
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: For the given
Concept introduction:
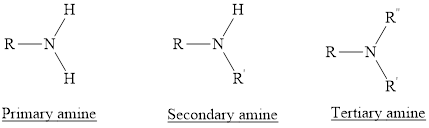
Amines are the hydrocabons which have nitrogen
(1) Primary Amines: The nitrogen atoms is substituted by one alkyl group and two hydrogen atoms are also attached to nitrogen atom is called as primary amine. For example,
(2) Secondary Amines: The nitrogen atoms is substituted by two alkyl groups and one hydrogen atom is also attached to nitrogen atom is called as secondary amine.
(3) Tertiary Amines: The nitrogen atoms is substituted by three alkyl groups and no hydrogen atom is attached to nitrogen atom is called as tertiary amine.
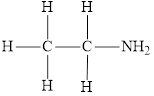
(a)
Answer to Problem 47PS
The molecular formula of the given amine is
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of the given amine can be written by using its given name ethylamine.
The ethyl group
Therefore molecular formula will have on ethyl group and two hydrogen atoms attached to nitrogen atom, that is
The structural formula for this amine is drawn as follows,

(b)
Interpretation: For the given amines structural formula has to be drawn and also their molecular formula has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Amines are the hydrocabons which have nitrogen
(1) Primary Amines: The nitrogen atoms is substituted by one alkyl group and two hydrogen atoms are also attached to nitrogen atom is called as primary amine. For example,
(2) Secondary Amines: The nitrogen atoms is substituted by two alkyl groups and one hydrogen atom is also attached to nitrogen atom is called as secondary amine.
(3) Tertiary Amines: The nitrogen atoms is substituted by three alkyl groups and no hydrogen atom is attached to nitrogen atom is called as tertiary amine.

(b)
Answer to Problem 47PS
The molecular formula of the given amine is
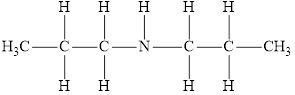
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of the given amine can be written by using its given name dipropylamine.
The two propyl groups
It is secondary amine as two alkyl groups are attached to nitrogen atom.
Therefore molecular formula will have two propyl groups and one hydrogen atom attached to nitrogen atom, that is
The structural formula for this amine is drawn as follows,

(c)
Interpretation: For the given amines structural formula has to be drawn and also their molecular formula has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Amines are the hydrocabons which have nitrogen
(1) Primary Amines: The nitrogen atoms is substituted by one alkyl group and two hydrogen atoms are also attached to nitrogen atom is called as primary amine. For example,
(2) Secondary Amines: The nitrogen atoms is substituted by two alkyl groups and one hydrogen atom is also attached to nitrogen atom is called as secondary amine.
(3) Tertiary Amines: The nitrogen atoms is substituted by three alkyl groups and no hydrogen atom is attached to nitrogen atom is called as tertiary amine.

(c)
Answer to Problem 47PS
The molecular formula of the given amine is
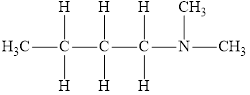
Explanation of Solution
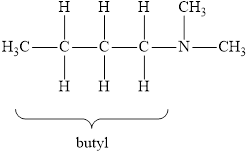
The molecular formula of the given amine can be written by using its given name butyl dimethylamine.
The two methyl groups
It is tertiary amine as three alkyl groups are attached to nitrogen atom.
Therefore molecular formula will have two methyl groups, one butyl group and no hydrogen atom attached to nitrogen atom, that is
The structural formula for this amine is drawn as follows,
(d)
Interpretation: For the given amines structural formula has to be drawn and also their molecular formula has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Amines are the hydrocabons which have nitrogen
(1) Primary Amines: The nitrogen atoms is substituted by one alkyl group and two hydrogen atoms are also attached to nitrogen atom is called as primary amine. For example,
(2) Secondary Amines: The nitrogen atoms is substituted by two alkyl groups and one hydrogen atom is also attached to nitrogen atom is called as secondary amine.
(3) Tertiary Amines: The nitrogen atoms is substituted by three alkyl groups and no hydrogen atom is attached to nitrogen atom is called as tertiary amine.

(d)
Answer to Problem 47PS
The molecular formula of the given amine is
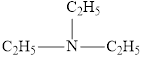
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of the given amine can be written by using its given name triethylamine.
The three ethyl groups
It is tertiary amine as three alkyl groups are attached to nitrogen atom.
Therefore molecular formula will have three ethyl groups, no hydrogen atom attached to nitrogen atom, that is
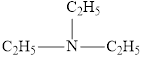
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
- indicates the structure of the acyl chloride and the amine that was used to prepare the compound N-dimethylbenzamidearrow_forwardDraw all the possible amide isomers with C3H7NO molecular formula.arrow_forwardDraw the structures for the four amines of molecular formula C 3H 9N. Give the systematic name for each amine.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co



