
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The type of reaction that occurs in step 1 of a turn of the
Concept Introduction:
The
Dehydrogenation reaction, hydration reaction, and thiolysis reactions occur in the
In dehydrogenation reaction, hydrogen molecule
(a)
Answer to Problem 25.30EP
Dehydrogenation reaction occurs in step 1 of a turn of the
Explanation of Solution
In step 1 of a turn of the
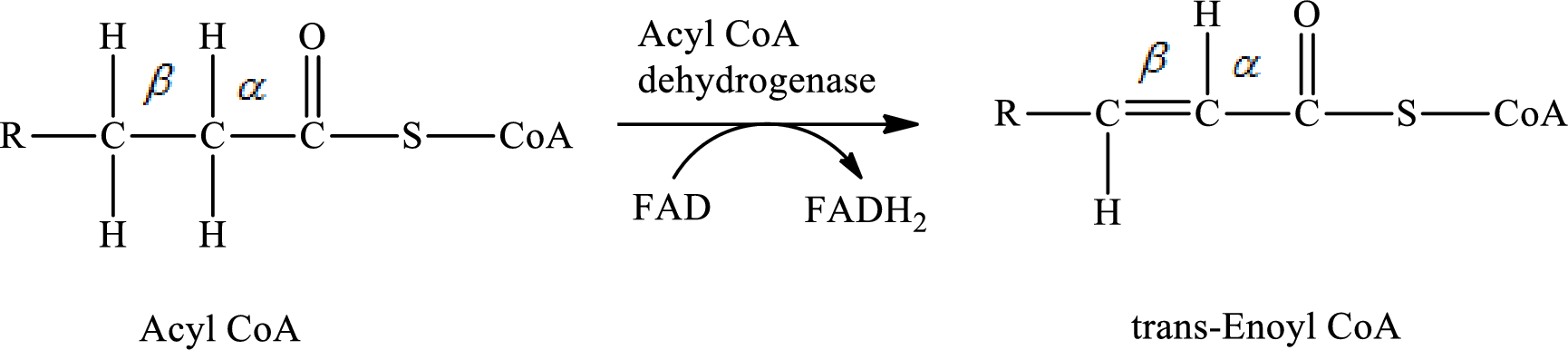
The hydrogen molecule is removed from
(b)
Interpretation:
The type of reaction that occurs in step 2 of a turn of the
Concept Introduction:
The
Dehydrogenation reaction, hydration reaction, and thiolysis reactions occur in the
In dehydrogenation reaction, hydrogen molecule
(b)
Answer to Problem 25.30EP
Hydration reaction occurs in step 2 of a turn of the
Explanation of Solution
In step 2, a water
The reaction for step 2 is as follows:
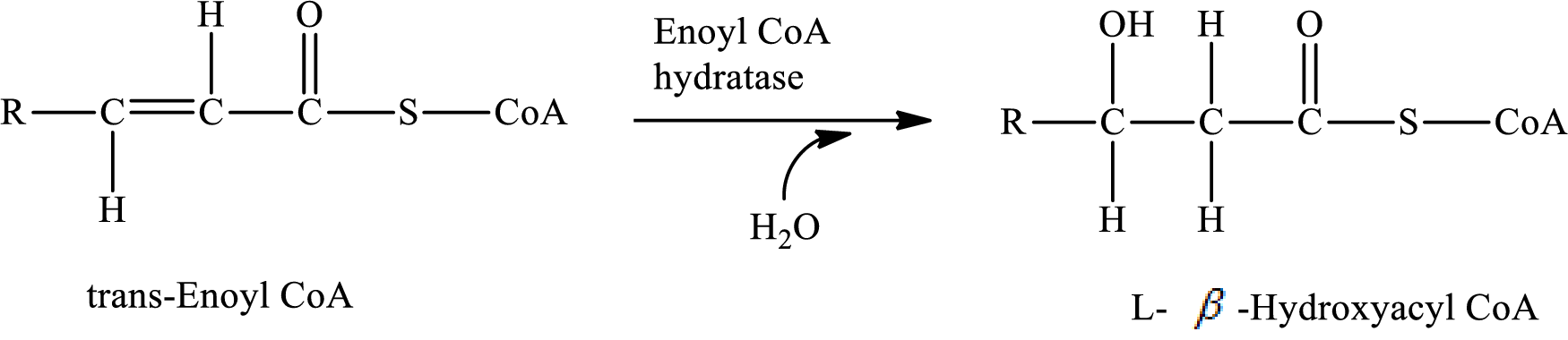
A water molecule is added in step 2, therefore; the reaction in step 2 of a turn of the
(c)
Interpretation:
The type of reaction that occurs in step 3 of a turn of the
Concept Introduction:
The
Dehydrogenation reaction, hydration reaction, and thiolysis reactions occur in the
In dehydrogenation reaction, hydrogen molecule
(c)
Answer to Problem 25.30EP
Dehydrogenation reaction occurs in step 3 of a turn of the
Explanation of Solution
In step 3 of a turn of the
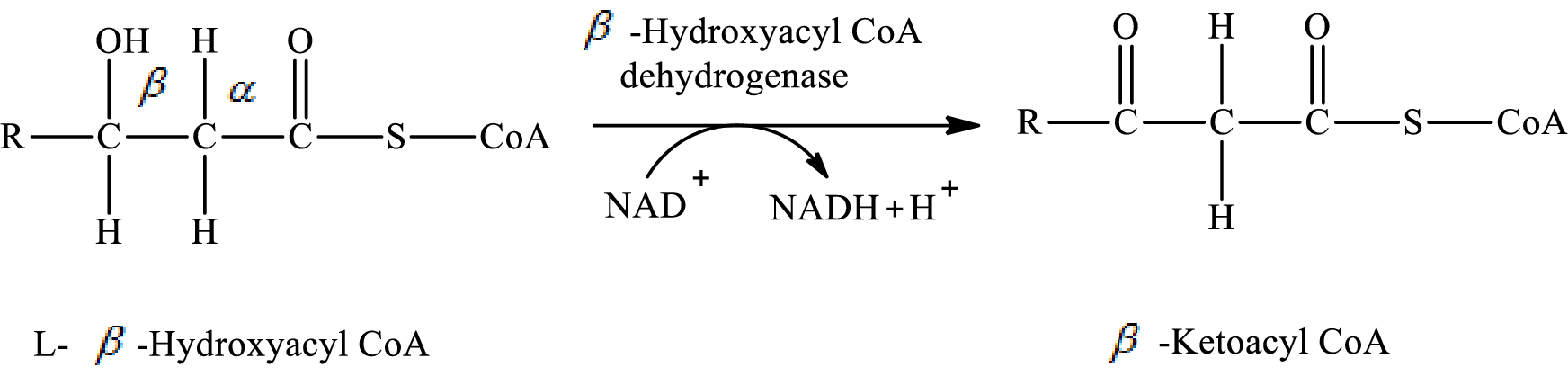
The hydrogen
(d)
Interpretation:
The type of reaction that occurs in step 4 of a turn of the
Concept Introduction:
The
Dehydrogenation reaction, hydration reaction, and thiolysis reactions occur in the
In dehydrogenation reaction, hydrogen molecule
(d)
Answer to Problem 25.30EP
Thiolysis reaction occurs in step 4 of a turn of the
Explanation of Solution
In step 4 of a turn of the
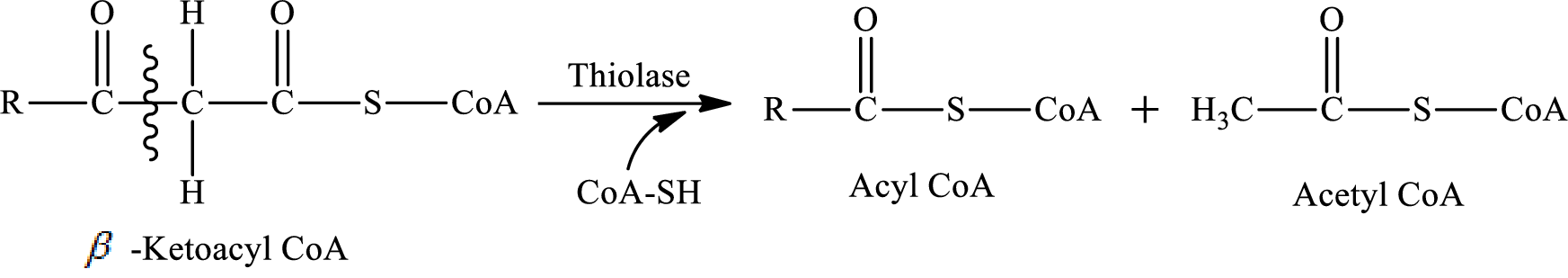
The carbon-carbon bond in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
- What type(s) of extremophiles are used in oil well drilling operations?arrow_forwardWhich nutrient provides energy in its most concentrated form?arrow_forwardIf produces large amount of acetyl CoA that result in the production of ketone bodies healhy conduction or harmful to the body? And why . Related to biochemistryarrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning





