
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305580350
Author: William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 24, Problem 24.25P
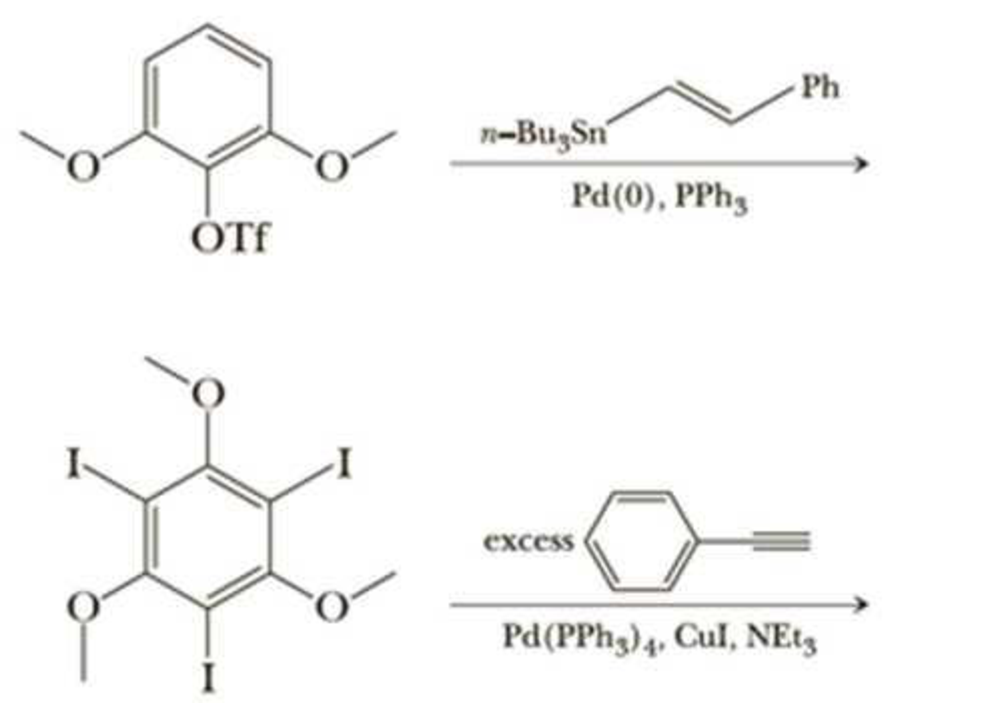
It is typically very difficult to do a substitution reaction on an
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Aldehydes undergo nucleophilic addition reactions with potent nucleophiles such as water, alcohol and amino compounds. Which of the following nucleophiles will exhibit the greatest ability to attack the electrophilic carbon in the carbonyl group of ethanal?
Group of answer choices
cyclohexyl alcohol
para-chlorophenol
isoamyl alcohol
ortho-aminophenol
An aromatic ring should satisfy Huckel’s rule, wherein the number of electrons participating in the cyclic conjugation should be equal to 4n + 2. Which of the following cyclic structures does NOT obey Huckel’s rule?
Group of answer choices
Cyclobutadienyl dianion
Tetrahydrofuran ring
Cyclopropene structure
Pyrimidine ring structure
Investigate the mechanism and reaction condition via which carbon side chains can be introduced into an aromatic ring via an electrophilic aromatic substitution process?
Alkyl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution and elimination reactions. When the kinetics of the reaction are measured, if the rate of the reaction is found to be dependent only upon the concentration of the alkyl halide the reaction is first order. The substitution reaction is thus termed SN1, and the elimination reaction is termed E1. These reactions are unimolecular and occur in two steps. The first step is rate-limiting and involves the loss of the leaving group to form a carbocation. In the second, fast, step the nucleophile adds to the carbocation in the SN1 reaction or elimination occurs to give an alkene in the E1 reaction. Because the carbocation is planar, the nucleophile can add to either face and therefore racemization is usually observed although solvent effects can influence this somewhat. E1 elimination follows Zaitsev’s rule and typically yields the most substituted alkene as the major product.
Conditions which favor the SN1/E1 pathway include the use of a weak…
Chapter 24 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 24.3 - Prob. 24.1PCh. 24.3 - Prob. 24.2PCh. 24.4 - Prob. 24.3PCh. 24.5 - Show how the following compound can be prepared...Ch. 24.5 - Prob. 24.5PCh. 24.5 - Prob. 24.6PCh. 24.6 - Prob. 24.7PCh. 24 - Prob. 24.8PCh. 24 - Prob. 24.9PCh. 24 - Prob. 24.10P
Ch. 24 - Treatment of cyclohexene with iodobenzene under...Ch. 24 - Prob. 24.12PCh. 24 - Prob. 24.13PCh. 24 - The aryl diene undergoes sequential Heck reactions...Ch. 24 - Heck reactions take place with alkynes as well as...Ch. 24 - Prob. 24.16PCh. 24 - The following transformation involves a series of...Ch. 24 - Show the sequence of Heck reactions by which the...Ch. 24 - Prob. 24.19PCh. 24 - Write the steps that are critical in the following...Ch. 24 - Prob. 24.21PCh. 24 - Prob. 24.22PCh. 24 - Prob. 24.23PCh. 24 - Show how the following compound could be prepared...Ch. 24 - It is typically very difficult to do a...Ch. 24 - The compound eutypine is an antibacterial agent...Ch. 24 - Prob. 24.27PCh. 24 - Prob. 24.28PCh. 24 - Prob. 24.29PCh. 24 - Prob. 24.30PCh. 24 - Prob. 24.31PCh. 24 - Prob. 24.32PCh. 24 - Prob. 24.33PCh. 24 - The following transformation can be accomplished...Ch. 24 - Prob. 24.35PCh. 24 - Prob. 24.36PCh. 24 - Prob. 24.37PCh. 24 - Prob. 24.38PCh. 24 - E. J. Coreys 1964 total synthesis of...Ch. 24 - Prob. 24.40P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Alkyl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution and elimination reactions. When the kinetics of the reaction are measured, if the rate of the reaction is found to be dependent only upon the concentration of the alkyl halide the reaction is first order. The substitution reaction is thus termed SN1, and the elimination reaction is termed E1. These reactions are unimolecular and occur in two steps. The first step is rate-limiting and involves the loss of the leaving group to form a carbocation. In the second, fast, step the nucleophile adds to the carbocation in the SN1 reaction or elimination occurs to give an alkene in the E1 reaction. Because the carbocation is planar, the nucleophile can add to either face and therefore racemization is usually observed although solvent effects can influence this somewhat. E1 elimination follows Zaitsev’s rule and typically yields the most substituted alkene as the major product. Conditions which favor the SN1/E1 pathway include the use of a weak…arrow_forwardso we know that fischer esterification is a type of organic reaction that involves the formation of an ester from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst. am I correct to assume that a fisher esterification mechanism would look different than the above nucleophilic addition reaction? If they are different you you present the Fisher esterification mechanism of the reaction of acetic acid with pentanol in the presence of an acid catalyst, sulfuric acid and explain the mechanismarrow_forwardDetermine which nucleophilic aromatic substitutions are likely, and proposemechanisms for both the addition–elimination type and the benzyne type.arrow_forward
- Indicate the following statement as true/false. Groups that donate electrons to the ring are formed in a shorter time under mild conditions, increasing the electron density of the ring. Some of the groups pre-bonded to an aromatic ring cause electrophilic aromatic substitution to occur mainly at the ortho and para sites. Others lead to the meta location. Groups that donate electrons to the ring are formed in a shorter time under mild conditions, increasing the electron density of the ring.arrow_forwardDraw the products of each of the following reactions and indicate whether the reaction occurs by: a) Aromatic electrophilic substitution, b) Aromatic nucleophilic substitution: Addition elimination, c) Aromatic nucleophilic substitution: Mechanism of benzene:arrow_forwardAldehydes undergo nucleophilic addition reactions with potent nucleophiles such as water, alcohol and amino compounds. Which of the following nucleophiles will exhibit the greatest ability to attack the electrophilic carbon in the carbonyl group of ethanal? cyclohexyl alcohol para-chlorophenol isoamyl alcohol ortho-aminophenol An aromatic ring should satisfy Huckel’s rule, wherein the number of electrons participating in the cyclic conjugation should be equal to 4n + 2. Which of the following cyclic structures does NOT obey Huckel’s rule? Cyclobutadienyl dianion Tetrahydrofuran ring Cyclopropene structure Pyrimidine ring structure What is the role of H • ions in the nucleophilic substitution of alcohols usinghydrogen halides? Removal of an alkyl groupProtonation of -OH groupStabilization of carbocationActivation of oxygen radicalarrow_forward
- Given that five isomeric compounds (A, B, C, D, E) with the molecular formula C5H10O were subjected to chemical tests after undergoing Clemmensen reduction compounds A,B, and C all yielded n-pentane, the results of these tests are provided in the table below. Can you draw the structures of compounds A to E based on the outcomes of the chemical tests?arrow_forwardA problem often encountered in the oxidation of primary alcohols to acids is that esters are sometimes produced as by-products. For example, oxidation of ethanol yields acetic acid and ethyl acetate: Propose a mechanism to account for the formation of ethyl acetate. Take into account the reversible reaction between aldehydes and alcohols:arrow_forwardThe formation of the following cyclic compound has been observed in the hydration of the following alkene, write a mechanism that explains the product.arrow_forward
- Draw the structural formula of the alkene that reacts with ozone followed by dimethyl sulfide to give product or set of products.arrow_forwardFor the following reaction scheme, identify by drawing the reagents b and d and the intermediate c that are formed in the synthesis of benzoic acid.arrow_forwardName, draw and describe the organic product of the reaction between 2-methylbut-1-ene and H2O in the presence of H2SO4 and provide a clear rationale as to why this is the major product of the reaction.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Alcohols, Ethers, and Epoxides: Crash Course Organic Chemistry #24; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j04zMFwDeDU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY