
Concept explainers
- a. The isoelectric point (pl) of phenylalanine is pH 5.5. Draw the structure of the major form of phenylalanine at pH values of 1, 5.5, and 11.
- b. The isoelectric point of histidine is pH 7 6. Draw the structures of the major forms of histidine at pH values of 1, 4, 7.6, and 11. Explain why the nitrogen in the histidine ring is a weaker base than the α-amino group.
- c. The isoelectric point of glutamic acid is pH 3.2. Draw the structures of the major forms of glutamic acid at pH values of 1,3.2, 7, and 11. Explain why the side-chain
carboxylic acid is a weaker acid than the acid group next to the α-carbon atom.
(a)
Interpretation:
The structures of the major form of phenylalanine at
Concept introduction:
The more acidic strength increases the formation of the hydrogen ions and decreases the
Answer to Problem 24.27SP
The structures of the major form of phenylalanine at
Explanation of Solution
The structures of the major forms of phenylalanine at
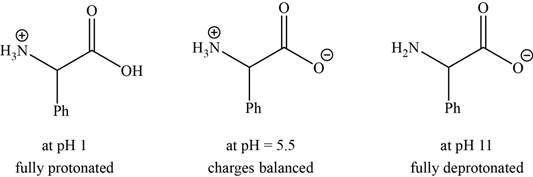
Figure 1
It is conferred from the above reaction that phenylalanine at
(b)
Interpretation:
The structures of the major forms of histidine at
Concept introduction:
The more acidic strength increases the formation of the hydrogen ions and decreases the
Answer to Problem 24.27SP
The structures of the major forms of histidine at
Explanation of Solution
The structures of the major forms of histidine at
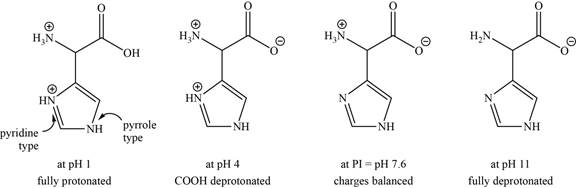
Figure 2
It is conferred from the above reaction that histidine at
(c)
Interpretation:
The structures of the major forms of glutamic acid at
Concept introduction:
The more acidic strength increases the formation of the hydrogen ions and decreases the
Answer to Problem 24.27SP
The structures of the major forms of glutamic acid at
Explanation of Solution
The structures of the major forms of glutamic acid at
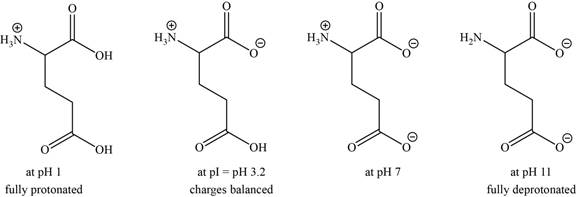
Figure 3
It is conferred from the above reaction that glutamic acid at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (9th Edition)
- (a) The isoelectric point (pI) of phenylalanine is pH 5.5. Draw the structure of the major form of phenylalanine at pHvalues of 1, 5.5, and 11.(b) The isoelectric point of histidine is pH 7.6. Draw the structures of the major forms of histidine at pH values of 1, 4,7.6, and 11. Explain why the nitrogen in the histidine ring is a weaker base than the a-amino group.(c) The isoelectric point of glutamic acid is pH 3.2. Draw the structures of the major forms of glutamic acid at pH valuesof 1, 3.2, 7, and 11. Explain why the side-chain carboxylic acid is a weaker acid than the acid group next to thea-carbon atomarrow_forwardConsider the amino acid and its pKa values:Lysine: pKa1= 2.18 pKa2= 8.95, pKaR=10.79 a. Calculate the isoelectric point.b. What will be the net charge on lysine at the isoelectric point?c. In what direction will the lysine move when placed in an electric field at a pH value of 6.68d. Which form of the lysine is the least soluble in water?e. Draw the structure of the lysine which is the least soluble in water?arrow_forwardThe amino acid His is triprotic with pK1 (α-COOH) = 1.82, pK2 (α-NH3+) = 9.17, and pK3 (side chain) = 6.00. What is the net charge on His at pH 8?arrow_forward
- a) A solution of amino acid having carboxylic side chain was titrated against NaOH. If initial pH of the solution was 2.8. Describe the state of the functional groups of the amino acid at the initial pH and at 10.5.b) Briefly explain how you will separate amino acids mixture using the charge difference between the amino acids. c) A given glycine solution was titrated against NaOH and pH of the final solution was 4.8. Given that pKa1 and pKa2 of glycine are 2.34 and 9.60, respectively. Calculate the concentration of the dissociated amino acid in terms of the undissociated amino acid, if [x] and [y] are the concentrations of dissociated and undissociated amino acid, respectively.arrow_forwardThe pKa values for the amino and carboxyl groups of alanine are 9.69 and 2.35, respectively. Calculate the pH of 10 mL of 50 mM alanine buffer (pH 10) following the addition of: a. 0.1 mL of 1.5 M HCl b. 0.3 mL of 1.5 M HClarrow_forward10. Use the information in the table below to draw the structure of the predominant form of each amino acid at physiological pH (pH = 7.4) R side chain pKa (a-COOH) -CH₂CH(CH3)2 -(CH2)4NH2 -(CH2)2CO2H Amino acid Leucine Lysine Glutamic acid L-leucine L-lysine L-glutamic acid 2.36 2.18 2.19 pKa (α-NH3*) pKa (side chain) 9.60 8.95 9.67 10.79 4.25arrow_forward
- At very low pH, alanine is a diprotic acid that can be represented as H3N1-CH(CH3)-COOH. The pKa of the carboxyl group is 2.3, and the pKa of the UNH1 3 group is 9.7.(a) At pH 7, what fraction of the amino acid molecules dissolved in an aqueous solution will have the form H3N1-CH(CH3)-COO2?(b) What fraction of the molecules at this pH will havethe form H2N-CH(CH3)-COOH?arrow_forwardArginine has pka values of 2.1, 9, and 12.1. It is abbrevaited as H3A±. Calculate pH of 0.02 M solution of arginine added as sodium salt NaHA.Does this answer make sense, why or why not.arrow_forward(a) One amino acid that is likely to have a net negative charge at pH 8.(b) One amino acid that may be dehydrated with H2SO4.(c) One polar uncharged amino acid. (d) One nonpolar aromatic amino acid.(e) The nonpolar amino acid with the highest molar mass that was not previously selected.arrow_forward
- Draw the peptide CHEMISTRY. a. What is the full name and 3-letter abbreviation of this peptide? b. Give the different forms (charges) of the peptide as it is titrated from pH 1.5 until pH 12.0. c. What is the isoelectric point of the peptide?arrow_forwardMark the TRUE alternative for the following peptide: a) For a pH of 7.0 this peptide will migrate to the anode. b) This peptide will have a basic nature. c) For a pH of 5.5 this peptide will migrate to the cathode. d) For a pH of 4.0 the predominant species will have a negative charge. e) This peptide will have an isoelectric point equal to 6.0.arrow_forward1. (a) Draw a circle around one amino acidin the structure. ( b) Draw a box around one amino acid side chain. (c) Indicate whether the side chain you chose is hydrophobic or hydrophilic. (d) Draw an arrow pointing to a peptide bond 2. If the peptide segment shown above was part of a beta sheet, which of its functional groups would be involved in forming and stabilizing the beta sheet? 3. Which amino acid (also called amino acid residue)would be more likely to occur on the surface of a protein: an aspartate residue or a methionine residue? Explain your choice.arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,

