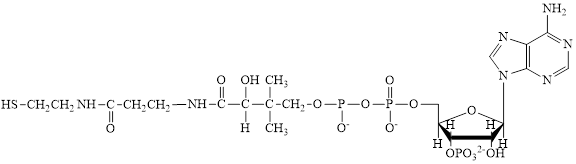
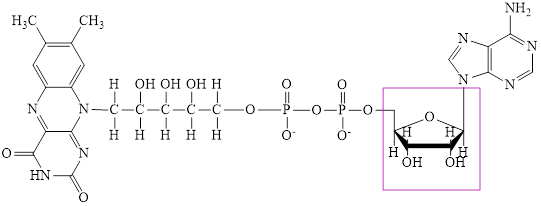
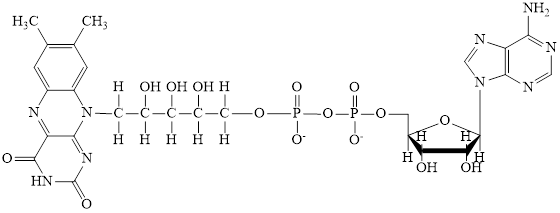
Flavin adenine dinucleotide exists in two forms: oxidized form
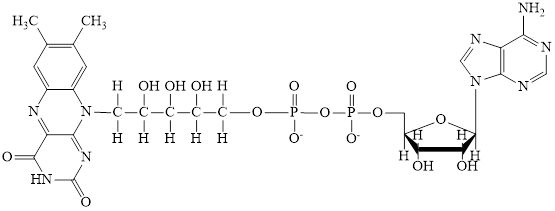
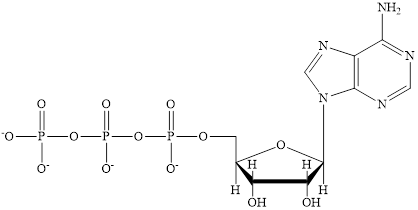
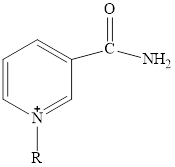
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Here,
(a)
Answer to Problem 23.46EP
ATP and
Explanation of Solution
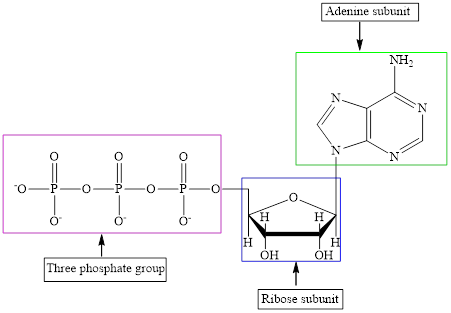
The structure of ATP is:
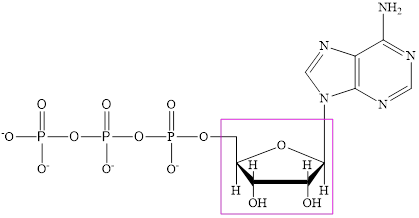
The structure of
The structure of

Here,
The structure of
The structure of coenzyme A (CoA) is:
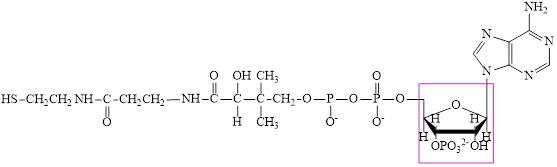
The ribose subunit in each of the metabolic intermediate is highlighted. Here, the structure of
(b)
Interpretation: To identify the substances ATP, CoA–SH,
Concept introduction: The sum of various chemical reactions occurring in the human body is called metabolism and the reactions individually are known as metabolic reactions. During these metabolic reactions, the various metabolic intermediates are formed for the short time to complete the reactions.ATP,
ATP is a nucleotide which provides energy for the completion of various metabolic reactions occurring in our human body. The structure of ATP consists of adenine base, ribose sugar unit and the three phosphate group connected to each other by phosphoanhydride bonds.
The structure of ATP is:
Coenzyme A (CoA) is a coenzyme which is utilized in various metabolic reactions. The functions of coenzyme A include oxidation of pyruvate in the citric cycle and fatty acid oxidation. The structure of Coenzyme A (CoA) is:
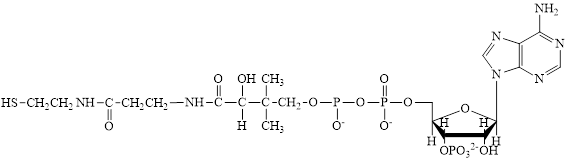
Flavin adenine dinucleotide exists in two forms: oxidized form
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide

Here,
(b)
Answer to Problem 23.46EP
CoA–SH consists of one phosphorylated ribose subunit in its structure.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of CoA–SH is:
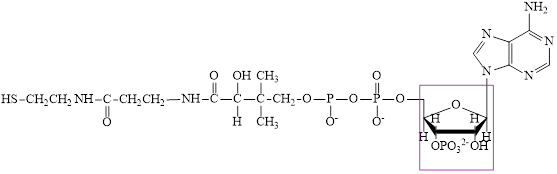
The structure of ATP is:
The structure of
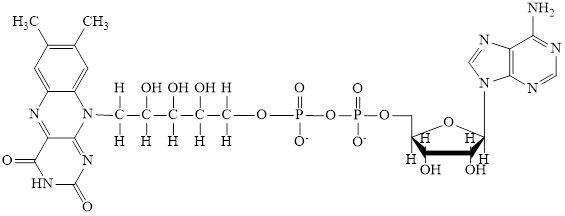
The structure of
The structure of

Here,
The phosphorylated ribose subunit in each of the metabolic intermediate is highlighted. Here, the structure ofCoA–SH consists of one phosphorylated ribose unit. Hence, the correct answer is CoA–SH.
(c)
Interpretation: To identify the substances ATP, CoA–SH,
Concept introduction: The sum of various chemical reactions occurring in the human body is called metabolism and the reactions individually are known as metabolic reactions. During these metabolic reactions, the various metabolic intermediates are formed for the short time to complete the reactions.ATP,
ATP is a nucleotide which provides energy for the completion of various metabolic reactions occurring in our human body. The structure of ATP consists of adenine base, ribose sugar unit and the three phosphate group connected to each other by phosphoanhydride bonds. The structure of ATP is:

Coenzyme A (CoA) is a coenzyme which is utilized in various metabolic reactions. The functions of coenzyme A include oxidation of pyruvate in the citric cycle and fatty acid oxidation.
The structure of Coenzyme A (CoA) is:
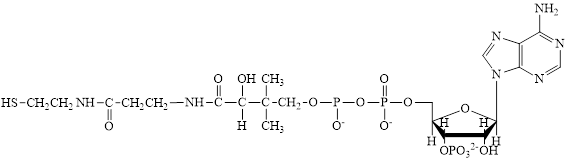
Flavin adenine dinucleotide exists in two forms: oxidized form

Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide

Here,
(c)
Answer to Problem 23.46EP
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
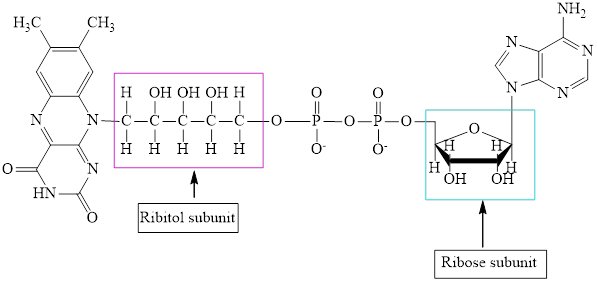
The structure of CoA–SH is:
The structure of ATP is:

The structure of
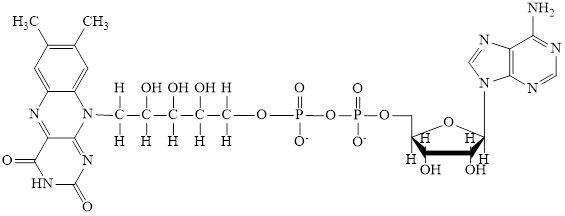
The structure of

Here,
The structure of
The ribose and ribitol subunit in each of the metabolic intermediate is highlighted. Here, the structure of
(d)
Interpretation: To identify the substances ATP, CoA–SH,
Concept introduction: The sum of various chemical reactions occurring in the human body is called metabolism and the reactions individually are known as metabolic reactions. During these metabolic reactions, the various metabolic intermediates are formed for the short time to complete the reactions.ATP,
ATP is a nucleotide which provides energy for the completion of various metabolic reactions occurring in our human body. The structure of ATP consists of adenine base, ribose sugar unit and the three phosphate group connected to each other by phosphoanhydride bonds. The structure of ATP is:
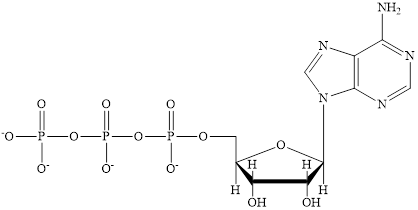
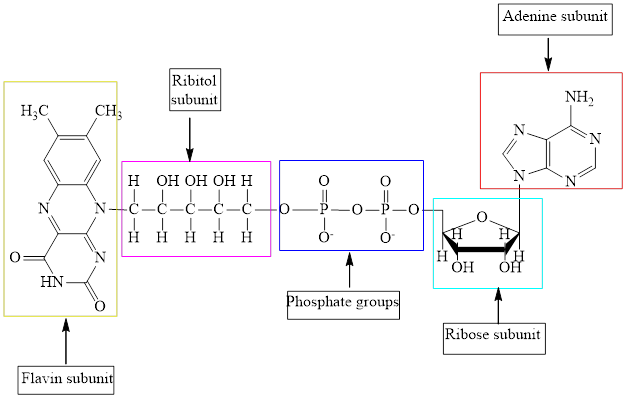
Coenzyme A (CoA) is a coenzyme which is utilized in various metabolic reactions. The functions of coenzyme A include oxidation of pyruvate in the citric cycle and fatty acid oxidation.
The structure of Coenzyme A (CoA) is:

Flavin adenine dinucleotide exists in two forms: oxidized form

Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide

Here,
(d)
Answer to Problem 23.46EP
CoA–SH and
Explanation of Solution
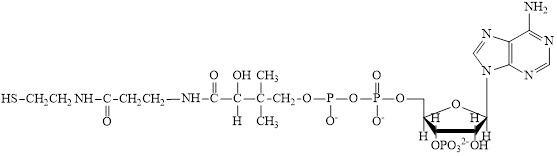
The structure of CoA–SH is:
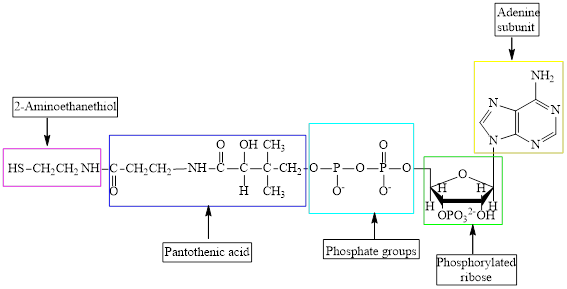
The structure of
The structure of ATP is:
The structure of
Here,
The different kinds of subunit in metabolic intermediate are highlighted Here, the structure of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning



