
Concept explainers
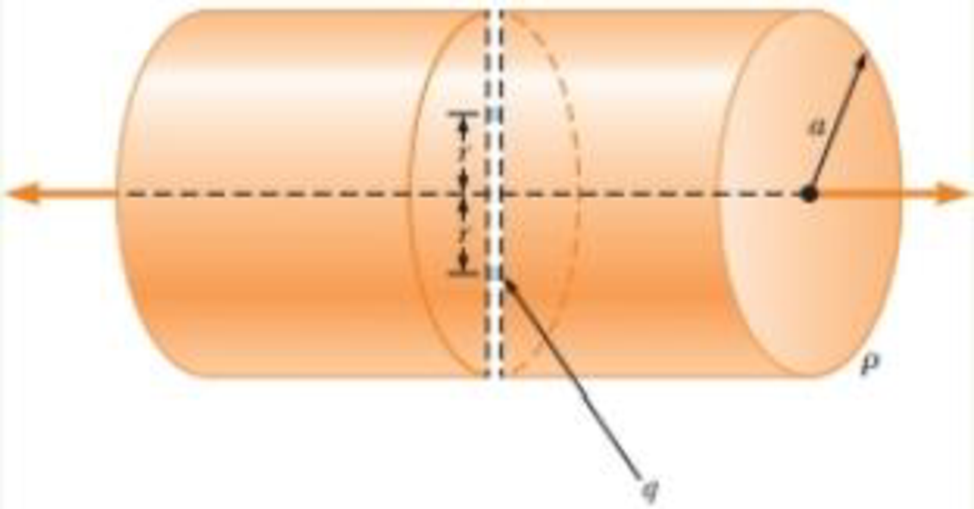
You are working for the summer at a research laboratory. Your research director has devised a scheme for holding small charged particles at fixed positions. The scheme is shown in Figure P23.36. An insulating cylinder of radius a and length L >> a is positively charged and carries a uniform volume charge density ρ. A very thin tunnel is drilled through a diameter of the cylinder and two small spheres with charge q are placed in the tunnel. These spheres are represented by the blue dots in the figure. They find equilibrium positions at a distance of r on opposite sides of the axis of the cylinder. Your research director has had great success with this scheme. (a) Determine the specific value of rat which equilibrium exists. (b) Your research director asks you see if he can extend the system as follows. Determine if it is possible to add transparent plastic tubes as extensions of the tunnel and have the small spheres be in equilibrium at a position for which r > a.
Figure P23.36
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
Physics: Principles with Applications
Physical Science
University Physics Volume 3
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
- A very long, thin wire fixed along the x axis has a linear charge density of 3.2 C/m. a. Determine the electric field at point P a distance of 0.50 m from the wire. b. If there is a test charge q0 = 12.0 C at point P, what is the magnitude of the net force on this charge? In which direction will the test charge accelerate?arrow_forwardA conducting rod carrying a total charge of +9.00 C is bent into a semicircle of radius R = 33.0 cm, with its center of curvature at the origin (Fig.P24.75). The charge density along the rod is given by = 0 sin , where is measured clockwise from the +x axis. What is the magnitude of the electric force on a 1.00-C charged particle placed at the origin?arrow_forwardA coaxial cable is formed by a long, straight wire and a hollow conducting cylinder with axes that coincide. The wire has charge per unit length = 20, and the hollow cylinder has net charge per unit length = 30. Use Gausss law to answer these questions: What are the charges per unit length on a. the inner surface and b. the outer surface of the hollow cylinder? c. What is the electric field a radial distance d from the axis of the coaxial cable?arrow_forward
- A uniform electric field given by E=(2.655.35j)105N/C permeates a region of space in which a small negatively charged sphere of mass 1.30 g is suspended by a light cord (Fig. P24.53). The sphere is found to be in equilibrium when the string makes an angle = 23.0. a. What is the charge on the sphere? b. What is the magnitude of the tension in the cord? FIGURE P24.53arrow_forwardA When we find the electric field due to a continuous charge distribution, we imagine slicing that source up into small pieces, finding the electric field produced by the pieces, and then integrating to find the electric field. Lets see what happens if we break a finite rod up into a small number of finite particles. Figure P24.77 shows a rod of length 2 carrying a uniform charge Q modeled as two particles of charge Q/2. The particles are at the ends of the rod. Find an expression for the electric field at point A located a distance above the midpoint of the rod using each of two methods: a. modeling the rod with just two particles and b. using the exact expression E=kQy12+y2 c. Compare your results to the exact expression for the rod by finding the ratio of the approximate expression to the exact expression. FIGURE P24.77 Problems 77 and 78.arrow_forwardThe infinite sheets in Figure P25.47 are both positively charged. The sheet on the left has a uniform surface charge density of 48.0 C/m2, and the one on the right has a uniform surface charge density of 24.0 C/m2. a. What are the magnitude and direction of the net electric field at points A, B, and C? b. What is the force exerted on an electron placed at points A, B, and C? FIGURE P25.47arrow_forward
- A sphere with a charge of 3.50 nC and a radius of 1.00 cm is located at the origin of a coordinate system. a. What is the electric field 1.75 cm away from the center of the sphere along the positive y axis? b. If a particle with a charge of 5.39 nC were placed at that location, what would be the electrostatic force on this charge?arrow_forwardA positively charged disk of radius R = 0.0366 m and total charge 56.8 C lies in the xz plane, centered on the y axis (Fig. P24.35). Also centered on the y axis is a charged ring with the same radius as the disk and a total charge of 34.1 C. The ring is a distance d = 0.0050 m above the disk. Determine the electric field at the point P on the y axis, where P is y = 0.0100 m above the origin. FIGURE P24.35 Problems 35 and 36.arrow_forwardFigure P24.51 shows four small charged spheres arranged at the corners of a square with side d = 25.0 cm. a. What is the electric field at the location of the sphere with charge +2.00 nC? b. What is the total electric force exerted on the sphere with charge +2.00 nC by the other three spheres? FIGURE P24.51arrow_forward
- (a) A charge of −335e is uniformly distributed along a circular arc of radius 4.20 cm, which subtends an angle of 44°. What is the linear charge density along the arc? _______C/m(b) A charge of −335e is uniformly distributed over one face of a circular disk of radius 2.15 cm. What is the surface charge density over that face? _________C/m2(c) A charge of −335e is uniformly distributed over the surface of a sphere of radius 2.15 cm. What is the surface charge density over that surface?______ C/m2(d) A charge of −335e is uniformly spread through the volume of a sphere of radius 2.15 cm. What is the volume charge density in that sphere? _______C/m3 (please include units so that I can follow the steps easier)arrow_forward(a) What total (excess) charge q must the disk in the figure have for the electric field on the surface of the disk at its center to have the magnitude 3.0 × 106 N/C, the E value at which air breaks down electrically, producing sparks? Take the disk radius as 3.0 cm. (b) Suppose each surface atom has an effective cross-sectional area of 0.015 nm2. How many atoms are needed to make up the disk surface? (c) The charge calculated in (a) results from some of the surface atoms having one excess electron. What fraction of these atoms must be so charged?arrow_forward(a) A charge -300e is uniformly distributed along a circular arc of radius 4.00 cm, which subtends an angle of 40.What is the linear charge density along the arc? (b) A charge -300e is uniformly distributed over one face of a circular disk of radius 2.00 cm.What is the surface charge density over that face? (c) A charge -300e is uniformly distributed over the surface of a sphere of radius 2.00 cm.What is the surface charge density over that surface? (d) A charge -300e is uniformly spread through the volume of a sphere of radius 2.00 cm. What is the volume charge density in that sphere?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
