
Concept explainers
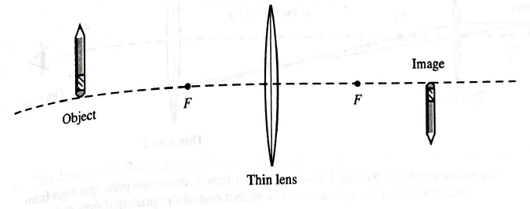
Reproduced below is a side view diagram of the situation described in section II of the tutorial.
Determine an expression for the lateral magnification,
To calculate:.
The expression for the lateral magnification
Answer to Problem 1TH
The expression for the lateral magnification is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
An object is placed before a thin lens as follows :
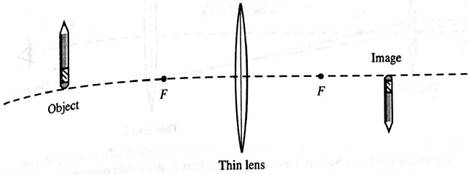
Formula used :
In similar triangles ABC and DEF , corresponding sides are in equal proportions or,
AB / BC = DE / EF
AB / AC = DE /DF
Calculation:
Ray diagram showing the principal ray from the tip of pencil that is object, is given below;
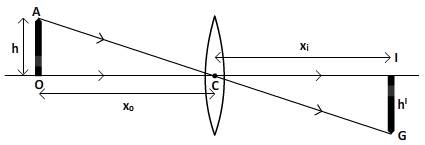
In the above diagram, two triangles given that are
are similar.
So that,
Here,
And,
Therefore,
Hence, lateral magnification is given below;
Conclusion:
Therefore, the lateral magnification,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
University Physics Volume 1
Sears And Zemansky's University Physics With Modern Physics
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
- As shown, what happens to the image point I as the object point O moves toward the right-hand surface of the material of index of refraction n1? (a) It always remains between O and the surface, arriving at the surface just as Odoes. (b) It moves toward the surface more slowly than O so that eventually O passes I. (c) It approaches the surface and then moves to the right of the surface.arrow_forwardCase 7: Consider the case of an object (draw yourself on the diagram, an arrow erect on the optical axis) located at d0 > 2F'. Draw the following rays in the figure: ray parallel to the optical axis, focal ray, central ray, draw the image of the arrow, indicate in the same figure from where to where di is (image-lens distance). Don't forget to put the direction on each ray, both the incident rays and the transmitted rays. Image characteristics for case 7: object located at d0 > 2F'. Choose the ones that apply: a) Virtual b) Real c) Inverted d) Increased e) No image is formed f) Equal size g) Reduced h) Erect Case 10: Consider the case of an object (draw yourself on the diagram, an arrow erect on the optical axis) located within the focus F', that is do < F'. Draw the following rays in the figure: ray parallel to the optical axis, focal ray, central ray, draw the image of the arrow, indicate in the same figure from where to where di is (image-lens distance). Don't forget to…arrow_forwardin step 1 why is the image distance -4 cm?arrow_forward
- If the radius of curvature of the mirror in diagram A is 15 cm and the object which is 10 cm long is placed 20 cm away from the mirror, then the location of the image is 12 cm and the size of the image is 6 cm. 1. What is the location of the image? (between F and C, at C etc.) 2. What is the orientation of the image? (inverted or upright) 3. What is the size of the image? (reduced, same, bigger) 4. What is the type of the image? (real or virtual)arrow_forwardDraw a ray diagram for each of the following, and then draw the image formed. Please provide complete labels in the diagrams, as well as the size, orientation, type, and position of the image. You can also opt to only answer number 3 if all is not allowed. Thank you so much! 1. Object location at 2F’ 2. Object location at F’ 3. Object location beyond 2F’arrow_forward1.Place your object at a distance equal to the focal length (f) of your diverging lens. Where is your image located? Describe the type of image formed based on size, orientation, and condition and provide a screenshot of your set-up. 2.Place your object at a distance less than the focal length (f) of your diverging lens. Where is your image located? Describe the type of image formed based on size, orientation, and condition and provide a screenshot of your set-up.arrow_forward
- Thank you so much in advance. The diagram shows a lens with a positive focal length 11 cm. (a) If we place an object at a distance of 25 cm from the lens, where will the resulting image position on the other side of the lens be found? Include units in answer, (b) With the object at 25 cm from the lens, what will the magnification be for the image at this position? (c) If we place an object at a distance of 4 cm from the lens, where will the resulting image position be found? (d) With the object at 4 cm from the lens, what will the magnification be for the image at this position?arrow_forwardCan you answer part c of problem 1 in the image?arrow_forwardTwo convex lenses which share a common principal axis are separated by a distance which is greater than the sum of their focal lengths, as shown. Part (a) An object is placed a distance do,1=22 cm to the left of lens 1 which has focal length F1=4.2 cm. Ignore the existence of lens 2 for the moment. What is the position of the image, di,1 created by lens 1? Include the sign which is consistent with standard sign conventions. Part (b) Calculate the magnification, M1, of lens 1 for the object as positioned in the previous step. Be certain to include the sign that is consistent with the standard conventions. Part (c) Which statement best describes the image created by lens 1? Part (d) Lens 2 is placed a distance L=20.0cm to the right of lens 1, and the image of lens 1 becomes the object of lens 2. Calculate the object distance, do,2, relative to lens 2. Be certain to include the sign as consistent with the standard sign conventions. Part (e) Which statement best describes the…arrow_forward
- Four ray diagrams are shown below. f1, f2 are the focal points for the lenses respectively as shown from left to right. when both focal points occur at the same point their position is designated as "f1/f2". Identify the TWO ray diagrams that show the correct position for the FINAL image for the two-lens systems shown below.arrow_forwardYou are imaging a pencil through a thin, converging lens as shown in the image below. If p (the distance from the object to the center of the thin lens) is 10m and the focal length of the thin lens is 1.26m, how far away (in meters) from the center of the thin lens is the real image located (the real image will be on the right side of the lens in this particular example illustrated below)?arrow_forwardCan you answer part a of problem 1 in the image?arrow_forward
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
