
Concept explainers
Sustainable Use of Horseshoe Crabs Horseshoe crab blood clots immediately upon exposure to bacterial toxins, so it can be used to test injectable drugs for the presence of dangerous bacteria. To keep horseshoe crab populations stable, blood is extracted from captured animals, which are then returned to the wild. Concerns about the survival of animals after bleeding led researchers to do an experiment. They compared survival of animals captured and maintained in a tank with that of animals captured, bled, and kept in a similar tank. FIGURE 24.28 shows the results.
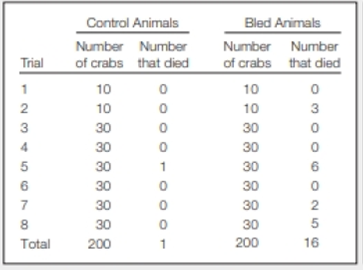
FIGURE 24.28 Mortality of young male horseshoe crabs kept in tanks during the 2 weeks after their capture. Half the animals were bled on the day of their capture. Control animals were handled, but not bled. This procedure was repeated 8 times with different sets of horseshoe crabs.
In which trial did the most control crabs die? In which did the most bled crabs die?
To explain: The trial in which the most control crabs died.
Introduction: Horseshoe crabs belong to the Phylum Arthropod. They are normally found around shallow ocean waters. Horseshoe crabs are living fossils. The horseshoe crabs though they look like crustaceans are marine arachnids.
Explanation of Solution
The uniqueness of horseshoe crabs is that they clot upon encountering bacteria. Therefore, they are used in experiments where highly virulent bacteria are involved. The blood of horseshoe crabs is taken and then let out in their habitat in order to conserve their population, but this might also lead to their death. Therefore, experiments were conducted to check their survival after taking their blood.
In trial 5, the number of control crabs is 30, and 1 crab died out of it.
The trial group 5 marked the highest number of control crabs that died.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Concepts and Investigations
MARINE BIOLOGY
Biology Illinois Edition (Glencoe Science)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
HUMAN ANATOMY
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
- Sustainable Use of Horseshoe Crabs Horseshoe crab blood clots immediately upon exposure to bacterial toxins, so it can be used to test injectable drugs for the presence of dangerous bacteria. To keep horseshoe crab populations stable, blood is extracted from captured animals, which are then returned to the wild. Concerns about the survival of animals after bleeding led researchers to do an experiment. They compared survival of animals captured and maintained in a tank with that of animals captured, bled, and kept in a similar tank. FIGURE 24.28 shows the results. FIGURE 24.28 Mortality of young male horseshoe crabs kept in tanks during the 2 weeks after their capture. Half the animals were bled on the day of their capture. Control animals were handled, but not bled. This procedure was repeated 8 times with different sets of horseshoe crabs. Based on these results, would you conclude that bleeding harms horseshoe crabs more than capture alone does?arrow_forwardSustainable Use of Horseshoe Crabs Horseshoe crab blood clots immediately upon exposure to bacterial toxins, so it can be used to test injectable drugs for the presence of dangerous bacteria. To keep horseshoe crab populations stable, blood is extracted from captured animals, which are then returned to the wild. Concerns about the survival of animals after bleeding led researchers to do an experiment. They compared survival of animals captured and maintained in a tank with that of animals captured, bled, and kept in a similar tank. FIGURE 24.28 shows the results. FIGURE 24.28 Mortality of young male horseshoe crabs kept in tanks during the 2 weeks after their capture. Half the animals were bled on the day of their capture. Control animals were handled, but not bled. This procedure was repeated 8 times with different sets of horseshoe crabs. Looking at the overall results, how did the mortality of the two groups differ?arrow_forwardSCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY, AND SOCIETY Imagine that you are a graduate student working with university scientists on the effects on sea turtles of the 2010 oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico. What technologies might you employ to collect data for your research? Knowing that the turtles life cycle includes laying eggs on beaches, how would you involve local communities in your research?arrow_forward
- Discuss Concepts Many city-dwellers have noted that the density of cockroaches in apartment kitchens appears to vary with the habits of the occupants: people who wrap food carefully and clean their kitchen frequently tend to have fewer arthropod roommates than those who leave food on kitchen counters and clean less often. Interpret these observations from the viewpoint of a population ecologist.arrow_forwardHow would you apply this in a Lamarckian explanation? Tiger Moths (Bertholdia trigona) produce high pitched ultrasonic clicking (at a rate of 4500 clicks/sec) when they hear the echolocation calls of bats (bats eat moths). As a result, the bat's sonar is jammed and the Tiger Moth escapes without being caught, killed, and eaten. Please use your knowledge of Evolution by Natural Selection to explain the process by which this remarkable anti-predator defense evolved in Tiger Moths. Please use your Knowledge of Evolution by Natural Selection to explain the process by which this remarkable anti-predator defense evolved in Tiger Moths.arrow_forwardBats mostly hunt insects at night. They are able to determine the distance and speed of any prey they are chasing, which has helped them to become excellent nocturnal predators. One potential prey, the tiger moth, has developed two separate methods of evading predation. First, tiger moths emit a toxin that is distasteful to bats, birds, and most other vertebrate predators. Second, they use an organ called a "tymbal" to create a series of high-pitched clicks that only bats can hear, and which identify the tiger moths as something the bats don't like to eat. Bats who prey on tiger moths discover they don't taste very good, learn to identify tiger moths by their clicks, and avoid eating them. Use this information to answer the questions below. Question 1: The scenario above describes a distinct evolutionary interaction. What is it?Can you explain? Question 2: Why is it necessary for the moth to produce both a tymbal click and a toxin? Why not just a toxin? Do you think there are…arrow_forward
- Zoology experiment: The Predator-prey Interactions Between Zebrafish and Daphnia1. Six 1-L beakers were filled with aged tap water.2. To test the effect of light on the survival of Daphnia, the 6 beakers were divided equally into 2 treatments: light & dark. Beakers assigned to the dark treatment were covered w/ aluminum foil.3. One zebrafish (about 2-3 cm) starved for 24 hours was placed in each beaker.4. Fifty (50) Daphnia sp. individuals were added in each beaker containing the starved zebrafish. The top of the beakers assigned to the dark treatment were covered with aluminum foil.5. One hour after, the zebra fish was scooped out & the no. of surviving Daphnia in each set-up were counted. How did light exposure affect the survival of Daphnia when exposed to a predator? Are the results consistent with your expectations? Relate this to your hypothesis & explain. answer.arrow_forward24) Captive breeding would be effective in helping all of the following threatened species recover except Group of answer choices the peregrine falcon. the bald eagle. the northern spotted owl. the grey wolf.arrow_forwardCetaceans give birth to few well-developed calves at well-spaced intervals. They also feed and protect the calves for long periods. This is insharp contrast to most fishes, in which many eggs are spawned and theparents spend no time feeding and protecting the offspring. What do youthink is the best strategy? Has this strategy paid off in the great whales?arrow_forward
- . In the summer of 2000, only 10 percent of the lobster population in Long Island Sound survived after a massive die-off. Many lobstermen in New York and Connecticut lost small businesses that their families had owned for generations. Some believe the die-off followed heavier sprays of pesticides to control mosquitoes that carry the West Nile virus. Explain why a chemical substance that targets mosquitoes might also harm lobsters but not fish.arrow_forwardIntroduction The Rock Pocket Mouse The rock pocket mouse, Chaetodipus intermedius, is a small, nocturnal animal found in the deserts of thesouthwestern United States. Most rock pocket mice have a sandy, light-colored coat that enables them to blendin with the light color of the desert rocks and sand on which they live. However, populations of primarily dark-colored rock pocket mice have been found living in areas where the ground is covered in a dark rock calledbasalt caused by geologic lava flows thousands of years ago. Scientists have collected data from a population ofprimarily dark-colored mice living in an area of basalt called the Pinacate lava flow in Arizona, as well as from anearby light-colored population. Researchers analyzed the data from these two populations in search of thegenetic mutation responsible for the dark coat color. Their analyses led to the discovery of a mutation in theMc1r gene that is involved in coat-color determination. The MC1R Gene Two pigments…arrow_forwardConsider the figure attached. A student in a course on intelligent design theory claims that the graph in part (a) shows that losing the ability to respire actually is adaptive for yeast cells living in small populations. Please read the incomplete sentence that appears immediately below, assess as possible completions the lowercase-Roman-numeral-labelled statements that follow, and click each uppercase-letter-labelled response that is presented below and completes accurately the sentence. An astute student in an evolution course would respond that i. the graph in part (a) shows that selection among mitochondria within yeast cells can lead to fixation for traits that decrease mean fitness for that yeast population. ii. the student in the course on intelligent design is wrong; the yeast cells in the small population group retained completely the ability to respire, as they otherwise would have been unable to harvest energy. iii. a property (e.g., inability to respire) that is…arrow_forward
 Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





