
Concept explainers
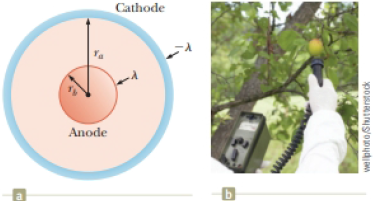
A Geiger–Mueller tube is a
(b) Show that the magnitude of the electric field in the space between cathode and anode is
where r is the distance from the axis of the anode to the point where the field is to be calculated.
Figure P24.42
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 24 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
- A glass sphere with radius 4.00 mm, mass 85.0 g, and total charge 4.00 C is separated by 150.0 cm from a second glass sphere 2.00 mm in radius, with mass 300.0 g and total charge 5.00 C. The charge distribution on both spheres is uniform. If the spheres are released from rest, what is the speed of each sphere the instant before they collide?arrow_forwardA simple pendulum has a small sphere at its end with mass m and charge q. The pendulums rod has length L and its weight is negligible. The pendulum is placed in a uniform electric field of strength E directed vertically upward. What is the period of oscillation of the sphere if the electric force is less than the gravitational force on the sphere? Assume the oscillations are small. FIGURE P24.63arrow_forwardA very long, thin wire fixed along the x axis has a linear charge density of 3.2 C/m. a. Determine the electric field at point P a distance of 0.50 m from the wire. b. If there is a test charge q0 = 12.0 C at point P, what is the magnitude of the net force on this charge? In which direction will the test charge accelerate?arrow_forward
- A thin wire with linear charge density =0y0(14+1y) extends from y0 = 1.00 m to infinity. If 0 = 1.45 105 C/m, what is the magnitude of the electric field due to this wire at the origin (y is measured in meters)?arrow_forwardA charged rod is curved so that it is part of a circle of radius R (Fig. P24.32). The excess positive charge Q is uniformly distributed on the rod. Find an expression for the electric field at point A in the plane of the curved rod in terms of the parameters given in the figure.arrow_forwardA positively charged disk of radius R = 0.0366 m and total charge 56.8 C lies in the xz plane, centered on the y axis (Fig. P24.35). Also centered on the y axis is a charged ring with the same radius as the disk and a total charge of 34.1 C. The ring is a distance d = 0.0050 m above the disk. Determine the electric field at the point P on the y axis, where P is y = 0.0100 m above the origin. FIGURE P24.35 Problems 35 and 36.arrow_forward
- What are the magnitude and direction of a uniform electric field perpendicular to the ground that is able to suspend a particle of mass m = 2.00 g carrying a charge of +6.00 C in midair, assuming gravity and the electrostatic force are the only forces exerted on the particle?arrow_forwardA solid sphere of radius R has a spherically symmetrical, nonuniform volume charge density given by (r) = A/r, where r is the radial distance from the center of the sphere in meters, and A is a constant such that the density has dimensions of M/L3. Sketch a graph of the magnitude of the electric field as a function of distance for 0 r 3R.arrow_forwardA nonconducting wall carries charge with a uniform density of 8.15 µC/cm2. (a) What is the electric field 6.35 cm in front of the wall if 6.35 cm is small compared with the dimensions of the wall? magnitude: ____________ N/C direction: toward the wall or away from the wall? (b) Does your result change as the distance from the wall varies? (Assume that the distance from the wall is small compared to the width and height of the wall.) Explain.arrow_forward
- A laboratory has a region with a constant E = 1000N / C electric field in the vertical direction. A proton is thrown into this region at h = 1 m above the ground and with a horizontal velocity Vo = 106 m / s.a. What is the acceleration of the proton in the electric field region?b. What is the horizontal range (L) of the proton?c.How long does the proton cross the electric fieldThe mass of the proton is mp = 1.7x10-27kg, and its charge is qp = 1.6x10-19C.Neglect the force of gravity.arrow_forwardA device used to detect ionizing radiation consists of a thin positively charged wire surrounded by a concentric cylindrical conducting shell with an equal amount of negative charge on the outer shell. The length of the cylinder and the wire is 16 cm and the radius of the cylinder is of 1.4 cm. The wire at the center has negligible thickness. The electric field at the cylinders inner wall is 2.9 x 104 N/ A) Draw a diagram of the device labeling the direction ofthe electric field. B) Calculate the total charge on the central wire. C) Calculate the flux of electric field at the cylinders wall. D) If an electron were to become free at the outer cylinders wall, calculate the magnitude of acceleration the electron would initially experience.arrow_forwardA uniformly charged disk with radius R = 35.0 cm and uniform charge density ? = 7.10 ✕ 10−3 C/m2 lies in the xy-plane, with its center at the origin. What is the electric field (in MN/C) due to the charged disk at the following locations? (a) z = 5.00 cm MN/C (b) z = 10.0 cm Use the equation for the electric field for a disk derived in the textbook. MN/C (c) z = 50.0 cm MN/C (d) z = 200 cm MN/Carrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
