
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The geometry of the carbon atoms for the given structures is to be predicted. The most nucleophilic and most electrophilic species are to be identified and the species, which react with water to give
Concept Introduction:
The VSEPR theory is used to predict the geometry of the molecules, using the number of electron pairs surrounding the central atom.
The most nucleophilic atom is the atom with the highest negative charge.
The most electrophilic atom is the atom with the highest positive charge.
Answer to Problem 102AP
Solution:
(a) The geometry of three molecules is:
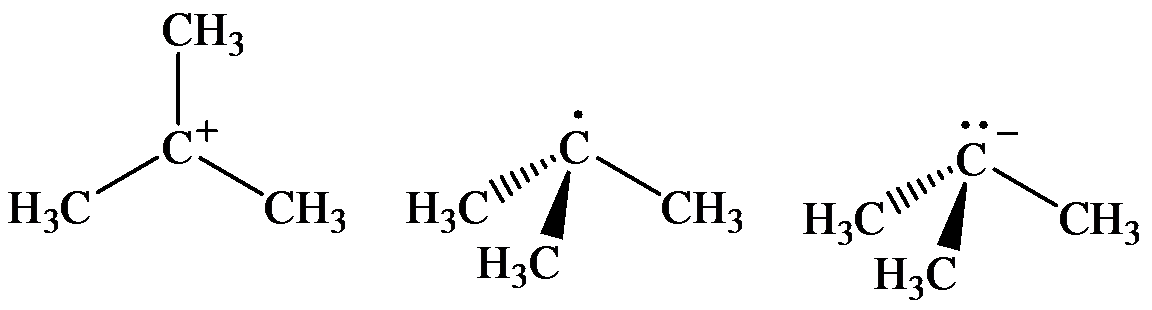
(b) The most nucleophilic atom will be tert-Butyl anion
(c) The species that reacts with water to form
(d) 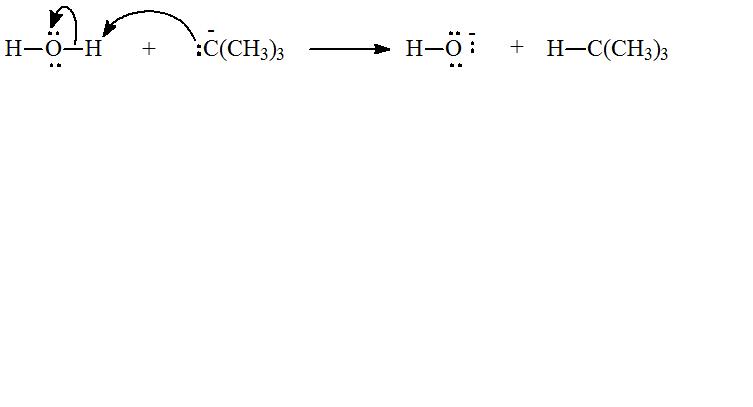
Explanation of Solution
a) The arrangement of bonds to the carton at left linear, tetrahedral, trigonal, trigonal pyramidal
The three molecules are as follows:
The geometry of tert-Butyl cation is:
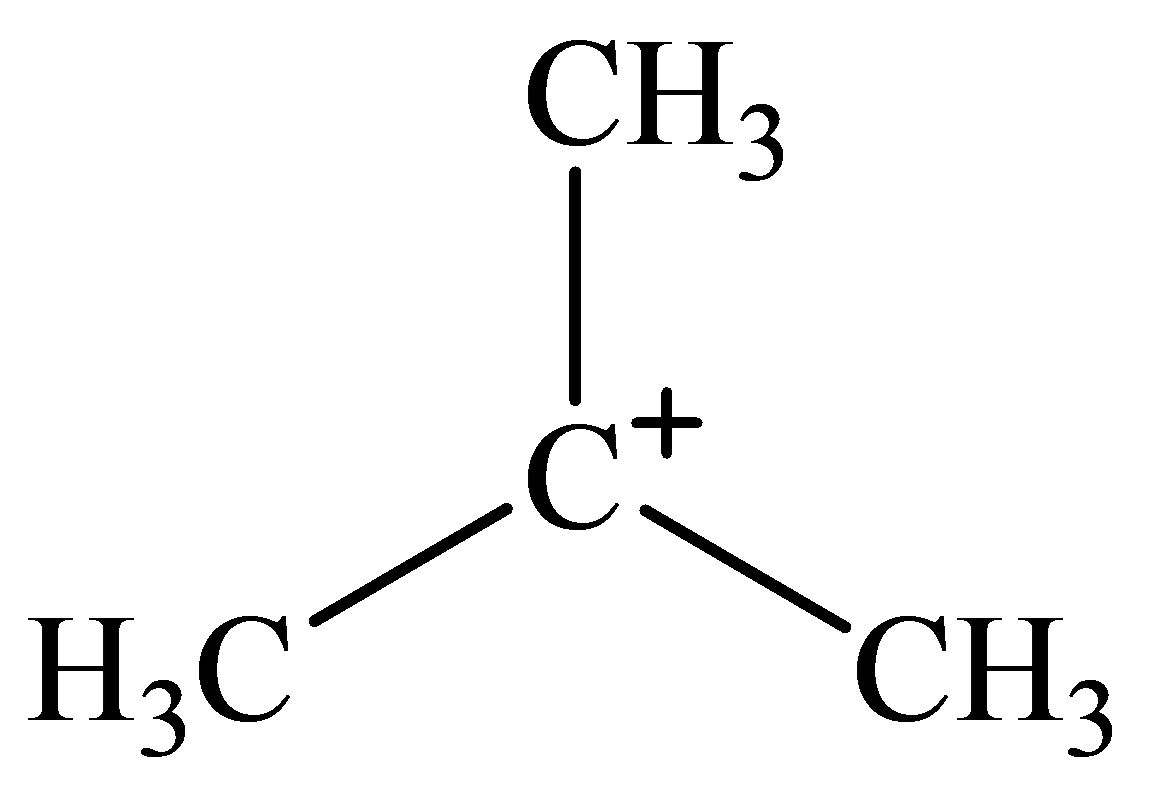
The
molecule has a total of three electron groups around the central atom. It has three bonding electron pairs and zero nonbonding electron pairs, which arrange themselves to make a bond angle of
that indicates trigonal planar geometry.
The geometry of tert-Butyl radical is:
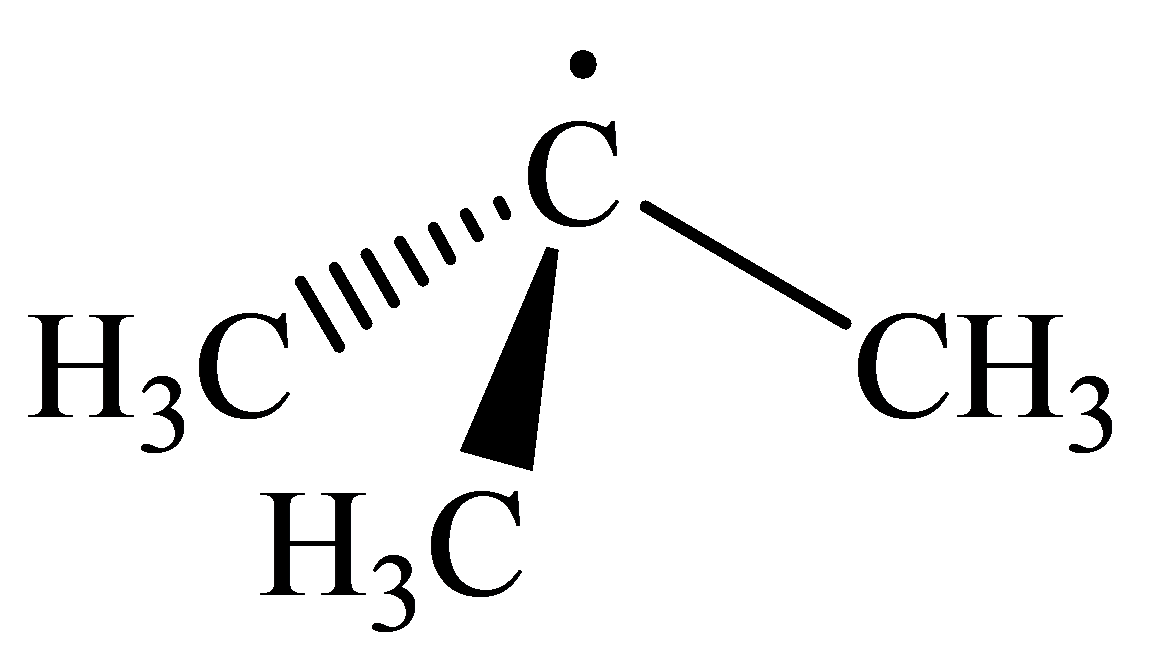
The
radicals have a total of three electron groups around the central atom. It has three bonding electron pairs and one nonbonding electron pair, which arrange themselves to make a bond angle, nearly, of
that indicates distorted trigonal planar geometry.
The geometry of tert-Butyl anion is:
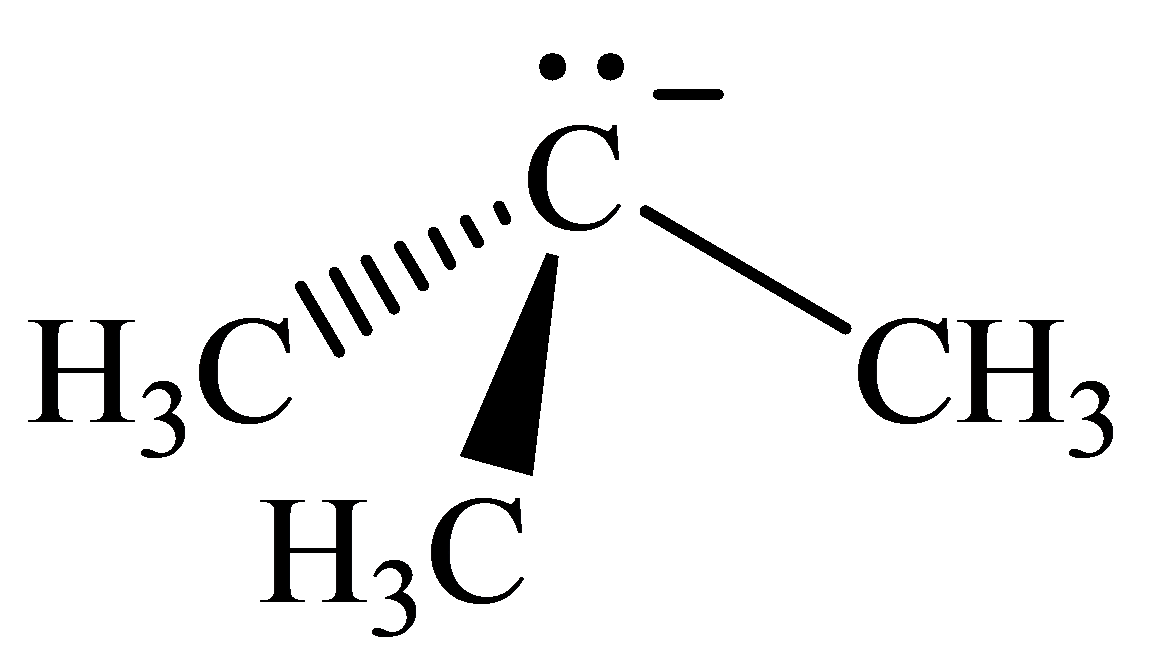
The
molecule has a total of five electron groups around the central atom. It has three bonding electron pairs and one nonbonding electron pair, which arrange themselves to make a bond angle of
that indicates trigonal pyramidal geometry.
b) The most nucleophilic and electrophilic atom
The most nucleophilic atom is the atom with the highest negative charge.
So, the most nucleophilic atom will be tert-Butyl anion,
The most electrophilic atom is the atom with the highest positive charge.
So, the most nucleophile atom will be tert-Butyl cation,
c) The species that reacts with water to give
The tert-Butyl anion has a lone pair that can pair with the proton of water, to form
Hence, the species that reacts with water to form
The reaction of water with species which gives
d) Chemical reaction for the reaction in part (c) and curve arrow to show flow of electron.
The chemical equation for reaction of tert-Butyl anion,
The flow of electrons can be shown as:

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Chemistry
- What is the difference between the hybridization of carbon atoms' valence orbitals in saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons?arrow_forwardPredict the approximate values for the H¬O¬C and O¬C¬C bond angles in vinyl alcohol?arrow_forwardC5H8 has two elements of unsaturation (right?), which may indicate the presence of either double bonds or triple bonds or rings. Show all the possible structuresarrow_forward
- 7. Give two structural formulas each for poly- and heterofunctional compounds of the composition C4H6O4.arrow_forwardWrite structures for the three isomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon xylene, C6H4(CH3)2.arrow_forwardWhat is the Lewis Structure of CH2Se, the steric number, the electron pair geometry, the molecular geometry, and how many double bonds does it have?arrow_forward
- How do you find the hydridization of the carbon atoms in the resonance hybrid of benzene?arrow_forwarddetermine the number of valence electrons in ethene (C₂H₄) and then draw the corresponding Lewis structure.arrow_forwardWhat is the meaning of the term tertiary (3) when it is used to classify alcohols? Draw a structural formula for the one tertiary (3) alcohol with the molecular formula C4H10O.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





