
Concept explainers
A dosed surface with dimensions a = b= 0.400 111 and c = 0.600 in is located as shown in Figure 1*24.63. The left edge of the closed surface is located at position x = a. The electric field throughout the region is non- uniform and is given by
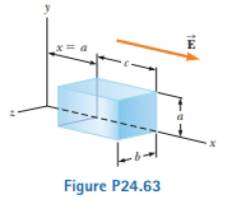
(a)
The net electric flux leaving the closed surface.
Answer to Problem 24.63CP
The net electric flux leaving the closed surface is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The dimensions of the closed surface are
The position of the closed surface is,
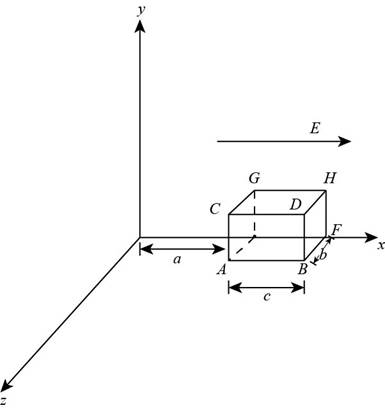
Figure (1)
From the figure (1) the electric field is perpendicular to the normal of area ABEF, area CDHG, area ABCD and the area EFGH. Therefore,
The formula to calculate electric flux is,
Here,
The electric field makes an angle
Substitute
Thus, the flux out of the surface ABEF, CDHG, ABCD and EFGH is zero for the surfaces.
From figure (1), the area of the surface ACGE is,
From figure (1), the area of the surface BFDH is,
The electric flux in the
From figure (1), substitute
From Figure (1), substitute
The net flux leaving closed surface,
Here,
Substitute
Simplify the above equation.
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the net electric flux leaving the closed surface is
(b)
The net charge enclosed by the surface.
Answer to Problem 24.63CP
The net charge enclosed by the surface is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The dimensions of the closed surface are
The flux enclosed by a closed surface is given by,
Here,
The permittivity of free space is
Substitute
Rearrange the above equation for
Conclusion:
Therefore, the net charge enclosed by the surface is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
- What is the electric flux through a 8.0 m x 2.0 m plane that has an area vector which is at a 78 degree angle to a uniform electric field of magnitude 5.6×106N/C?arrow_forwardAn electric flux of 144 N.m2/C passes through a flat horizontal surface that has an area of 0.72 m2. The flux is due to a uniform electric field. What is the magnitude of the electric field if the field points 15o above the horizontal?arrow_forwardA flat sheet is in the shape of a rectangle with sides of lengths 0.450 m and 0.675 m. The sheet is immersed in a uniform electric field of magnitude 75.0 N/C that is directed at 20 from the plane of the sheet. Find the magnitude of the electric flux through the sheet.arrow_forward
- What is the flux due to electric field E = 3 × 103,NC−1 through side of the square 10cm , when it is held parallel to E?arrow_forwardFind the flux through the top, left, and rights sides of a cube of side 0. 3 m when placed in a horizontal uniform electric field of 8.0 N/C directed to the right.arrow_forwardIn a symmetrical electric field of 58.3 x 101 N/C , a flat circle with a diameter of 30 cm is positioned. When the circle's face is perpendicular to the field lines, what is the electric flux through it?arrow_forward
- A uniform electric field with a magnitude of 1.25x105 N/C passes through a rectangle with sides of 2.50 m and 5.0 m . If the electric flux through the rectangle is 6.6x105 Nm2/C , find the angle between the electric field vector and the vector normal to the rectangular surface ?arrow_forwardIn free space, let D = 8xyz4ax + 4x2z4ay + 16x2yz3 az pC/m2.Find the total electric flux passing through the rectangularsurface z = 2, 0 < x < 2, 1 < y < 3, in the az direction. Find Eat P(2, −1, 3).arrow_forwardIf the electric field is given by 6i+3j+4k calculate the electric flux through a surface of area 20 units lying in y-z plane.arrow_forward
- Consider the uniform electric field E = (3.0ĵ + 7.0) ✕ 103 N/C. (a) What is its electric flux (in N · m2/C) through a circular area of radius 2.3 m that lies in the yz-plane? (Enter the magnitude.) (b) What is its electric flux (in N · m2/C) through a circular area of radius 2.3 m that lies 45.0° above the xy-plane? (Assume that the unit normal vector is n̂ = 1/(2)1/2(î+k). )arrow_forwardGiven that Q=8.4 μC, find the electric flux passing through surface S4.arrow_forwardA circular surface with a radius of 0.066 m is exposed to a uniform electric field of magnitude 1.90 × 104 N/C. The electric flux through the surface is 52 N·m2/C. What is the angle between the direction of the electric field and the normal to the surface?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
